The common or classic Fibonacci algorithm
//Util.h static unsigned long long factorialLoops; long double Fibonacci35(int len); //Util.cpp unsigned long long Util::factorialLoops=0; long double Util::Fibonacci35(int i) { Util::factorialLoops++; if(i==0 || i==1) { return 1; } else { return Fibonacci35(i-1)+Fibonacci35(i-2); } } //In main.cpp void recursion16(int i) { Util ul; long double fib = 0; for (int x = 0; x < i; x++) { fib = ul.Fibonacci35(x); cout <<fixed<< "Fib of " << x << " is " << fib << endl; } cout<<"The recursion loops is "<<Util::factorialLoops<<endl; } int main(int args, char **argv) { recursion16(atoi(argv[1])); return 0; }
Compile via g++ and run as ./h1 50.The following snapshot will illustrate the inefficient reasons which located at call the method itself 65902560146(65B) times.It's evitable that the redundant time cost located at more than 65 billion times call the Fibonacci itself
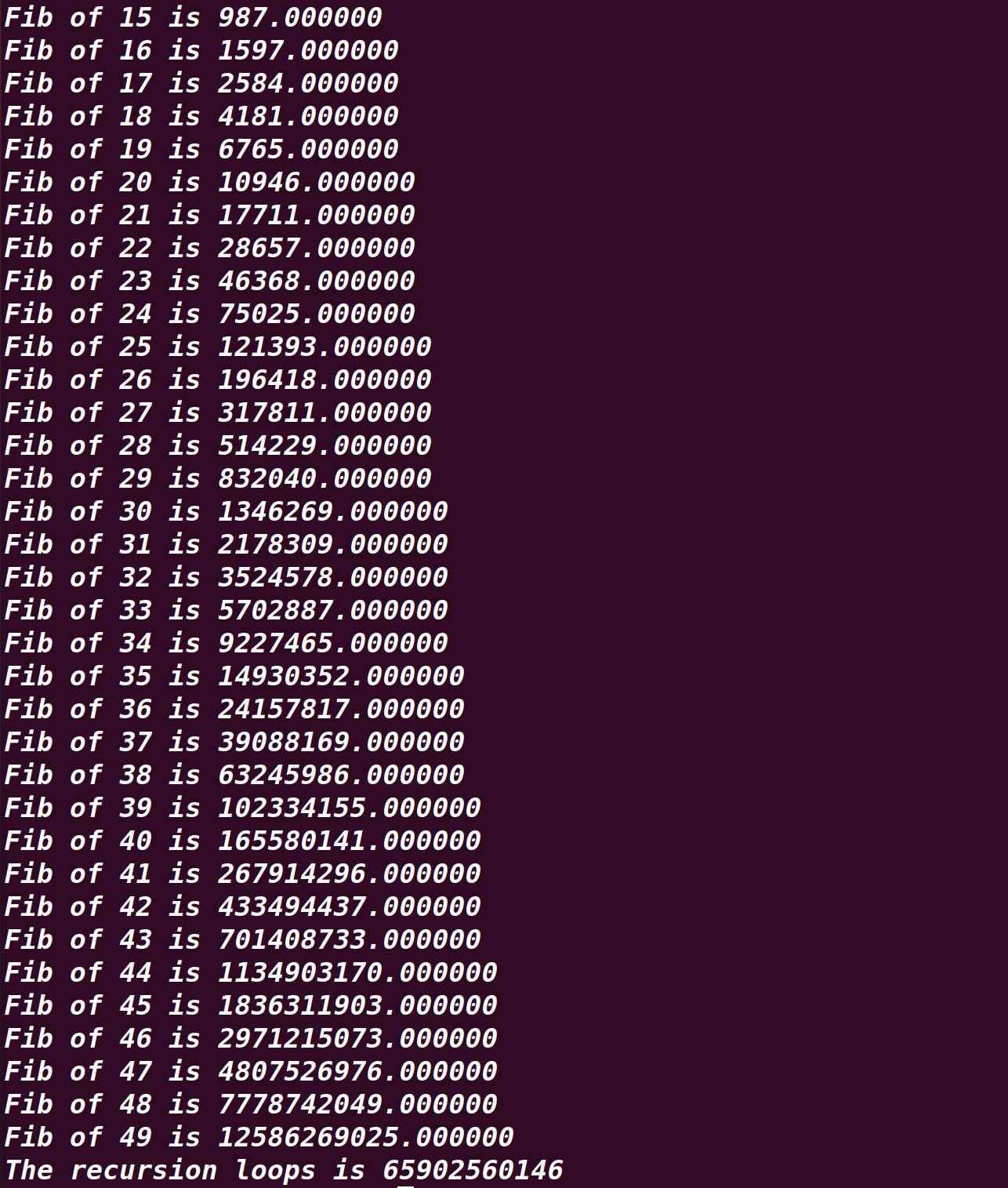
While in the optimized method
//Util.h static unsigned long long factorialLoops; static map<int,long double> mp; long double Fibnacci36(int len); //Uti.cpp unsigned long long Util::factorialLoops=0; map<int,long double>Util::mp; long double Util::Fibnacci36(int i) { Util::factorialLoops++; if(i==0 || i==1) { Util::mp.insert(pair<int,long double>(i,1)); } else { long double mpValue=(long double)(Util::mp.find(i-1)->second+Util::mp.find(i-2)->second); Util::mp.insert(pair<int,long double>(i,mpValue)); } return Util::mp.find(i)->second; } //main.cpp void recursion17(int x) { Util ul; for(int i=0;i<x;i++) { cout<<fixed<<"Fib of "<<i<<" is "<<ul.Fibnacci36(i)<<endl; } cout<<endl<<"The recursion loops is "<<Util::factorialLoops<<endl; } int main(int args, char **argv) { recursion17(atoi(argv[1])); return 0; }
Compile and run the optimized method as above,it will print the following snapshot immediately which demonstrates the third variable only ran 50 times.While the common or usual Fibonacci method will run more than 65 billion times.
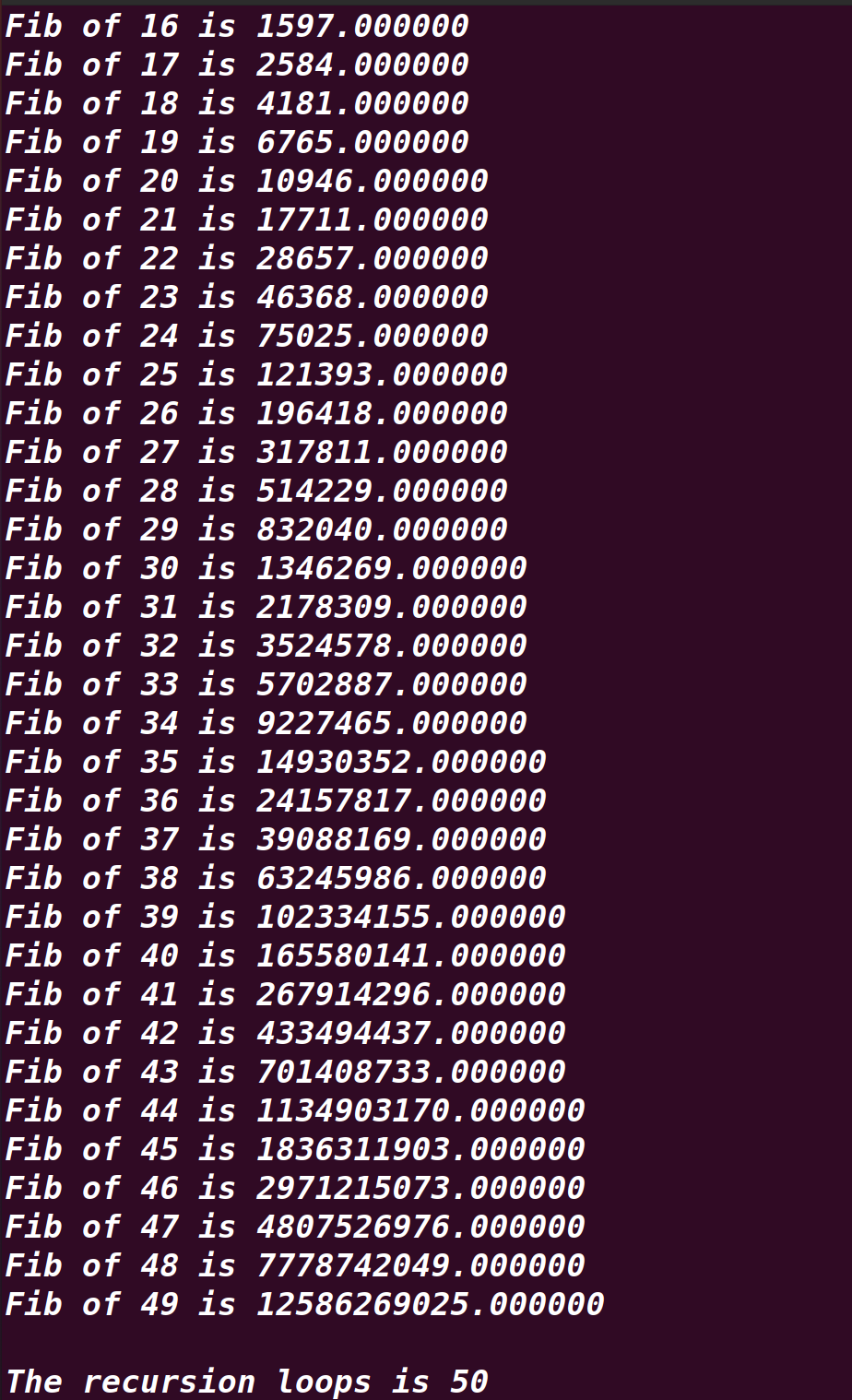
In the help of the third variable,we can found the root cause located at the help of the map collection which stores the computed result immediately and no need to calculte the expected former result from the scratch again and again.