(〇)考场上的一些ideas
其实这部分已经是正解了。
第一档部分分:
开考5min:
一个很显然的暴力:对于每次询问都从 (u) 找到 (v), 25ptsgets。
时间复杂度(Theta(nq))
第二档部分分((m leq 300)):
开考10min:
首先一个处理树上路径问题的套路:将 ((u,v)) 拆成 ((u, lca)), ((lca, v))
对于每一个节点,假设当前节点的颜色在排列中是第 (i) 个。
考虑用 (f(i, j)=x) 表示 (i) 沿着父边向上走遇到了连续 (j) 个排列的末端节点是 (x)。
对于每个节点的 (f) 都可以 (Theta(m)) 暴力求解(每个节点都一步步向上跳,记录当前遇到了连续多少个排列)。
注意: 由于路径 ((u, lca)) 与路径 ((lca, v)) 在树上的方向是相反的(一个向根走, 另一个向叶子走), 因此需要处理 (f_1) 和 (f_2) 分别表示向上走或者向下走。
对于每个询问, 可以树剖查询,然后二分查找最长路径。
时间复杂度:(Theta(nm+qlog nlog m))
第三档部分分 ((u_i=i,v_i=i+1)):
开考30min:
这是链的情况, 只需要考虑序列上如何做。
由于第二档部分分 (mleq 300) 给我们的启示, 我们可以用 (f(i, j)=x) 记录第 (i) 个位置的后连续 (j) 个排列末端所在的位置是 (x)。
但是,由于(mleq 2 imes 10^5), 开不下那么大的空间。
受到第二档部分分的启发, 可以考虑分块[1]。(通俗的说,就是用时间换空间)
既然我无法把后面的连续 (m) 个排列的位置全部记下来, 那我就只记后面连续的 (sqrt m) 个排列的位置。
每次查询, 都尽可能的往最远处跳, 最多只用跳 (sqrt m) 次。
这样一来, 就的到了一个十分“优秀”的算法。
时间复杂度: (Theta (nsqrt m+qsqrt m))
第四档部分分(正解):
开考45min:
实际上,只需要将以上两档部分分结合起来就是正解了。
正解包含了两档部分分中最麻烦的部分。
众所周知, 树剖就是将树上的问题转化为序列上的问题。
既然可以序列上对颜色分块, 那么是否也可以在树上对颜色分块呢? 答案是肯定的。
具体实现只需要用树剖将询问转化为序列上一段段的区间, 然后再套用序列上问题的做法即可。(注意同样要维护树上向上或是向下的路径)
时间复杂度:(Theta(nsqrt m+qsqrt mlog n))
接下来是我牢骚时刻, 建议跳过
咦, t1 just this? 于是再写正解的路上狂奔。
开考1h:
正解怎么这么难写呀!(coding...)
开考1.5h:
怎么细节这么多呀!!(debugging...)
开考2h:
终于调对了, 测 (gem2.in), 嗯, 找不到差异。
测 (gem3.in), ****, 怎么爆栈了, 怎么开栈(无能狂怒)
问监考员, 监考员:我好久没用 windows 了。(我也不知道怎么开栈)
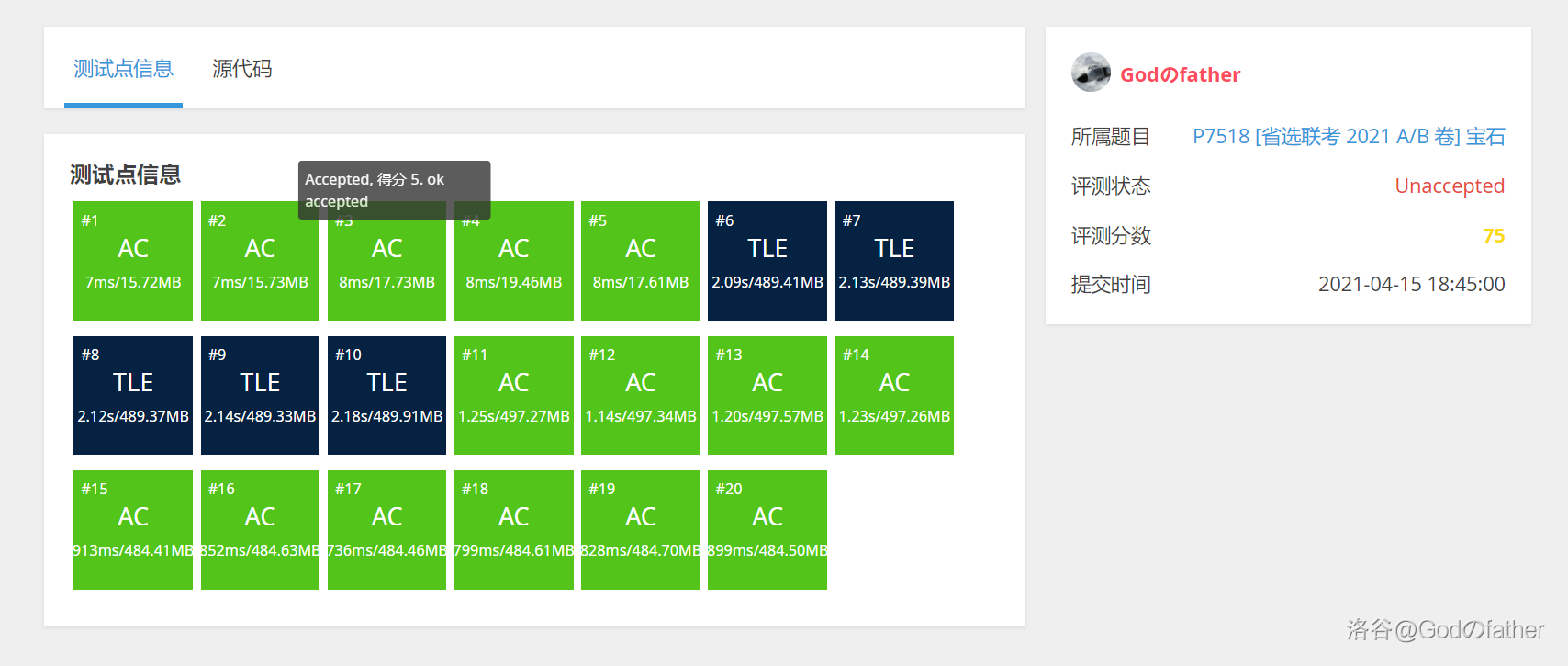
此时 Godのfather 不知道, 他将存颜色的数组开小了, 这是他噩梦的开始。
考场代码分数:

更改数组大小后分数(由于考场上不知所措, 时间复杂度也写假了):
(一)关于正解
也许调整一下块长分块就能过了呢?
事实上, 我们并不需要分块(来自一名被 (mleq 300) 误导, 认为是分块的菜鸡)。
倍增可以达到分块同样的效果。(并且常数更小, 代码更短)
(此时已经通过树剖将树上的问题转化为了序列上的问题)具体做法是, (f(i, j)=x) 表示位置 (i) 后连续 (2^j) 个排列的位置是 (x) 。
至于查询, 类似于倍增法求 (lca) , 先跳大步, 再跳小步逼近。
时间复杂度降到了:(Theta(nlog m+qlog mlog n))
code(分块):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){
int w = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' or ch > '9') {if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' and ch <= '9') w = w*10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
return w*f;
}
const int maxm = 5e4 + 5, maxn = 2e5 + 5;
int N, M, c, P[maxn], w[maxn], head[maxn], Next[maxn<<1], ver[maxn<<1], tot, p[maxm], blen;
void add(int x, int y){
ver[++tot] = y, Next[tot] = head[x], head[x] = tot;
}
int d[maxn], f[maxn], son[maxn], siz[maxn], top[maxn], id[maxn], cnt;
pair<int, int> nw[maxn];
int nxt[maxn][305][2], num, len[maxn][2];
vector<int> col[maxm];
struct node{
int l, r; bool res;
}ask[1005];
void dfs1(int x, int fa){
f[x] = fa, siz[x] = 1, d[x] = d[fa] + 1;
for(int i=head[x]; i; i=Next[i]){
int y = ver[i];
if(y == fa) continue;
dfs1(y, x);
siz[x] += siz[y];
if(siz[y] > siz[son[x]]) son[x] = y;
}
}
void dfs2(int x, int TOP){
top[x] = TOP, id[x] = ++cnt;
if(!son[x]) return ;
dfs2(son[x], TOP);
for(int i=head[x]; i; i=Next[i]){
int y = ver[i];
if(y == f[x] or y == son[x]) continue;
dfs2(y, y);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y){
while(top[x] != top[y]){
if(d[top[x]] < d[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
x = f[top[x]];
}
if(d[x] > d[y]) swap(x, y);
return x;
}
void get_up(int x, int y){
while(top[x] != top[y]){
ask[++num] = (node){id[top[x]], id[x], 1};
x = f[top[x]];
}
if(id[y] != id[x]) ask[++num] = (node){id[y], id[x], 1};
}
void get_down(int x, int y){
int s = num;
while(top[x] != top[y]){
ask[++num] = (node){id[top[x]], id[x], 0};
x = f[top[x]];
}
ask[++num] = (node){id[y], id[x], 0};
for(int i=1; i<=(num-s)/2; i++){
swap(ask[s+i], ask[num-i+1]);
}
}
int Find1(int x, int l){//这是我考场上时间复杂度写假的部分, 多了1个log
if(x < l or x == 0) return 0;
int L = 0, R = len[x][1];
while(L <= R){
int mid = (L+R)>>1;
if(nxt[x][mid][1] >= l) L = mid + 1;
else R = mid-1;
}
int sum = R;
if(R != 0) sum += Find1(nxt[x][R][1], l);
return sum;
}
int Find2(int x, int r){//同上
if(x > r or x == 0) return 0;
int L = 0, R = len[x][0];
while(L <= R){
int mid = (L+R)>>1;
if(nxt[x][mid][0] <= r) L = mid + 1;
else R = mid - 1;
}
int sum = R;
if(R != 0) sum += Find2(nxt[x][R][0], r);
return sum;
}
int main(){
N = read(), M = read(), c = read();
for(int i=1; i<=M; i++) P[i] = read(), p[P[i]] = i;
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) w[i] = read();
for(int i=1; i<N; i++){
int x = read(), y = read();
add(x, y), add(y, x);
}
dfs1(1, 0);//树剖
dfs2(1, 1);
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) nw[i] = make_pair(id[i], w[i]);
sort(nw+1, nw+N+1); //树上问题转序列上问题(根据dfs序)
blen = 300;//块长
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) col[nw[i].second].push_back(nw[i].first);
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){//分块:向下的路径
nxt[i][0][0] = i;
int s = p[nw[i].second];
for(int j=1; j<=min(blen, M); j++){
vector<int>::iterator it = lower_bound(col[P[s+j]].begin(), col[P[s+j]].end(), nxt[i][j-1][0]);
if(it != col[P[s+j]].end()) nxt[i][j][0] = *it, len[i][0] = j;
else break;
}
}
for(int i=N; i>=1; i--){//分块: 向上的路径
nxt[i][0][1] = i;
int s = p[nw[i].second];
for(int j=1; j<=min(blen, M); j++){
vector<int>::iterator it = lower_bound(col[P[s+j]].begin(), col[P[s+j]].end(), nxt[i][j-1][1]);
if(it != col[P[s+j]].begin()) nxt[i][j][1] = *(--it), len[i][1] = j;
else break;
}
}
int q = read();
while(q--){
int u = read(), v = read();
int LCA = lca(u, v);
num = 0;
get_up(u, LCA);//记录路径上划分出来的区间
get_down(v, LCA);
int cnt = 1;
for(int i=1; i<=num; i++){
if(cnt == M+1) break;
int l = ask[i].l, r = ask[i].r; bool res = ask[i].res;
if(res){//判断该区间在树上是向上还是向下
vector<int>::iterator it = upper_bound(col[P[cnt]].begin(), col[P[cnt]].end(), r);
if(it == col[P[cnt]].begin()) continue;
int s = *(--it);
if(s < l) continue;
cnt += Find1(s, l) + 1;
}
else{
vector<int>::iterator it = lower_bound(col[P[cnt]].begin(), col[P[cnt]].end(), l);
if(it == col[P[cnt]].end()) continue;
int s = *it;
if(s > r) continue;
cnt += Find2(s, r) + 1;
}
}
printf("%d
", cnt - 1);
}
return 0;
}
code(倍增)(只改动了一点):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){
int w = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' or ch > '9') {if(ch == '-') f = -f; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' and ch <= '9') w = w*10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
return w*f;
}
const int maxm = 5e4 + 5, maxn = 2e5 + 5;
int N, M, c, P[maxn], w[maxn], head[maxn], Next[maxn<<1], ver[maxn<<1], tot, p[maxm], blen;
void add(int x, int y){
ver[++tot] = y, Next[tot] = head[x], head[x] = tot;
}
int d[maxn], f[maxn], son[maxn], siz[maxn], top[maxn], id[maxn], cnt;
pair<int, int> nw[maxn];
int nxt[maxn][20][2], num, len[maxn][2];
vector<int> col[maxm];
struct node{
int l, r; bool res;
}ask[100005];
void dfs1(int x, int fa){
f[x] = fa, siz[x] = 1, d[x] = d[fa] + 1;
for(int i=head[x]; i; i=Next[i]){
int y = ver[i];
if(y == fa) continue;
dfs1(y, x);
siz[x] += siz[y];
if(siz[y] > siz[son[x]]) son[x] = y;
}
}
void dfs2(int x, int TOP){
top[x] = TOP, id[x] = ++cnt;
if(!son[x]) return ;
dfs2(son[x], TOP);
for(int i=head[x]; i; i=Next[i]){
int y = ver[i];
if(y == f[x] or y == son[x]) continue;
dfs2(y, y);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y){
while(top[x] != top[y]){
if(d[top[x]] < d[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
x = f[top[x]];
}
if(d[x] > d[y]) swap(x, y);
return x;
}
void get_up(int x, int y){
while(top[x] != top[y]){
ask[++num] = (node){id[top[x]], id[x], 1};
x = f[top[x]];
}
if(id[y] != id[x]) ask[++num] = (node){id[y], id[x], 1};
}
void get_down(int x, int y){
int s = num;
while(top[x] != top[y]){
ask[++num] = (node){id[top[x]], id[x], 0};
x = f[top[x]];
}
ask[++num] = (node){id[y], id[x], 0};
for(int i=1; i<=(num-s)/2; i++){
swap(ask[s+i], ask[num-i+1]);
}
}
int Find1(int x, int l){// 改动: 倍增先跳大步, 再跳小步
int sum = 0;
for(int i=15; i>=0; i--){
if(nxt[x][i][1] == 0) continue;
if(nxt[x][i][1] >= l){
x = nxt[x][i][1];
sum += (1<<i);
}
}
return sum;
}
int Find2(int x, int r){//同上
int sum = 0;
for(int i=15; i>=0; i--){
if(nxt[x][i][0] == 0) continue;
if(nxt[x][i][0] <= r){
x = nxt[x][i][0];
sum += (1<<i);
}
}
return sum;
}
int main(){
N = read(), M = read(), c = read();
for(int i=1; i<=M; i++) P[i] = read(), p[P[i]] = i;
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) w[i] = read();
for(int i=1; i<N; i++){
int x = read(), y = read();
add(x, y), add(y, x);
}
dfs1(1, 0);
dfs2(1, 1);
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) nw[i] = make_pair(id[i], w[i]);
sort(nw+1, nw+N+1);
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) col[nw[i].second].push_back(nw[i].first);
for(int i=N; i>=1; i--){//改动: 换成了倍增
int s = p[nw[i].second];
vector<int>::iterator it = upper_bound(col[P[s+1]].begin(), col[P[s+1]].end(), i);
if(it != col[P[s+1]].end()){
nxt[i][0][0] = *it;
for(int j=1; j<=15; j++) nxt[i][j][0] = nxt[nxt[i][j-1][0]][j-1][0];
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
int s = p[nw[i].second];
vector<int>::iterator it = upper_bound(col[P[s+1]].begin(), col[P[s+1]].end(), i);
if(it != col[P[s+1]].begin()){
nxt[i][0][1] = *(--it);
for(int j=1; j<=15; j++) nxt[i][j][1] = nxt[nxt[i][j-1][1]][j-1][1];
}
}
int q = read();
while(q--){
int u = read(), v = read();
int LCA = lca(u, v);
num = 0;
get_up(u, LCA);
get_down(v, LCA);
int cnt = 1;
for(int i=1; i<=num; i++){
if(cnt == M+1) break;
int l = ask[i].l, r = ask[i].r; bool res = ask[i].res;
if(res){
vector<int>::iterator it = upper_bound(col[P[cnt]].begin(), col[P[cnt]].end(), r);
if(it == col[P[cnt]].begin()) continue;
int s = *(--it);
if(s < l) continue;
cnt += Find1(s, l) + 1;
}
else{
vector<int>::iterator it = lower_bound(col[P[cnt]].begin(), col[P[cnt]].end(), l);
if(it == col[P[cnt]].end()) continue;
int s = *it;
if(s > r) continue;
cnt += Find2(s, r) + 1;
}
}
printf("%d
", cnt - 1);
}
return 0;
}
(三)结束语
GDOI 2021就这样草草结束了。 离别是如此突然。
zhendelan 发挥较为正常(day1有较大的失误), 但最终还是与省队失之交臂。
MCAdam Day1挂了很多分, 与预期相差许多。
总而言之, 希望两位学长能够在文化课上披荆斩棘, 弥补未能进队的遗憾吧。
还有学长 lrw04, Conless,
没有你们, 也就没有我一年来在 ss 学习 OI 的美好时光。
无论接下来是走是留,
无论她带给了我多少泪水,
我从未后悔。
--END--
实际上,可以通过倍增达到 (Theta(log m)) 的复杂度, 后文会具体阐述。 ↩︎