CF1039C Network Safety
-
题面
The Metropolis computer network consists of nn servers, each has an encryption key in the range from (0) to (2^k-1) assigned to it. Let (c_i) be the encryption key assigned to the (i) -th server. Additionally, mm pairs of servers are directly connected via a data communication channel. Because of the encryption algorithms specifics, a data communication channel can only be considered safe if the two servers it connects have distinct encryption keys. The initial assignment of encryption keys is guaranteed to keep all data communication channels safe.You have been informed that a new virus is actively spreading across the internet, and it is capable to change the encryption key of any server it infects. More specifically, the virus body contains some unknown number (x) in the same aforementioned range, and when server (i) is infected, its encryption key changes from (ci) to (ci) (oplus) (x), where (oplus) denotes the bitwise XOR operation.
Sadly, you know neither the number (x) nor which servers of Metropolis are going to be infected by the dangerous virus, so you have decided to count the number of such situations in which all data communication channels remain safe. Formally speaking, you need to find the number of pairs ((A,i)), where (A) is some (possibly empty) subset of the set of servers and (x) is some number in the range from (0) to (2^k-1), such that when all servers from the chosen subset (A) and none of the others are infected by a virus containing the number (x) , all data communication channels remain safe. Since this number can be quite big, you are asked to find its remainder modulo (10^9+7).
-
题意
给出一个由 (n) 个点 (m) 条边组成的图,每个点有一个权值 (c_i)。保证给出的图是“安全”的。((n leq 500000,m leq min(frac{n*(n-1)}{2},500000),c_i leq 2^k-1,k leq 60))
对于“一个‘安全’的图”的定义是:对于这个图里所有的边的两端点都满足 (c_l ot = c_r)。
现在对于任意一个 (x) ((x leq 2^k-1)),图中任意数量的点组成的点集 (s),求 (s) 中所有的点 (xor) (x) 后,图仍然为“安全”的图,这样的 (x) 和 (s) 组合的方案数,答案对 (10^9+7) 取模。
- 题解
考虑下面这个样例 (n=4,m=4,k=2) 的情况,很明显,当 (x=0,2,3) 时都有 (2^4) 种方案。
只有当 (x=1) 时,(0 oplus 1=1),会使图出现不安全的情况,那么使图为安全的方案只有全部 (xor) (x) 和全部不 (xor) (x) 两种方案。
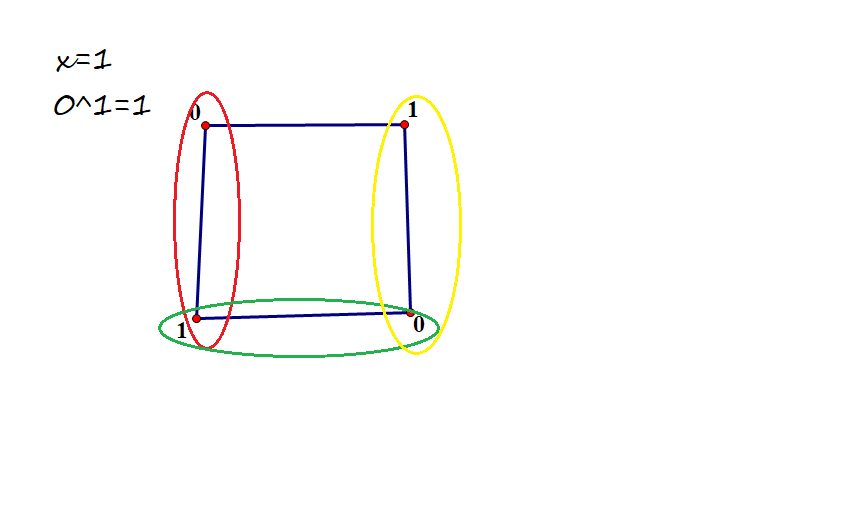
那么就可以归纳出:如果对于一个 (x),它对图是否安全不会产生影响(无论怎么操作,一定不会产生使图“不安全”的 (x)),它对答案的贡献一定是 (2^n)。所以我们只要考虑会对图是否“安全”产生影响的 (x) 即可。
对于一条边,当 (c_l oplus x=c_r) 时,要使图为安全的,只有这条边上两个点全部 (xor) (x) 和全部不 (xor) (x) 这两种情况,也就是都取,或者都不取两种情况。那么就可以抽象地把两个点看成一个点,用并查集去维护合并点的过程,每次合并点数都 (-1)。(如图中情况,每次把每条边上的两个点看成一个点,最终得到的只有一个点,那么就只有这个点 (xor) (x) 和不 (xor) (x) 两种方案。)
- 接下来就是一点也不激动人心的代码了:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
/* Forever_chen */
#define RT register
#define M 1000000007
#define int long long
using namespace std;
template<class t> inline t read(t &x){
char c=getchar();bool f=0;x=0;
while(!isdigit(c)) f|=c=='-',c=getchar();
while(isdigit(c))x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48),c=getchar();
if(f)x=-x;return x;
}
template<class t>inline void write(t x){
if(x<0)putchar('-'),write(-x);
else{if(x>9)write(x/10);putchar('0'+x%10);}
}
template<class t>inline void writeln(t x){
write(x);putchar('
');
return;
}
template<class t>inline void write_blank(t x){
write(x);putchar(' ');
return;
}
int n,m,k,a[500010],f[500010],cnt[500010],tot,ans,p[500010];
vector<int> qx[500010],qy[500010];
map<int,int>vis;
namespace bsfc{
int quick_power(int x,int y){
int ans=1,cnt=x;
while(y){
if(y&1){
ans=ans*cnt%M;
}
cnt=cnt*cnt%M;
y>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
int find(int k){
if(f[k]==k){
return k;
}
return f[k]=find(f[k]);
}
}
signed main(){
//freopen(".in","r",stdin);
//freopen(".out","w",stdout);
read(n);
read(m);
read(k);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
f[i]=i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
read(a[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
cnt[i]=n;
}
for(int i=1,l,r;i<=m;i++){
read(l);
read(r);
if(vis[a[l]^a[r]]==0){
tot++;
vis[a[l]^a[r]]=tot;
}
p[vis[a[l]^a[r]]]++;
qx[vis[a[l]^a[r]]].push_back(l);
qy[vis[a[l]^a[r]]].push_back(r);
}
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++){
for(int j=0;j<p[i];j++){
int fx=bsfc::find(qx[i][j]),fy=bsfc::find(qy[i][j]);
if(fx!=fy){
f[fx]=fy;
cnt[i]--;
}
}
for(int j=0;j<p[i];j++){
f[qx[i][j]]=qx[i][j];
f[qy[i][j]]=qy[i][j];
}
ans=(ans+bsfc::quick_power(2,cnt[i]))%M;
}
ans=(ans+((1ll<<k)-tot)%M*bsfc::quick_power(2,n)%M)%M;
writeln(ans);
//system("pause");
return 0;
}