1.本节学习路线图
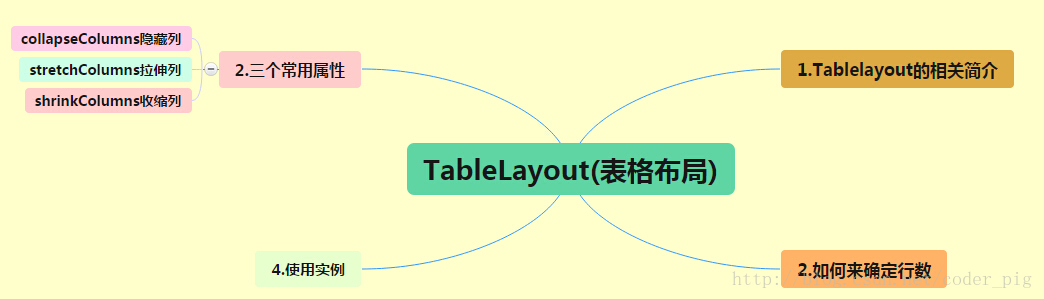
路线图分析: 从上面的路线图,可以看出TableLayout的用法还是很简单的,无非就是确定表格的行数,以及使用 那三个属性来设置每一行中的第某列的元素隐藏,拉伸,或者收缩即可!
2.TableLayout的介绍
相信学过HTML的朋友都知道,我们可以通过< table >< tr >< td >就可以生成一个HTML的表格, 而Android中也允许我们使用表格的方式来排列组件,就是行与列的方式,就说我们这节的TableLayout! 但却不像我们后面会讲到的Android 4.0后引入的GridLayout(网格)布局一样,直接就可以设置多少行与多少列!
3.如何确定行数与列数
- ①如果我们直接往TableLayout中添加组件的话,那么这个组件将占满一行!!!
- ②如果我们想一行上有多个组件的话,就要添加一个TableRow的容器,把组件都丢到里面!
- ③tablerow中的组件个数就决定了该行有多少列,而列的宽度由该列中最宽的单元格决定
- ④tablerow的layout_width属性,默认是fill_parent的,我们自己设置成其他的值也不会生效!!! 但是layout_height默认是wrapten——content的,我们却可以自己设置大小!
- ⑤整个表格布局的宽度取决于父容器的宽度(占满父容器本身)
- ⑥有多少行就要自己数啦,一个tablerow一行,一个单独的组件也一行!多少列则是看tableRow中 的组件个数,组件最多的就是TableLayout的列数
4.三个常用属性
android:collapseColumns:设置需要被隐藏的列的序号
android:shrinkColumns:设置允许被收缩的列的列序号
android:stretchColumns:设置运行被拉伸的列的列序号以上这三个属性的列号都是从0开始算的,比如shrinkColunmns = "2",对应的是第三列!
可以设置多个,用逗号隔开比如"0,2",如果是所有列都生效,则用"*"号即可
除了这三个常用属性,还有两个属性,分别就是跳格子以及合并单元格,这和HTML中的Table类似:android:layout_column="2":表示的就是跳过第二个,直接显示到第三个格子处,从1开始算的!
android:layout_span="4":表示合并4个单元格,也就说这个组件占4个单元格
属性使用示例:
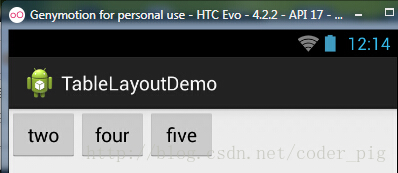
①collapseColumns(隐藏列)
流程:在TableRow中定义5个按钮后,接着在最外层的TableLayout中添加以下属性: android:collapseColumns = "0,2",就是隐藏第一与第三列,代码如下:
<TableLayout android:id="@+id/TableLayout2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:collapseColumns="0,2" > <TableRow> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="one" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="two" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="three" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="four" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="five" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
运行效果图:
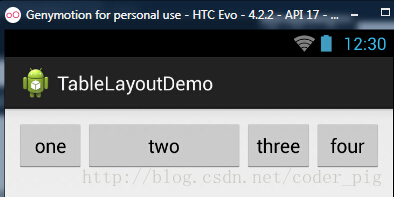
②stretchColumns(拉伸列)
流程:在TableLayout中设置了四个按钮,接着在最外层的TableLayout中添加以下属性: android:stretchColumns = "1"
设置第二列为可拉伸列,让该列填满这一行所有的剩余空间,代码如下:
<TableLayout android:id="@+id/TableLayout2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:stretchColumns="1" > <TableRow> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="one" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="two" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="three" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="four" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
运行效果图:
③shrinkColumns(收缩列)
步骤:这里为了演示出效果,设置了5个按钮和一个文本框,在最外层的TableLayout中添加以下属性: android:shrinkColumns = "1"
设置第二个列为可收缩列,代码如下:
<TableLayout android:id="@+id/TableLayout2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:shrinkColumns="1" > <TableRow> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="one" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="two" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="three" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="four" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="five" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="文本XX" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
运行截图:
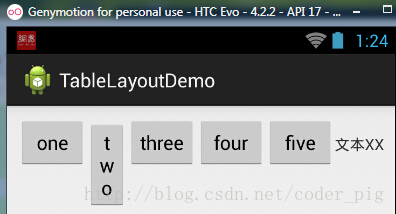
从图中我们可以看到two这个按钮被挤压成条条状,这个就是收缩,为了保证表格能适应 父容器的宽度!至于另外两个属性就不讲解了,用法和HTML相同!有兴趣的可以研究下!
5.使用实例
使用TableLayout来完成简单的登录界面,运行效果图如下:
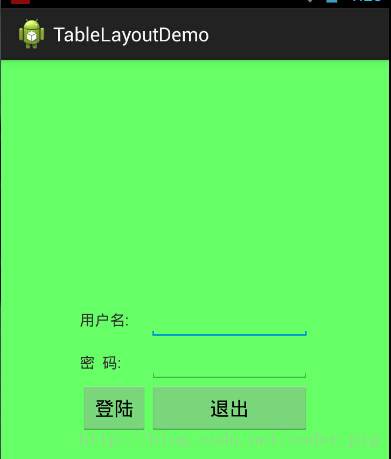
流程解析:
①调用gravity属性,设置为center_vertical,让布局里面的组件在竖直方向上居中
②将TableLayout中的第一和第四列设置为可拉伸
③在每个TableRow中添加两个TextView,用于拉伸填满该行,这样可以让表格水平居中
android:stretchColumns="0,3" 设置为0.3,是为了让两边都充满,那么中间部分就可以居中了
详细代码如下:
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/TableLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" android:stretchColumns="0,3" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:background="#66FF66" > <TableRow> <TextView /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="用户名:"/> <EditText android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:minWidth="150dp"/> <TextView /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="密 码:" /> <EditText android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:minWidth="150dp" /> <TextView /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="登陆"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="退出"/> <TextView /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
6.发现的问题
相信大家在使用这个这TableLayout的TableRow的时候会遇到这个警告:
当然,程序还是可以运行的,不过或许你是强迫症患者,看到黄色感叹号你就不爽的话! 而解决这个警告的方法也是很奇葩的:只要你的TableLayout里面有2个或以上的TableRow就可以了!
本节小结:
好的,关于Android的第三个布局:TableLayout就到这里~无非就是五个属性的使用而已,实际开发 表格布局我们用的不多,知道简单的用法就可以了!