阅读文章前需要了解的知识,纹理:https://learnopengl-cn.github.io/01%20Getting%20started/06%20Textures/
过程简述:利用 FreeImage 库加载图像数据,再创建 OpenGL 纹理,通过 Canvas2D 画布绘制,最后又 Renderer 渲染器渲染
本来想用 soil 库加载图像数据的,虽然方便,但是加载有些格式的图像文件时会出现一些问题。最后,改用 FreeImage 库来加载图像了。
添加 FreeImage 库到工程
解压 FreeImage.rar 文件后得到三个文件

将其分别拷贝到 debug文件夹、External 文件夹、Lib 文件夹中,再链接上 lib 库。
绘制图片
创建一个纹理结构,储存纹理索引、大小以及纹理坐标
struct DLL_export Texture { Rect size; Vec2 texcoords[4]; GLuint texture; };
创建一个纹理管理器类 TextureManager,用于创建和管理纹理。
利用 FreeImage 库加载纹理
Texture* TexrureManager::createTexture(const char* filename) { GLuint texture = -1; std::string fullName = PathHelper::fullPath(filename); unsigned char* image_data = nullptr; FIBITMAP* bmp = nullptr; /* 初始化 FreeImage */ FreeImage_Initialise(TRUE); /* 获取图像文件类型 */ FREE_IMAGE_FORMAT fif = FIF_UNKNOWN; fif = FreeImage_GetFileType(fullName.c_str()); if ( fif == FIF_UNKNOWN ) { fif = FreeImage_GetFIFFromFilename(fullName.c_str()); } /* 加载所支持图像类型的图像 */ if ( (fif != FIF_UNKNOWN) && FreeImage_FIFSupportsReading(fif) ) { bmp = FreeImage_Load(fif, fullName.c_str(), JPEG_DEFAULT); } if ( !bmp ) return nullptr; int w = FreeImage_GetWidth(bmp); int h = FreeImage_GetHeight(bmp); int pixel_count = w * h; int byte_per_pixel = FreeImage_GetLine(bmp) / w; image_data = ( unsigned char* ) malloc(sizeof( unsigned char ) * pixel_count * 4); unsigned char* bits = FreeImage_GetBits(bmp); int current_pixel = 0; if ( byte_per_pixel == 4 ) { for ( int i = 0; i < pixel_count; i++ ) { image_data[i * 4 + 2] = bits[current_pixel++]; image_data[i * 4 + 1] = bits[current_pixel++]; image_data[i * 4 + 0] = bits[current_pixel++]; image_data[i * 4 + 3] = bits[current_pixel++]; } } else { for ( int i = 0; i < pixel_count; i++ ) { image_data[i * 4 + 2] = bits[current_pixel++]; image_data[i * 4 + 1] = bits[current_pixel++]; image_data[i * 4 + 0] = bits[current_pixel++]; image_data[i * 4 + 3] = 255; } } if ( bmp ) FreeImage_Unload(bmp); FreeImage_DeInitialise(); glGenTextures(1, &texture); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture); /* 设置纹理选项 */ glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, w, h, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, image_data); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0); free(image_data); Texture* tex = new Texture(); tex->texture = texture; tex->size.set(0, 0, w, h); tex->texcoords[0].set(0, 0); tex->texcoords[1].set(0, 1); tex->texcoords[2].set(1, 1); tex->texcoords[3].set(1, 0); return tex; }
在函数中,使用 FreeImage 库加载纹理数据,然后创建 OpenGL 2D纹理,将创建的纹理保存到 Texture 结构中,并设置了纹理坐标。
在 Canvas2D 中绘制纹理
void Canvas2D::drawTexture(int x, int y, Texture* texture, Color& color) { int w = texture->size.w; int h = texture->size.h; this->resizeVector(4, 6); vPositions[0].set(x + 0, y + 0, 0); vPositions[1].set(x + 0, y + h, 0); vPositions[2].set(x + w, y + h, 0); vPositions[3].set(x + w, y + 0, 0); vIndices[0] = 0; vIndices[1] = 2; vIndices[2] = 1; vIndices[3] = 0; vIndices[4] = 3; vIndices[5] = 2; static RenderUnit unit; unit.pPositions = &vPositions[0]; unit.nPositionCount = 4; unit.pTexcoords = texture->texcoords; unit.pIndices = &vIndices[0]; unit.nIndexCount = 6; unit.color = color; unit.texture = texture; unit.renderType = RENDER_TYPE_TEXTURE; pRenderer->pushRenderUnit(unit); }
函数很简单,设置了顶点数据并填充了 RenderUnit,再传到 渲染器中渲染。与绘制几何图形相比,多了纹理坐标,并把渲染类型设置为 渲染纹理。
渲染器 Renderer 渲染纹理
添加成员
std::map<Texture*, VertexData*> textureDatas;
每张纹理都有其相应的顶点数据,这样可以把多张相同纹理的顶点数据放到一个缓冲区中渲染,保证了渲染多张相同纹理时只使用使用一个 DrawCall(调用 函数 glDrawElements 进行绘制的次数),提高渲染效率。
在 pushRenderUnit 函数中
else if ( unit.renderType == RENDER_TYPE_TEXTURE ) { auto it = textureDatas.find(unit.texture); if ( it == textureDatas.end() ) { vertexData = new VertexData(); vertexData->bHasTexcoord = true; vertexData->renderType = RENDER_TYPE_TEXTURE; textureDatas.insert(std::make_pair(unit.texture, vertexData)); } else { vertexData = it->second; } }
索引出纹理对应的 VertexData,然后填充数据。最后的渲染函数中添加填充纹理坐标代码
/* 设置纹理 */ if ( vertexData->bHasTexcoord ) { glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, texcoordBuffer); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof( Vec2 ) * vertexData->nPositionCount, &vertexData->texcoords[0], GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW); glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texrure); glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "defaulteTexture"), 0); }
为了能够渲染纹理需要更改着色程序
顶点着色器
#version 330 core layout(location = 0) in vec3 Position; layout(location = 1) in vec2 Texcoord; layout(location = 2) in vec4 Color; out vec2 texcoord; out vec4 color; uniform int bRenderTexture; void main() { gl_Position = vec4(Position, 1.0f); color = Color; if( bRenderTexture != 0 ){ texcoord = Texcoord; } }
片段着色器
#version 330 core out vec4 Color; in vec2 texcoord; in vec4 color; uniform sampler2D defaultTexture; uniform int bRenderTexture; void main() { if( bRenderTexture != 0 ){ Color = texture(defaultTexture, texcoord) * color * color.w; } else{ Color = color; } }
为了开启 Alpha 效果,设置OpenGL 的混合状态
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
在主函数中添加绘制图像的代码
Texture* texture = TexrureManager::instance()->getTexture("image.png"); Texture* texture1 = TexrureManager::instance()->getTexture("image.jpg");
canvas.drawTexture(180, 0, texture1, Color(1, 1, 1, 1)); canvas.drawTexture(120, 100, texture, Color(1, 1, 1, 0.8));
程序的运行结果
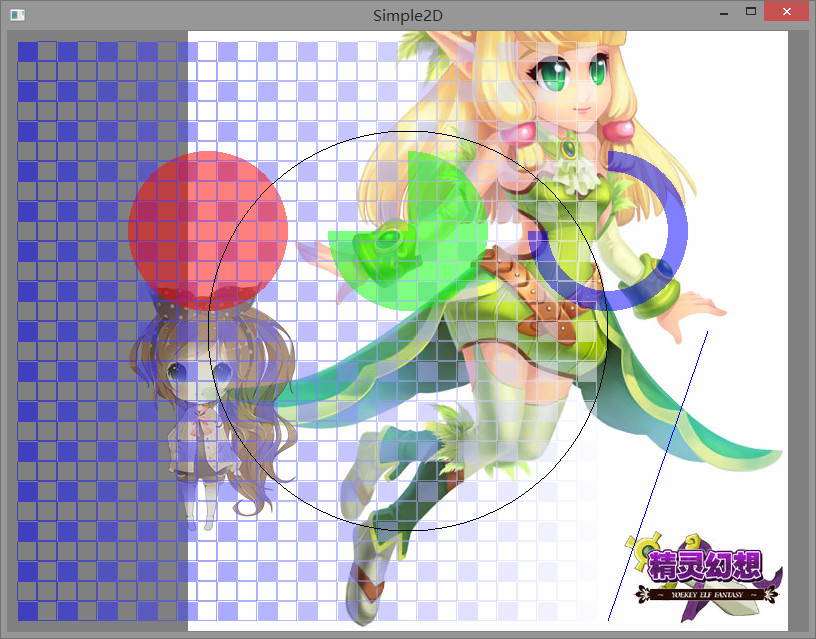
这里绘制了 png 和 jpg 格式的图像