1.程序和进程
程序:二进制文件,占用磁盘空间
进程:启动的程序
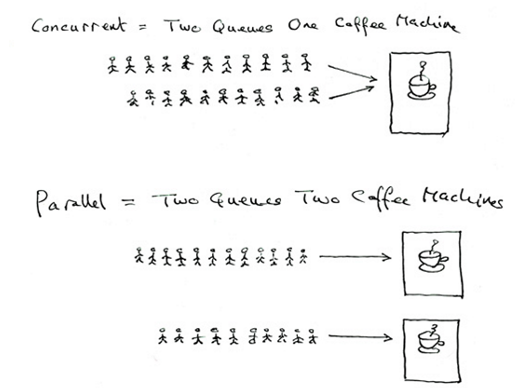
2.并行与并发
并行:时间点概念
并发:时间段概念
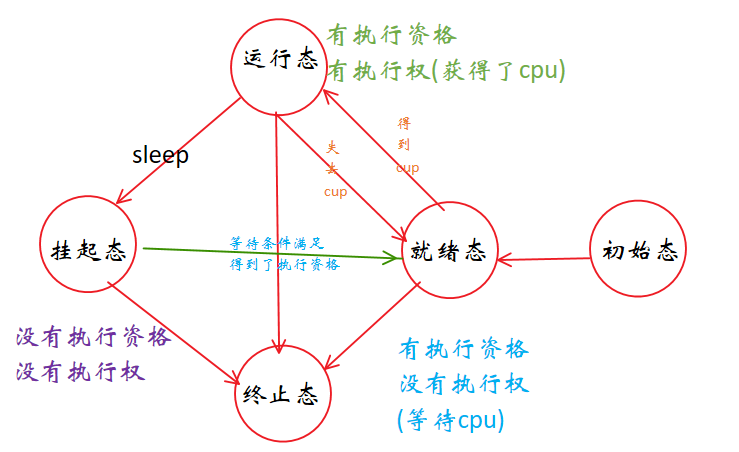
3.进程5种状态
4.循环创建多个子进程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
int counter = 100;
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
pid_t pid;
int i=0;
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
{
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0)
{
break;
}
}
// 父进程
if(i == 3)
{
counter += 100;
printf("parent process, pid = %d, ppid = %d, %d
", getpid(), getppid(), counter);
// sleep(1);
}
// 子进程
else if(i == 0)
{
// 1th
counter += 200;
printf("child process, pid = %d, ppid = %d, %d
", getpid(), getppid(), counter);
}
else if(i == 1)
{
// 2th
counter += 300;
printf("child process, pid = %d, ppid = %d, %d
", getpid(), getppid(), counter);
}
else if(i == 2)
{
// 3th
counter += 400;
printf("child process, pid = %d, ppid = %d, %d
", getpid(), getppid(), counter);
}
return 0;
}
5.ps、kill
```
ps aux | grep myhello
ps ajx
kill:向指定进程发送信号
kill -l 查看信号
kill -9 杀死进程
```
6.exec函数族
让父子进程执行不相干操作(替换进程地址空间中代码段)
执行一个另外的程序不需要创建额外的地址空间
execl()

#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
printf("hello, world
");
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == -1)
{
perror("fork error");
exit(1);
}
// 子进程执行程序
if(pid == 0)
{
execl("hello", "xxxx", NULL);
//execl("/home/kevin/hello", "xxxx", NULL);
perror("execl");
exit(1);
}
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
printf(" i = %d
", i);
}
return 0;
}
execlp()

#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
printf("hello, world
");
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == -1)
{
perror("fork error");
exit(1);
}
// 子进程执行程序
if(pid == 0)
{
execlp("ps", "pssdfsdf", "aux", NULL);
perror("execlp");
exit(1);
}
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
printf(" i = %d
", i);
}
return 0;
}
7.wait、waitpid
进程结束之后,能够释放用户空间,释放不了内核空间,需有父进程回收








