CSS3 给我们新增了选择器,可以更加便捷,更加自由的选择目标元素。
1.属性选择器
2.结构伪类选择器
3.伪元素选择器
1.属性选择器
属性选择器可以根据元素特定属性的来选择元素。 这样就可以不用借助于类或者id选择器。

注意:类选择器、属性选择器、伪类选择器,权重为 10。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>CSS3新增属性选择器</title> <style> /* 必须是input 但是同时具有 value这个属性 选择这个元素 [] */ /* input[value] { color:pink; } */ /* 只选择 type =text 文本框的input 选取出来 */ input[type=text] { color: pink; } /* 选择首先是div 然后 具有class属性 并且属性值 必须是 icon开头的这些元素 */ div[class^=icon] { color: red; } section[class$=data] { color: blue; } div.icon1 { color: skyblue; } /* 类选择器和属性选择器 伪类选择器 权重都是 10 */ </style> </head> <body> <!-- 1. 利用属性选择器就可以不用借助于类或者id选择器 --> <!-- <input type="text" value="请输入用户名"> <input type="text"> --> <!-- 2. 属性选择器还可以选择属性=值的某些元素 重点务必掌握的 --> <input type="text" name="" id=""> <input type="password" name="" id=""> <!-- 3. 属性选择器可以选择属性值开头的某些元素 --> <div class="icon1">小图标1</div> <div class="icon2">小图标2</div> <div class="icon3">小图标3</div> <div class="icon4">小图标4</div> <div>我是打酱油的</div> <!-- 4. 属性选择器可以选择属性值结尾的某些元素 --> <section class="icon1-data">我是安其拉</section> <section class="icon2-data">我是哥斯拉</section> <section class="icon3-ico">哪我是谁</section> </body> </html>
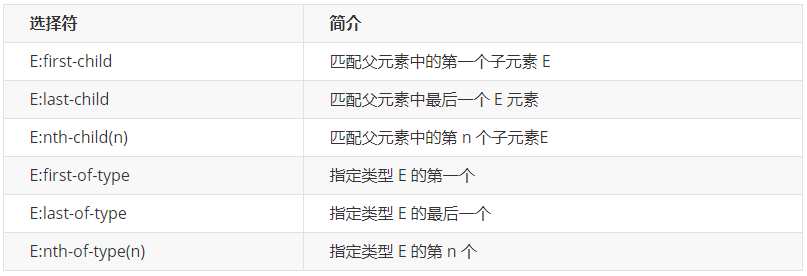
2. 结构伪类选择器
结构伪类选择器主要根据文档结构来选择器元素, 常用于根据父级选择器里面的子元素
注意:类选择器、属性选择器、伪类选择器,权重为 10。
nth-child(n) 选择某个父元素的一个或多个特定的子元素(重点)
n 可以是数字,关键字和公式
n 如果是数字,就是选择第 n 个子元素, 里面数字从1开始…
n 可以是关键字:even 偶数,odd 奇数
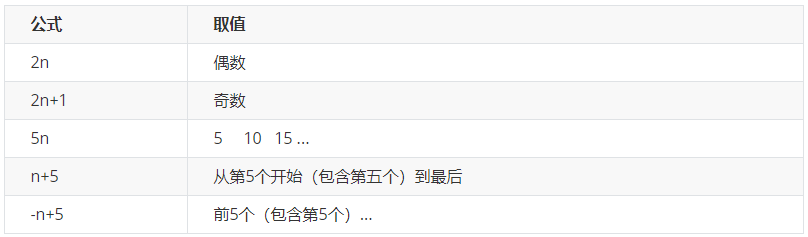
n 可以是公式:常见的公式如下 ( 如果n是公式,则从0开始计算,但是第 0 个元素或者超出了元素的个数会被忽略 )
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>CSS3新增结构伪类选择器-nth-child</title> <style> /* 1.把所有的偶数 even的孩子选出来 */ ul li:nth-child(even) { background-color: #ccc; } /* 2.把所有的奇数 odd的孩子选出来 */ ul li:nth-child(odd) { background-color: gray; } /* 3.nth-child(n) 从0开始 每次加1 往后面计算 这里面必须是n 不能是其他的字母 选择了所有的孩子*/ /* ol li:nth-child(n) { background-color: pink; } */ /* 4.nth-child(2n)母选择了所有的偶数孩子 等价于 even*/ /* ol li:nth-child(2n) { background-color: pink; } ol li:nth-child(2n+1) { background-color: skyblue; } */ /* ol li:nth-child(n+3) { background-color: pink; } */ ol li:nth-child(-n+3) { background-color: pink; } </style> </head> <body> <ul> <li>我是第1个孩子</li> <li>我是第2个孩子</li> <li>我是第3个孩子</li> <li>我是第4个孩子</li> <li>我是第5个孩子</li> <li>我是第6个孩子</li> <li>我是第7个孩子</li> <li>我是第8个孩子</li> </ul> <ol> <li>我是第1个孩子</li> <li>我是第2个孩子</li> <li>我是第3个孩子</li> <li>我是第4个孩子</li> <li>我是第5个孩子</li> <li>我是第6个孩子</li> <li>我是第7个孩子</li> <li>我是第8个孩子</li> </ol> </body> </html>
区别:
1.nth-child 对父元素里面所有孩子排序选择(序号是固定的) 先找到第n个孩子,然后看看是否和E匹配
2.nth-of-type 对父元素里面指定子元素进行排序选择。 先去匹配E ,然后再根据E 找第n个孩子
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>CSS3新增选择器nth-type-of</title> <style> ul li:first-of-type { background-color: pink; } ul li:last-of-type { background-color: pink; } ul li:nth-of-type(even) { background-color: skyblue; } /* nth-child 会把所有的盒子都排列序号 */ /* 执行的时候首先看 :nth-child(1) 之后回去看 前面 div */ section div:nth-child(1) { background-color: red; } /* nth-of-type 会把指定元素的盒子排列序号 */ /* 执行的时候首先看 div指定的元素 之后回去看 :nth-of-type(1) 第几个孩子 */ section div:nth-of-type(1) { background-color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <ul> <li>我是第1个孩子</li> <li>我是第2个孩子</li> <li>我是第3个孩子</li> <li>我是第4个孩子</li> <li>我是第5个孩子</li> <li>我是第6个孩子</li> <li>我是第7个孩子</li> <li>我是第8个孩子</li> </ul> <!-- 区别 --> <section> <p>光头强</p> <div>熊大</div> <div>熊二</div> </section> </body> </html>
小结
结构伪类选择器一般用于选择父级里面的第几个孩子
nth-child 对父元素里面所有孩子排序选择(序号是固定的) 先找到第n个孩子,然后看看是否和E匹配
nth-of-type 对父元素里面指定子元素进行排序选择。 先去匹配E ,然后再根据E 找第n个孩子
关于 nth-child(n) 我们要知道 n 是从 0 开始计算的,要记住常用的公式
如果是无序列表,我们肯定用 nth-child 更多
类选择器、属性选择器、伪类选择器,权重为 10。
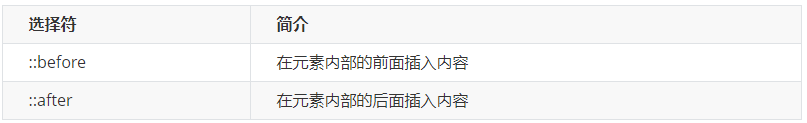
3. 伪元素选择器(重点)
伪元素选择器可以帮助我们利用CSS创建新标签元素,而不需要HTML标签,从而简化HTML结构。
注意:
before 和 after 创建一个元素,但是属于行内元素
新创建的这个元素在文档树中是找不到的,所以我们称为伪元素
语法: element::before {}
before 和 after 必须有 content 属性
before 在父元素内容的前面创建元素,after 在父元素内容的后面插入元素
伪元素选择器和标签选择器一样,权重为 1
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>伪元素选择器before和after</title> <style> div { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: pink; } /* div::before 权重是2 */ div::before { /* 这个content是必须要写的 */ /* display: inline-block; */ content: '我'; /* 30px; height: 40px; background-color: purple; */ } div::after { content: '小猪佩奇'; } </style> </head> <body> <div> 是 </div> </body> </html>
使用样例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>伪元素选择器使用场景2-仿土豆网显示隐藏遮罩案例</title> <style> .tudou { position: relative; width: 444px; height: 320px; background-color: pink; margin: 30px auto; } .tudou img { width: 100%; height: 100%; } .tudou::before { content: ''; /* 隐藏遮罩层 */ display: none; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; background: rgba(0, 0, 0, .4) url(images/arr.png) no-repeat center; } /* 当我们鼠标经过了 土豆这个盒子,就让里面before遮罩层显示出来 */ .tudou:hover::before { /* 而是显示元素 */ display: block; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="tudou"> <img src="images/tudou.jpg" alt=""> </div> <div class="tudou"> <img src="images/tudou.jpg" alt=""> </div> <div class="tudou"> <img src="images/tudou.jpg" alt=""> </div> <div class="tudou"> <img src="images/tudou.jpg" alt=""> </div> </body> </html>