第1章--JDBC
JDBC基础
通过Java Database Connectivity可以实现Java程序对后端数据库的访问
一个完整的数据库部署架构,通常是由客户端和服务器端两部分组成
客户端封装数据库请求,并发送给服务器端,服务器端执行完毕后将结果返回给客户端
常见客户端工具:
MySQL Workbench(图形化工具操作简单,但只能实现简单的查询)
JDBC(驱动程序jar包)
命令行工具(直接敲入SQL语句进行查询)
市面上多种数据库不尽相同,学习成本高,数据库迁移的移植性
-- JDBC(普通的Java类库): 应用程序通过统一的接口,即可实现对任意数据库的访问。
对于数据库厂商来说,JDBC就是一套接口规范,每一个数据库都需要实现JDBC定义的接口,用户通过接口访问数据库即可。
JDBC优势:对数据库的访问简单,开发快捷、省时间,面向不同数据库时的移植性强,在JDBC上可以定制功能强大的框架(如MyBatis)
体系架构:
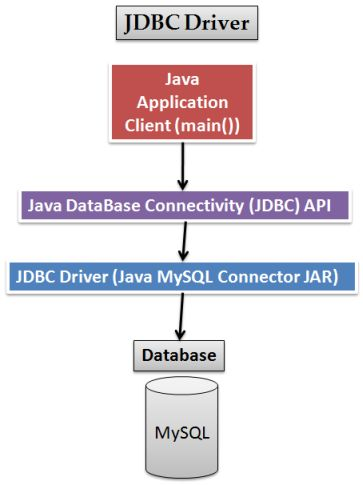
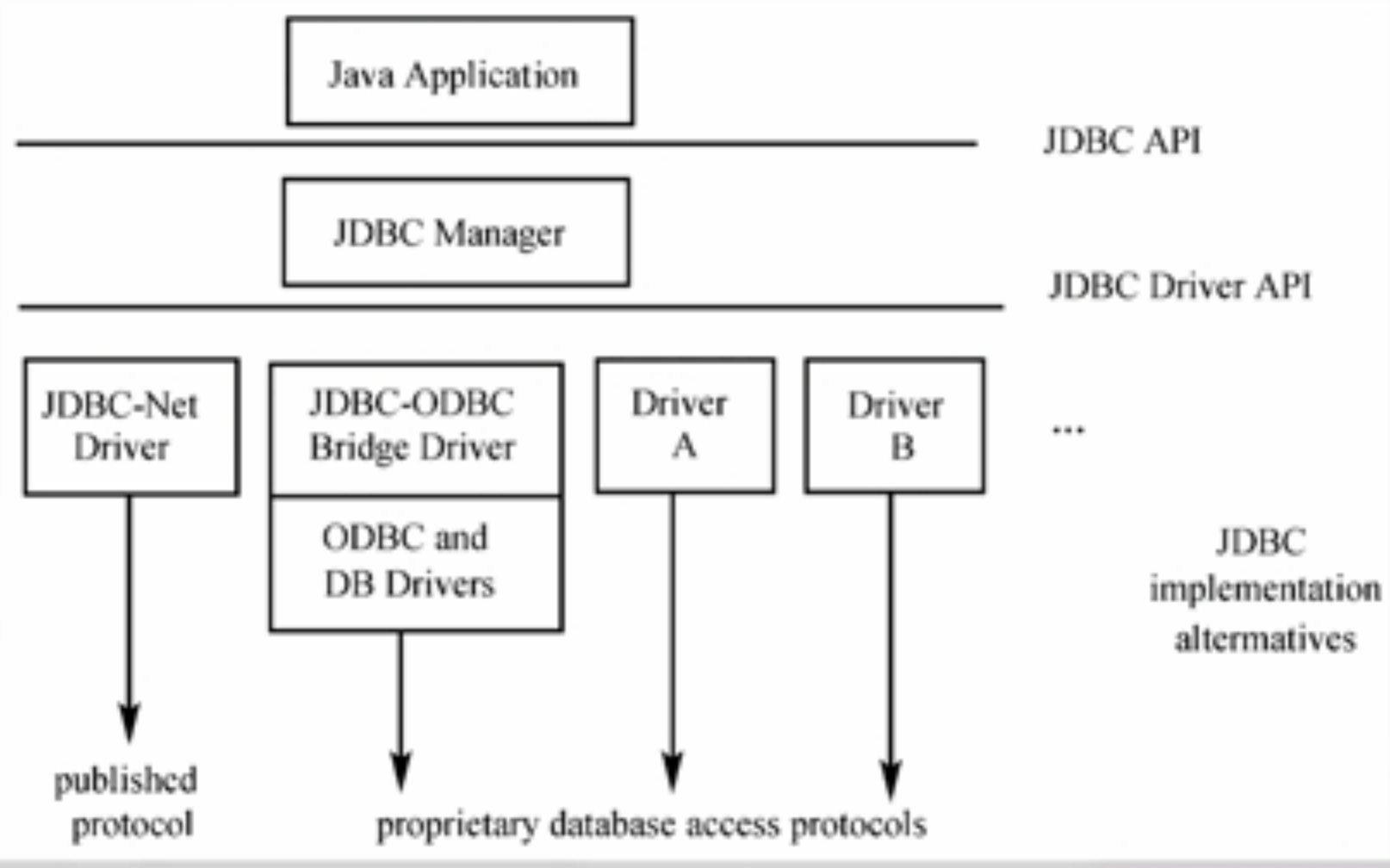
上层API层负责与Java Web程序之间的通信
JDBC API:
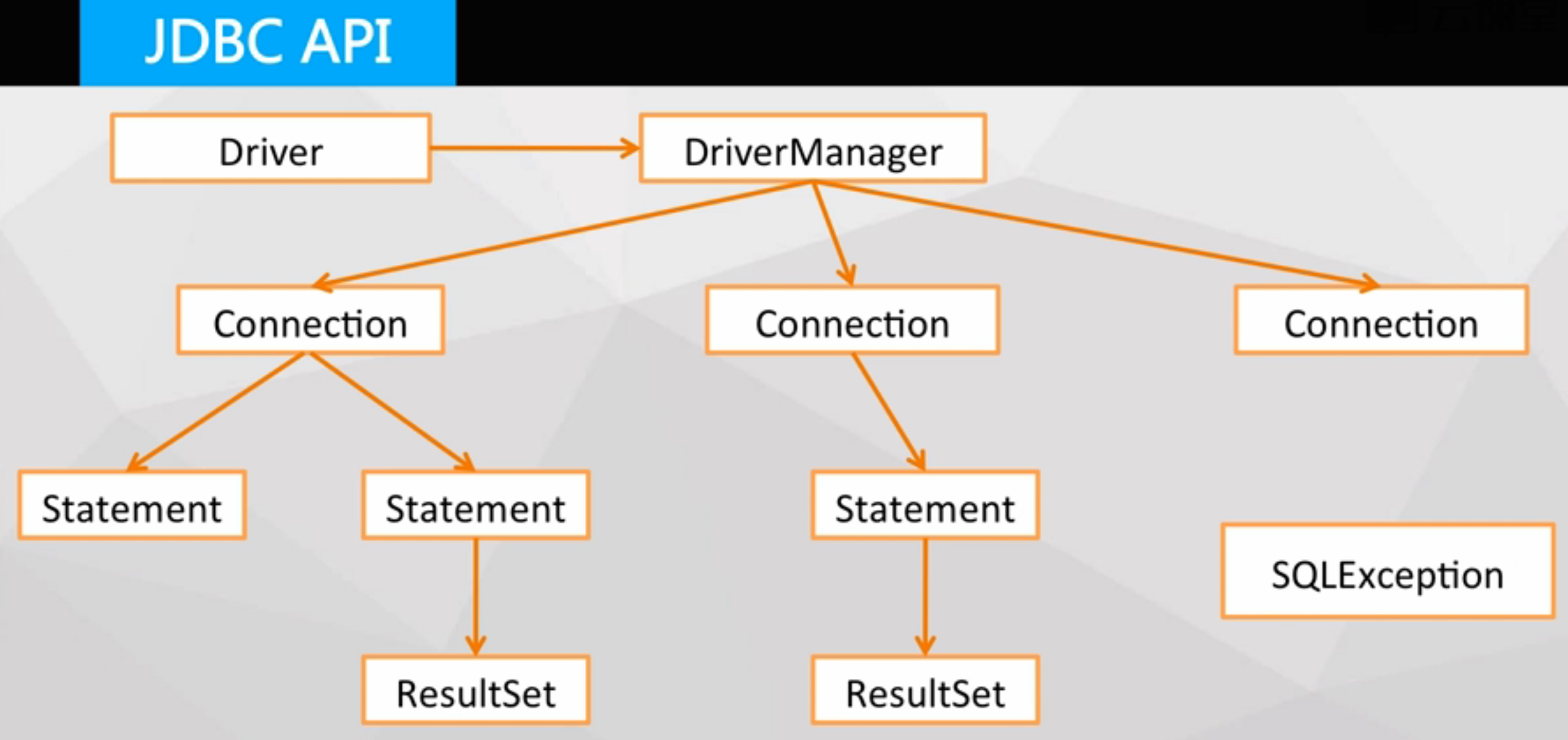
Driver & DriverManager:
Driver是驱动程序的抽象,通过操作Driver接口,可以实现对各个驱动程序的操作
DriverManager是驱动程序的管理类,用户通过Class.forname(DriverName)向DriverManager注册一个驱动程序,
之后通过DriverManager的getConnection方法调用该驱动程序建立到后端数据库的物理连接。
DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS));
// USER和PASS在部署数据库时获得
// DB_URL是后端数据库实例的唯一标识符
i.e. jdbc : mysql : //10.164.172.20:3306/cloud_study
协议 子协议 子名称(主机 端口 数据库)
(子协议不同,子名称的格式也略有不同。)
Connection:通过DriverManager的getConnection方法获得的到后端数据库的物理连接
Java应用程序对后端数据库的一条物理连接
通过这些连接,可以执行一些SQL语句:
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); // sql statement
Statement:sql语句的容器,用于承载sql语句,在该容器中,可以进行增删改查等操作
通过executeQuery方法,执行数据库查询并得到返回结果的集合,以ResultSet类的对象来表示:
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select userName from user");
通过executeUpdate方法,执行数据库更新、删除语句,返回的是int值的对象,代表被影响的数据库记录数量
ResultSet对象表示一个sql语句查询的结果。
关系型数据库:二元表 -- ResultSet对象也是由行和列组成的
ResultSet对象内部有一个指针,指向当前对应的行记录(默认指向第一行记录)
.next():将指针移动到下一行
.previous():将指针移动到下一行
.absolute():将指针定位在某一行
.beforeFirst():将指针移到第一行的之前(通过.next()才能到第一行)
.afterLast():将指针移到最后一行之后
.getString(ColumnName/Index):(index从0开始)获取对应列的值
.getInt(ColumnName/Index):
.getObject(ColumnName/Index):
SQLException:在执行过程中MySQL可能会抛出一些异常
通过捕获SQLException对象来进行异常的处理
下层Driver API层负责与具体的数据库建立连接,一般而言下层的driver都是由数据库厂商提供的。
安装JDBC:
JDBC已经集成在JDK中,可以直接引用,无需安装。
需要安装的是数据库的驱动程序
对于MySQL数据库:
登陆Oracle账号,下载jar包,添加到java web project中。
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/ 下载Connector/J 5.1.43
构建完整的Java Web程序:
NB. 使用JDBC之前,需要准备一个数据库的后端实例,创建一个user表
构建步骤:
装载驱动程序:向DriverManager注册一个驱动程序Driver
建立数据库连接:DriverManager.getConnection()
执行SQL语句:Statement.execute...()
获取执行结果:ResultSet对象
清理环境:关闭Connection, Statement, ResultSet对象
public class HelloJDBC { static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/helloworld"; static final String USER = "matt"; static final String PASSWORD = "matt"; public static void helloworld() throws ClassNotFoundException { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; // 1. 装载驱动程序 Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER); // 2. 建立数据库连接 try { conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASSWORD); // 3. 执行SQL语句
stmt = conn.createStatement(); rs = stmt.executeQuery("select userName from user"); // 4. 获取执行结果 while(rs.next()) { System.out.println("Hello" + rs.getString("userName")); } } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 5. 清理环境 try { if (conn != null) { // 若conn创建成功 conn.close();// conn.close()也可能有异常 } if (stmt != null) { stmt.close(); } if (rs != null) { rs.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { // ignore e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { helloworld(); } }
代码找茬:
public static void test() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; ResultSet rs1 = null; // 1. 装载驱动程序 Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER); // 2. 建立数据库连接 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASSWORD); // 3. 创建statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); // 4. 执行SQL语句 rs = stmt.executeQuery("select userName from user"); // 5. 获取执行结果 while(rs.next()) { System.out.println("Hello" + rs.getString("userName")); } }
1. try-catch block
2. close the connection to the database in finally block with another try-catch block
MySQL安装与初始化:
MySQL安装:http://www.jianshu.com/p/fd3aae701db9
MySQL之终端(Terminal)管理MySQL: http://www.cnblogs.com/GarveyCalvin/p/4297221.html
MySQL之终端(Terminal)管理数据库、数据表、数据的基本操作: http://www.cnblogs.com/GarveyCalvin/p/4297282.html
Maven+MySQL入门: https://www.kancloud.cn/digest/javaframe/125574
JDBC MYSQL CONNECTION TUTORIAL:http://theopentutorials.com/tutorials/java/jdbc/jdbc-mysql-connection-tutorial/#Java_MySQL_Connector
安装与初始化:
在https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/下载安装
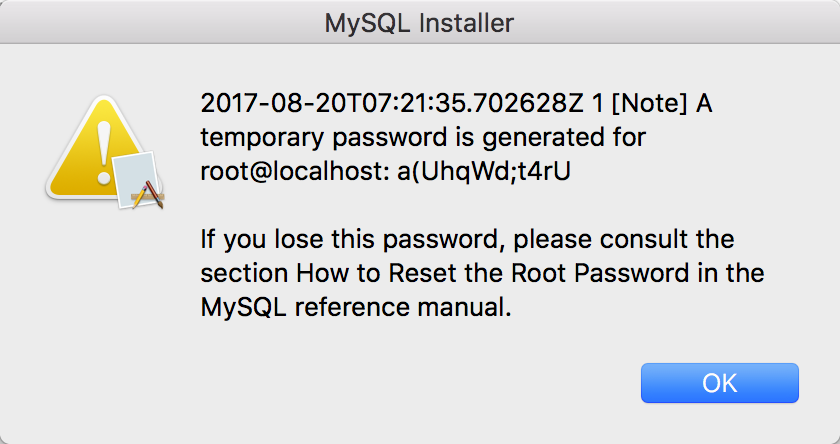
(安装过程中会告诉一个临时密码)安装路径为/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql
配置环境变量PATH="$PATH":/usr/local/mysql/bin
启动MySQL server的服务,需要到system preference中查看MySQL选项,点击start MySQL server
之后在终端输入 mysql -uroot -p和密码a(UhqWd;t4rU即可
试着输入命令,返回:
ERROR 1820 (HY000): You must reset your password using ALTER USER statement before executing this statement.
solution:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/alter-user.html
输入SET PASSWORD = PASSWORD('root'); // 设密码为root
返回Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
创建用户:
insert into mysql.user(Host,User,Password) values ("localhost","matthew",password("1234"));
返回错误:ERROR 1054 (42S22): Unknown column 'Password' in 'field list'
原因:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/30692812/mysql-user-db-does-not-have-password-columns-installing-mysql-on-osx
尝试解决:
use mysql;
show tables; // 返回所有的table名,里面有一个为user table
describe user; // 查询user table,发现里面有Host,有User,但是没有Password field。
// the password field is named ' authentication_string'.
解决方案:(documentation)https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/create-user.html
CREATE USER 'matt'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'matt';
以root身份登陆后创建数据库:
create database helloworld;
查看所有的数据库:show databases; // 看是否创建成功
授权matt拥有该数据库的所有权限:GRANT privileges ON dbname.tablename TO 'username'@'host'
grant all privileges on helloworld.* to matt@localhost identified by 'matt';
刷新系统权限表:
flush privileges;
切换用户:
exit;
mysql -u matt -p;
使用helloworld数据库:use helloworld;
查看该数据库中的所有表:show tables;
给数据库helloworld初始化数据:
CREATE TABLE User ( ID int AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, userName varchar(20) not null);
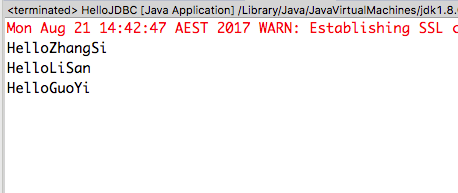
INSERT INTO User VALUES (null, 'ZhangSi');
INSERT INTO User VALUES (null, 'LiSan');
INSERT INTO User VALUES (null, 'GuoYi');
在Eclipse中创建Java project:
HelloJDBC, 新建类文件。
Then, you need to add the downloaded Java MySQL Connector JAR in client project’s classpath . To do this, right click on your Java Project (JDBCMySQLSample) -> Properties -> Buildpath -> Libraries -> Add External JAR and select “mysql-connector-java-5.1.14-bin.jar” JAR file.
Run the project:
JDBC进阶
业务场景一:过滤条件弱,一次可能读出较多记录
业务场景二:需要海量数据读取
产生结果:Java内存的溢出异常
原因分析:Java程序是运行在JVM中的,而JVM有内存大小限制,当我们把数据库中的记录一次性全部读入到内存中,必须考虑内存中是否放得下这些数据。
解决方法:将数据分批读入内存并处理。
游标:提供一种客户端读取部分服务器端结果集的机制
游标的使用:
1. 开启游标:在DB_URL中加入参数 useCursorFetch=true
DB_URL: jdbc:mysql://<IP>:<Port>/<database> ?useCursorFetch=true
2. PreparedStatement接口(继承自Statement)
使用PreparedStatement对象替换原来的Statement对象
需要在创建时传入sql语句(sql语句是参数格式化的,即用?表示参数)
后续通过setString()等来设置这些参数
SetFetchSize()接口可以帮助实现游标的功能:设置客户端每次从服务器端取回的记录数量
PreparedStatement ptmt = null; String sql = "select * from user where sex = ?"; ptmt = conn.preparedStatement(sql); ptmt.setFetchSize(10); ptmt.setString(1, "男"); rs = ptmt.executeQuery();
业务场景三:某一条记录的数据为大字段
产生结果:和多条记录读取相同,出现Java内存你的溢出异常
解决方法:
流方式(与游标相似):将大字段的数据按照二进制流的方式进行划分
流方式的使用:ResultSet.getBinaryStream();
while (rs.next()){ // 获取对象流 InputStream in = rs.getBinaryStream("blog"); File f = new File(FILE_URL); OutputStream out = null; out = new FileOutputStream(f); int temp = 0; while((temp = in.read()) != -1) { // 边读边写 out.write(temp); } in.close(); out.close(); }
业务场景四:数据录入:大量数据的插入操作
产生结果:插入数据的速度太慢
原因分析:每次进行executeUpdate()操作时,都是一次客户端到服务端发送sql的过程,发送和接受sql浪费了很多时间,降低了效率
解决方法:一次发送多条sql语句
批处理:一次提交多条SQL语句,节省网络开销
批处理的使用:
Statement:.addBatch(); .executeBatch(); .clearBatch();
addBatch():batch指执行sql的一个单元,addBatch即将一条条sql加入到batch这个单元中
executeBatch():执行一批sql语句
clearBatch():执行完毕,即可清空batch中的sql语句
private static void insertUsers(Set<String> users) throws ClassNotFoundException { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; // 1. 装载驱动程序 Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER); // 2. 建立数据库连接 try { conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASSWORD); // 3. 执行SQL语句 stmt = conn.createStatement(); // !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! // add Batch for (String user: users) { stmt.addBatch("insert into User values (null,'" + user +"');"); } // execute Batch stmt.executeBatch(); // clear Batch stmt.clearBatch(); // !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 4. 清理环境 try { if (conn != null) { // 若conn创建成功 conn.close();// conn.close()也可能有异常 } if (stmt != null) { stmt.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { // ignore e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { Set<String> users = new HashSet<String>(); users.add("GuoYi"); users.add("ZhangSi"); users.add("LiSan"); insertUsers(users); }
业务场景五:中文字符集
JDBC字符集需要和数据库的字符集相同
数据库的内部编码:
mysql> show variables like '%character%';
+--------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| character_set_client | utf8 |
| character_set_connection | utf8 |
| character_set_database | latin1 |
| character_set_filesystem | binary |
| character_set_results | utf8 |
| character_set_server | latin1 |
| character_set_system | utf8 |
| character_sets_dir | /usr/local/mysql-5.7.19-macos10.12-x86_64/share/charsets/ |
+--------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
8 rows in set (0.02 sec)
里面有个character_set_server:server级别的编码
character_set_database:database级别的编码
(还可以设置表级别Table、字段级别column等级别的编码)
优先级:Server -> Database -> Table -> column
设置JDBC的编码:
DB_URL = DB_URL + "characterEncoding=urt8";
JDBC 单元测试
以下哪项不是使用JDBC为我们编写应用程序访问数据库带来的好处?
- A.JDBC提供的仅仅是基础接口,基于这些接口,我们可以定制更加灵活方便的数据库框架。
- B.JDBC屏蔽了数据库客户端与服务器端繁琐的交互协议,降低了开发者使用数据库的门槛。
- C.JDBC 限定了数据库的使用方式,对于一些特殊的数据库协议,JDBC无法支持。
- D.应用程序使用标准的JDBC API接口,可以访问多个数据库,使得应用程序访问数据库的接口具有跨数据库特性。
有关JDBC的描述,哪项是不正确的?
- A.JDBC只是一个抽象的调用规范,底层程序实际上依赖各个数据库的驱动程序。
- B.JDBC的体系架构分为API层和Driver层:API层负责提供统一的接口给应用程序调用;Driver层负责实现到具体数据库的通信协议。
- C.JDBC提供了图形化的操作页面,程序员通过页面操作即可完成对数据库的管理。
- D.JDBC仅能在Java程序中使用,不能在C++程序中使用。
一个正确的JDBC操作步骤包括:
-
释放资源
-
获得数据库物理连接
-
执行SQL命令、
-
注册JDBC Driver
-
创建Statement
-
如果有结果集,处理结果集
- A.423561
- B.42356
- C.243561
- D.425361
下列哪个方法用于获取关系数据库二元表中某一列的值?
- A..getString()
- B..absolute()
- C..previous()
- D..next()
当一次向数据库插入多条数据时,应该使用JDBC的哪项高级功能?
- A.游标
- B.设置字符集
- C.流方式
- D.批处理
当需要读取某个大字段内容时,应该采用哪种JDBC的高级功能实现?
- A.游标
- B.批处理
- C.设置字符集
- D.流方式
使用游标时,需要设置?
- A.在JDBC的URL参数中,增加useCursorFetch=true
- B.使用PreparedStatment接口的ExecuteQuery方法
- C.使用Statement接口的ExecuteQuery方法
- D.需要设置setFetchSize接口
JDBC 单元作业
-
-
Id: auto_increment,自增主键,商品唯一标识;
-
ProductName:varchar(100),商品名称;
-
Inventory: int 商品库存;
-
表中已经插入了一些商品,请编写一段Java程序,尝试读取商品ID为1的商品记录,输出商品名称和库存数量。
注意:程序中已经定义了一些常量,DRIVER_NAME、DB_URL、DB_USER_NAME、DB_PASSWORD,大家在编写程序时,可以直接引用。
| Id | ProductName | Inventory |
| 1 | bread | 11 |
| 2 | milk | 8 |
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.Statement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; public class ProductProcessing { // static final String DRIVER_NAME = ""; // static final String DB_URL = ""; // static final String DB_USER_NAME = ""; // static final String DB_PASSWORD = ""; public static void processing() throws ClassNotFoundException { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { Class.forName(DRIVER_NAME); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, DB_USER_NAME, DB_PASSWORD); stmt = conn.createStatement(); rs = stmt.executeQuery("select ProductName, Inventory from Product where Id=1"); while (rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getString("ProductName") + ": " + rs.getString("Inventory")); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(conn != null) { conn.close(); } if(stmt != null) { stmt.close(); } if(rs != null) { rs.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { processing(); } }