转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/l1028386804/article/details/56513205
膜拜大神···
一、需求
假设现在有个如此的需求:需要对一个这样的雇员列表进行排序,排序规则如下:
1、首先级别最高的排在前面,
2、如果级别相等,那么按工资排序,工资高的排在前面,
3、如果工资相当则按入职年数排序,入职时间最长的排在前面。
雇员对象包含级别、工资和入职年份,代码如下:
- package import /**
- * 雇员信息
- * @author liuyazhuang
- *
- */ publicclassimplements privatestaticfinallong * ID
- */ publicint * 级别
- */ publicint * 工资
- */ publicint * 入职年数
- */ publicint publicint return publicvoidint this publicint return publicvoidint this publicint return publicvoidint this publicint return publicvoidint this publicintintintint this this this this }
二、实现Comparator接口
这里我们实现Java.util.Comparator接口,用于对雇员列表进行排序,代码如下:
- package import import /**
- * 核心排序类
- * @author liuyazhuang
- *
- */ publicclassimplements
- publicint int;
- int if) {
- ) ? : -;
- else
- if) {
- ) ? : -;
- else
- if) {
- ) ? : -;
- return }
三、验证排序结果
下面用一个单元测试,来验证排序结果是否正确
- package import import import import import import /**
- * 测试排序类
- *
- * @author liuyazhuang
- *
- */ publicclass
- publicvoidthrows new new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new );
- );
- for , employee.getId(), employee.getLevel(), employee.getSalary(),
- );
- }
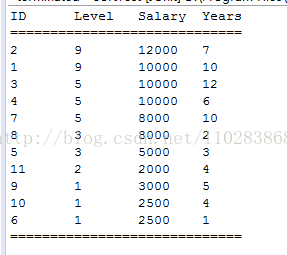
运行结果:
四、附录
java.util.Comparator接口源代码
- /*
- * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
- * contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
- * this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
- * The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
- * (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
- * the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
- *
- * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- *
- * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
- * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
- * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
- * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
- * limitations under the License.
- */ package /**
- * A {@code Comparator} is used to compare two objects to determine their ordering with
- * respect to each other. On a given {@code Collection}, a {@code Comparator} can be used to
- * obtain a sorted {@code Collection} which is <i>totally ordered</i>. For a {@code Comparator}
- * to be <i>consistent with equals</i>, its {code #compare(Object, Object)}
- * method has to return zero for each pair of elements (a,b) where a.equals(b)
- * holds true. It is recommended that a {@code Comparator} implements
- * {@link java.io.Serializable}.
- *
- * @since 1.2
- */ publicinterface * Compares the two specified objects to determine their relative ordering. The ordering
- * implied by the return value of this method for all possible pairs of
- * {@code (lhs, rhs)} should form an <i>equivalence relation</i>.
- * This means that
- * <ul>
- * <li>{@code compare(a,a)} returns zero for all {@code a}</li>
- * <li>the sign of {@code compare(a,b)} must be the opposite of the sign of {@code
- * compare(b,a)} for all pairs of (a,b)</li>
- * <li>From {@code compare(a,b) > 0} and {@code compare(b,c) > 0} it must
- * follow {@code compare(a,c) > 0} for all possible combinations of {@code
- * (a,b,c)}</li>
- * </ul>
- *
- * @param lhs
- * an {@code Object}.
- * @param rhs
- * a second {@code Object} to compare with {@code lhs}.
- * @return an integer < 0 if {@code lhs} is less than {@code rhs}, 0 if they are
- * equal, and > 0 if {@code lhs} is greater than {@code rhs}.
- * @throws ClassCastException
- * if objects are not of the correct type.
- */ publicint * Compares this {@code Comparator} with the specified {@code Object} and indicates whether they
- * are equal. In order to be equal, {@code object} must represent the same object
- * as this instance using a class-specific comparison.
- * <p>
- * A {@code Comparator} never needs to override this method, but may choose so for
- * performance reasons.
- *
- * @param object
- * the {@code Object} to compare with this comparator.
- * @return boolean {@code true} if specified {@code Object} is the same as this
- * {@code Object}, and {@code false} otherwise.
- * @see Object#hashCode
- * @see Object#equals
- */ publicboolean }