





题解:
第一题:大模拟,先把在一个循环里的连续k个相同都去掉,然后算出头和尾能消去的个数,然后就是每个循环剩余长度*(m-1)+仅去掉同一循环的剩余数的个数。

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long const int M = 1e5 + 10; ll st[M][2]; ll ans, tot; int main(){ freopen("guass.in","r",stdin); freopen("guass.out","w",stdout); ll n, k, m, cnt = 0; scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d", &n, &m, &k); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ int x;scanf("%d", &x); if(!cnt || st[cnt][0] != x){ st[++cnt][0] = x; st[cnt][1] = 1; } else st[cnt][1]++; if(st[cnt][1] >= k)st[cnt][1] -= k; if(!st[cnt][1])cnt--; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)tot += st[i][1]; int h = 1, t = cnt; while(h != t && st[h][0] == st[t][0]){ if((st[h][1] + st[t][1]) % k == 0)h++, t--; else { st[h][1] = (st[h][1] + st[t][1]) % k; st[t][1] = 0; break; } } if(h != t){ for(int i = h; i <= t; i++)ans += st[i][1]; ans *= (m - 1); ans += tot; } else { if(st[h][1]* m % k == 0)ans = 0; else { ans = tot - st[h][1] + st[h][1] * m % k; } } printf("%I64d ",ans); }
第二题:
当m<=2时,枚举分界点,预处理前缀和就好了
对于另外20%,直接dp[i][j]表示到点i,j的最优答案
对于100%,我们要求黄色部分: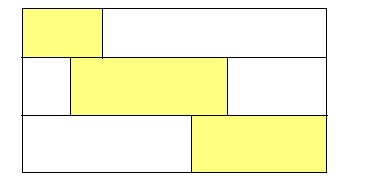
即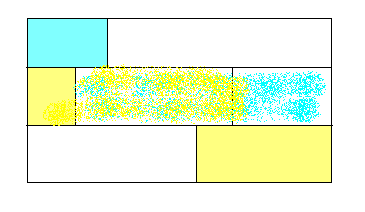
黄+蓝-第二行,我们先处理蓝-第二行,然后找到一个黄色模意义下第三行的最优贡献就好了,这个就可以用set维护,找前驱;
最优 两个数加起来<p, 最接近p, 或者>p, 则找一个最大的和他组合

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int M = 100005; #define ll long long ll p; int n, m, tot; ll sum[M], now[M], sum2[M], sum4[M], sum3[M], a[M], b[M], c[M], t[M]; set<ll>::iterator it, itt; set<ll> st; int main(){ freopen("candy.in","r",stdin); freopen("candy.out","w",stdout); int m, n; ll ans = 0; scanf("%d%d%I64d", &n, &m, &p); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ scanf("%I64d", &a[i]); sum[i] = (sum[i - 1] + a[i]) % p; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)scanf("%I64d", &b[i]); for(int i = n; i > 0; i--) sum2[i] = (sum2[i + 1] + b[i]) % p; if(m == 2){ for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)ans = max(ans, (sum[i] + sum2[i]) % p); printf("%I64d ", ans); } else { t[0] = p; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) now[i] = ( sum[i] + sum2[i] - sum2[1] + p ) % p; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)scanf("%I64d", &c[i]); for(int i = n; i > 0; i--){ sum4[i] = (sum4[i + 1] + c[i]) % p; sum3[i] = (sum4[i] - sum2[i + 1] + sum2[1] + p) % p; } for(int i = n; i > 0; i--){ st.insert(sum3[i]); ll cc = p - now[i]; it = st.lower_bound(cc); if(it != st.begin())it--; itt = st.end(); itt--; ll ans1 = (now[i] + *it) % p; ll ans2 = (now[i] + *itt) % p; ans = max(max(ans1, ans2), ans); } printf("%I64d ", ans); } }
第三题:
通过题目可以发现,我们要求的就是在使用最小的点权的情况下选中所有边,每条边都可以被他的两个端点选中,且出入点权可能不同,于是就可以发现这是一个最小点权覆盖。
建边:
1> 先建立虚拟源S和汇T,把每个点拆成两个,ia,ib。
2> 从S向ia连一条流量为wi-的边,从ib向T连一条流量为wi+的边。
3> 原图中的边从ua向vb连一条流量无穷大的边。
4> 然后跑最大流即可。

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int M = 205, ME = 2e4, inf = 2e9; int h[M], tot, d[M], hh[M], n, m, S, T; struct edge{int v,nxt,f;}G[ME]; int read(){ int x=0, f=1; char c=getchar(); while(c<'0'||c>'9'){if(c=='-')f=-1;c=getchar();} while(c>='0'&&c<='9'){x=x*10+c-'0';c=getchar();} return x*=f; } struct Netflow{ void init(){ tot = 1; S = 0, T = 2 * n + 1; } void add(int u, int v, int f){ G[++tot].v = v, G[tot].nxt = h[u], h[u] = tot, G[tot].f = f; G[++tot].v = u, G[tot].nxt = h[v], h[v] = tot, G[tot].f = 0; } bool bfs(){ queue <int> Q; memset(d, -1, sizeof(d)); d[S] = 1; Q.push(S); while(!Q.empty()){ int u = Q.front(); Q.pop(); for(int i = h[u]; i; i = G[i].nxt){ int v = G[i].v; if(d[v] != -1 || !G[i].f)continue; d[v] = d[u] + 1; Q.push(v); } } return d[T] != -1; } int dfs(int u, int q){ if(u == T || !q)return q; int ret = 0; for(int i = hh[u]; i; i = G[i].nxt){ int v = G[i].v; if(!G[i].v || d[v] != d[u] + 1)continue; int dd = dfs(v, min(q, G[i].f)); q -= dd; ret += dd; G[i].f -= dd; G[i^1].f += dd; hh[u] = i; } return ret; } int dinic(){ int ans = 0; while(bfs()){ for(int i = 0; i <= T; i++)hh[i] = h[i]; ans += dfs(S, inf); } return ans; } }Tr; int main(){ freopen("game.in","r",stdin); freopen("game.out","w",stdout); n = read(), m = read(); int u, v, w;// sum = 0; Tr.init(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ w = read(); Tr.add(i + n, T, w); //sum += w; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ w = read(); Tr.add(S, i, w); //sum += w; } for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){ u = read(), v = read(); Tr.add(u, v + n, inf); } int ans = Tr.dinic(); printf("%d ", ans); }
