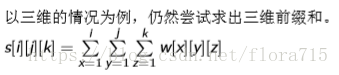一. 算法基础
复杂度
时间复杂度用来衡量程序的运行速度。
运行速度
程序运行一个在内存中寻址、赋值、加法、减法、乘法、除法、开方,
都认为可以在常数的时间内进行,这样的操作都被认为是基本操作。
基于对程序基本操作的说明,一个程序的运行时间不仅跟问题本身有关,
还跟硬件速度、问题规模有关。一般来说,问题的规模越大,
所需要运行的时间就越久;硬件速度越快、程序跑的就越快。
时间复杂度
忽略掉硬件优劣带来的差异,只考虑问题的规模大小对运行时间带来的影响。
以一个程序需要使用的基本操作次数作为衡量程序运行速度的标准:时间复杂度 T(n)。
大 O
对于一个函数 f(n),如果存在 g(n) 和常数 c,当 n 充分大的时候,
始终有 c∗g(n) ≥ f(n),则 g(n) 是 f(n) 的一个渐近上界,写成 f(n) = O(g(n))。
(差不多是到达终点最多可能使用的运行次数)
冒泡排序的复杂度
执行 n 轮,每一轮都会扫描一遍序列并交换相邻逆序对,时间复杂度 T(n) = O(n^2)。
不对?冒泡排序第 i 轮只用扫 n−i 对相邻的数,明明只会执行n(n−1)/2次比较?
在分析复杂度时,我们忽略较低次数的项和最高次项的常数。
归并排序的复杂度
每次分成两半,左右分别排序,递归排序,再将两侧排序好的数组合并。
(分治思想)复杂度 T(n) = 2T(n/2) +O(n) = O(nlogn)
void Merge(int a[],int left ,int mid,int right){ int i=left,j=mid+1,n=0,length=right-left; //i开始为左半部分最左边,j为右半部分最左边。temp数组是从下标0开始存数。 while(i<=mid&&j<=right){ if(a[i]>a[j]){ //左边比右边大。 temp[n++]=a[j++]; num+=mid-i+1; //从i到mid都是比a[j]大。 } else temp[n++]=a[i++]; } if(i>mid){ //因为前面的判断条件是i<=mid,这里说明的是左边全部填满了,那就是填右边了。 while(j<=right) temp[n++]=a[j++]; } else{ while(i<=mid) temp[n++]=a[i++]; } for(int k=0;k<=length;k++){ //最后赋值到原数组必须要有的。 a[left+k]=temp[k]; } } void mergesort(int a[],int left,int right){ if(left<right){ int mid=(left+right)/2; mergesort(a,left,mid); mergesort(a,mid+1,right); Merge(a,left,mid,right); } }
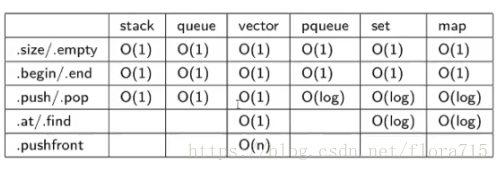
什么是 STL?
STL(Standard Template Library)是 C++ 标准模板库,里面提供了大量模板。
队列 (先进先出)
加载库:include < queue > 申明:queue < type > name
queue中元素在内存中不一定连续。
q.push(x) 向队列 q 末尾加入元素 x 。
q.front() 返回队列 q 开头元素。q.back() 返回队列 q 末尾元素。
q.size() 返回队列 q 元素个数。q.empty() 返回队列 q 是否为空。
应用:SPFA算法,BFS。(需要先来先走的情况,扩展节点)
栈 (后进先出)
加载库:include < stack > 申明:stack < type > name
stack中元素在内存中不一定连续。
t.top() 返回 t 栈顶元素。t.pop() 弹出 t 栈顶元素。
t.push(x) 将元素 x 压入 t 栈顶。
vector (不定长数组)
加载库:include < vector > 申明:vector < type > name (从0开始)
vector中元素在内存中连续,支持随机寻址(任意询问任一元素)。
v.push_back(x) 将元素 x 压入 v 末尾。v.clear() 清空 v 中所有元素。
v.begin() 指向 vector 中0号位置的元素的指针地址。
v.end() 指向 vector 中最后一个元素的下一个的指针地址。
应用:题目未知数组长度时,使用 vector 代替数组。
Q:迭代器 it ?(int类型)
A:指向内存中的地址。定义方式 vector<int> ::iterator it; 。
可以用它去遍历 vector 数组。用‘’*‘’取出指针,*it。
it++;//地址向后移一位 ( it+=2 在目前的部分版本中是可以的 )
输出地址指向的数:cout << (*it) << endl;(或 *(it+2) )
priority_queue (优先队列)
加载库:include < priority_queue > 申明:priority_queue < type > name
一般使用:priority_queue< int,vector<int>,greater<int> > q; //小根堆
( 注意有三个元素要写,vector<int>无意义,但要写;或者只写前面的一个也可以 )
重载小于号:
struct node{ //默认大根堆 int x,y; //先按和排序,再按x排序 bool operator<(const node &v) const { if(x+y!=v.x+v.y) return x+y < v.x+v.y; return x<v.x; } //重载之后变为从小到大排序 }; priority_queue<node> q;
优先队列就是堆,支持在队列中加入元素、取堆顶、删除堆顶。
q.top() 返回 q 中堆顶。q.pop() 弹出 q 中堆顶。
q.push(x) 将 x 压入 q 中。
set (去重并已经排序的集合)
加载库:include < set > 申明:set < type > name
set支持插入、删除、查找元素,并且支持查询大于(等于)某值的最小元素。
s.insert(x) 将 x 加入集合 s 中。s.begin() 返回集合 s 第一个元素的迭代器。
s.end() 返回集合最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器。
//↑↑↑已去重集合 for(set<int> ::iterator it=s.begin(); it!=s.end(); it++) cout<<(*it)<<endl; //↓↓↓未去重集合 for(multiset<int> ::iterator it=s.begin(); it!=s.end(); it++) cout<<(*it)<<endl;
multiset (可重集合)
加载库:include < multiset > 申明:multiset < type > name
multiset与 set 相同,但允许集合中有多个相同元素。
map (散列表&&映射关系)
加载库:include < map > 申明:map < type1,type2 > name
map是一种关联容器,提供一对一映射处理的能力。
map<int,int> a; int main(){ a[2]=5; a[3]=6; //pair<int,int> (2,5) cout << (*a.find(2)).first << endl; cout << (*a.find(2)).second << endl; cout << (a.find(2)==a.end()) << endl; //a.find(2)返回迭代器所表现的位置 }
pair (将2个数据组合成一个数据)
// 排序时,默认先比较第一关键字,再比较第二关键字。
typedef pair<int,int> mp; mp b[10]={mp(2,4),mp(3,5),mp(1,5),mp(2,3)}; int main(){ sort(b,b+4); for(int i=0;i<4;i++) cout<<b[i].first<<" "<<b[i].second<<endl; }
stl中复杂度的比较
auto (自动寻找元素类型)
二分 (logn)
二分答案的思想:二分答案可能的范围,判断是否可能,寻找最值。
vector / set / multiset 都提供了 lower_bound 函数。
lower_bound(b, e, x) 会返回 [b,e) 中第一个值不小于 x 的地址;
upper_bound(b, e, x) 会返回 [b,e) 中第一个值大于 x 的地址。(左闭右开)
#include <algorithm>//必须包含的头文件 #include <stdio.h> using namespace std; int main(){ int n,a[100],m; int left,right,i; scanf("%d",&n);//设初始数组内元素有n个 for(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); scanf("%d",&m);//插入的数为m left = upper_bound(a,a+n,m)-a;//按从小到大,m最多能插入数组a的哪个位置 right = lower_bound(a,a+n,m)-a;//按从小到大,m最少能插入数组a的哪个位置 printf("m最多能插入数组a的%d ",left); for(i=0;i<left;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]); printf("%d ",m); for(i=left;i<n;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]); printf(" "); printf("m最少能插入数组a的%d ",right); for(i=0;i<right;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]); printf("%d ",m); for(i=right;i<n;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]); return 0; }
二维前缀和
给定 n∗m 的网格,每个网格中有数值,Q 次询问,给定 (x1,y1) 与 (x2,y2),
求以 (x1,y1) 作为左下角,(x2,y2) 作为右上角形成的子矩形中数值之和。
数据范围 n,m ≤ 300, Q ≤ 10^5。
【分析】
【差分】若已知前缀和 s,求原数组 w 的过程叫做差分。
只需要利用 s[i][j] = s[i−1][j] +s[i][j−1]−s[i−1][j−1] +w[i][j]。
移项 w[i][j] = s[i][j]−s[i−1][j]−s[i][j−1] +s[i−1][j−1]。
高位前缀和
【分析】
二. 例题
1. tyvj 1359 收入计划 (二分答案)
有长度为 n 的数组,你要将其分成 m 段,使得数组中的每个数都恰好在一段中,
并且使得 m 段中和最大的一段最小,请求出这个最小的值。 数据范围 m≤n≤10^5。
【分析】考虑检验能否将数组分成 m 段使得每一段的和都不超过 x。
从头开始贪心,要超过 x 时切出新的一段 O(n)。
考虑 x 可以时,x+1 也一定可以,即有单调性。二分 x,检验 O(nlogn)。

#include <stdio.h> #include <algorithm> #include <string.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; const int N=100005; int n,m,data[N],l,r,mid,ans,Max,sum; bool check() { int cnt=1,sum=0; for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){ sum+=data[i]; //sum是滚动的 //尽量加在前一组,加不了,再重开一组 if (sum>mid) cnt++,sum=data[i]; if (cnt>m) return false; } return true; } int main() { cin>>n>>m; for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) { cin>>data[i]; Max=max(Max,data[i]); sum+=data[i]; } l=Max; r=sum; while (l<=r) { mid=(l+r)>>1; if (check()) ans=mid,r=mid-1; else l=mid+1; } cout<<ans<<endl; return 0; }
2. 51nod 1105 第 K 大的数
给定长度为 n 的数组 A 和 B,将数组 A 和 B 数组中的元素两两相乘,
得到长度为 n∗n 的数组 C,求 C 中第 K 大数。数据范围 n≤ 50000,ai,bi ≤ 10^9。
【分析】
n*log(n)的算法,二分里面再套一个二分。
二分答案,l = a[0]*b[0], r = a[n-1]*b[n-1] 判断 >=mid的数目。
(代码中是求的c中有多少数>=x)

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const int MAXN = 5e4+5; LL a[MAXN], b[MAXN]; LL Judge(LL x, int n){ //找 a[i]*b[j]>=x 的数目 LL sum = 0, tp; for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--){ //枚举a数组,二分b数组 if(x % a[i]) tp = x/a[i]+1; else tp = x/a[i]; int tmp = lower_bound(b,b+n,tp)-b; sum += n-tmp; if(sum == 0) break; } return sum; } int main(){ int n, k; while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&k)){ for(int i=0; i<n; i++) scanf("%I64d%I64d",&a[i],&b[i]); sort(a, a+n); sort(b, b+n); LL l = a[0]*b[0], r = a[n-1]*b[n-1]; while(l <= r){ //二分答案 LL mid = (l+r)>>1; LL tmp = Judge(mid, n); if(tmp < k) r = mid-1; else l = mid+1; } printf("%I64d ",l-1); } return 0; }
【分析】
4.纽约
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/U33405
Azone 决定花费 w 元津巴布韦币,购买一辆载重为 w 的汽车。
共有 n 件家具需要搬运,每件家具的重量为 wi 。
Azone 每次出发前,会搬若干件总重不超过 w 的物品上车:出发前,车是空载的,
Azone 会选择能搬上车的家具中最重的一件放上车(即该家具之前还未运走且放置该家具后汽车不会超载),
然后在剩下的家具中继续选择一件能被搬走的最重的上车,持续装车,直至剩下的家具都塞不上车。
装载完毕后,Azone 会开车运走这些家具,卸在目的地,再驾空车返回继续运送,直至转场完毕。
Azone 希望在运送次数不超过 R的情况下完成转场,求 Azone 最少需要购置价值多少的车。

#include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> using namespace std; int n,R,a[2003],l,r,mid; int ans,pre[2003],nxt[2003]; bool okk(int w){ for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) pre[i]=i-1,nxt[i]=i+1; pre[n+1]=n; //链式用于记录仍留下的家具(已按价值排序过) for(int i=1,s=0,x=n;s<n;x=pre[n+1],i++){ if(i>R) return false; for(int p=w;p>0 && x;x=pre[x]) if(p>=a[x]){ //寻找最大可放家具 s++; p-=a[x]; nxt[pre[x]]=nxt[x]; pre[nxt[x]]=pre[x]; } } return true; } int main(){ scanf("%d%d",&n,&R); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d",&a[i]); r+=a[i],l=max(l,a[i]); } sort(a+1,a+1+n); while(l<r){ mid=(l+r)>>1; if(okk(mid)) r=mid; else l=mid+1; } for(ans=l-50;ans<=l && !okk(ans);ans++); printf("%d",ans); return 0; }
——时间划过风的轨迹,那个少年,还在等你。