对比以下两种写法,思考一下为何可以这样写。
成绩在 [0,50)、[50,60)、[60,80)、[80,100)、100、其它
score = float(input("请输入你的成绩:")) if score == 100 : print('666呀,走吃大餐去') elif 80 <= score < 100 : print('还行,优秀,走,喝饮料去') elif 60 <= score < 80 : print('加油呀,弄明白点') elif 50 <= score < 60 : print('这可有点浪哟') elif 0 <=score < 50 : print('学不懂吗?') else : print('你输入的是啥?')
80 <= score < 100 为何可以写成 score >= 80 ? 上一条语句不满足时往下执行,这时 score <100 就不需要了;
注意: 如果把这些条件表达式的顺序换下,那么这种写法是错误的。
score = float(input("请输入你的成绩:")) if score == 100 : print('666呀,走吃大餐去') elif score >= 80 : print('还行,优秀,走,喝饮料去') elif score >= 60 : print('加油呀,弄明白点') elif score >= 50 : print('这可有点浪哟') elif score >= 0 : print('学不懂吗?') else : print('你输入的是啥?')
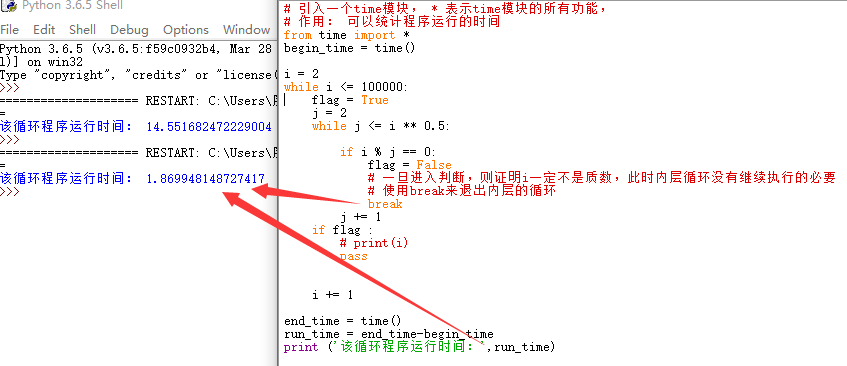
利用break进行程序运行时间的优化
在循环语句中,可以用break来退出不必要继续执行的循环
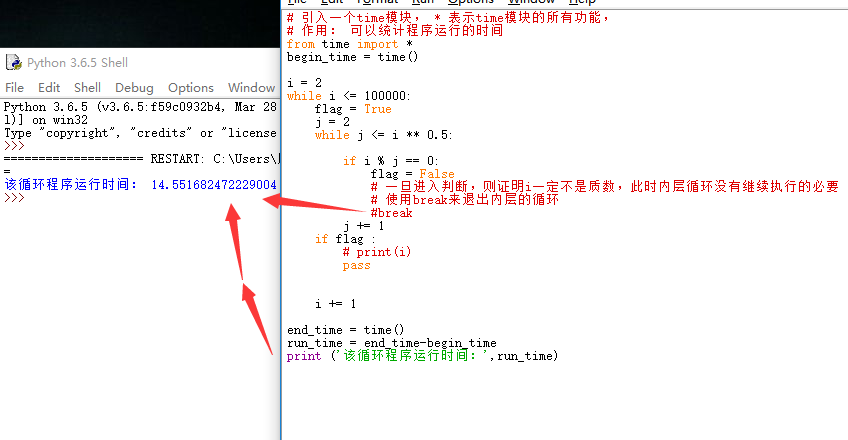
有break后