Crazy Tank
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3578 Accepted Submission(s): 637
Problem Description
Crazy Tank was a famous game about ten years ago. Every child liked it. Time flies, children grow up, but the memory of happy childhood will never go.
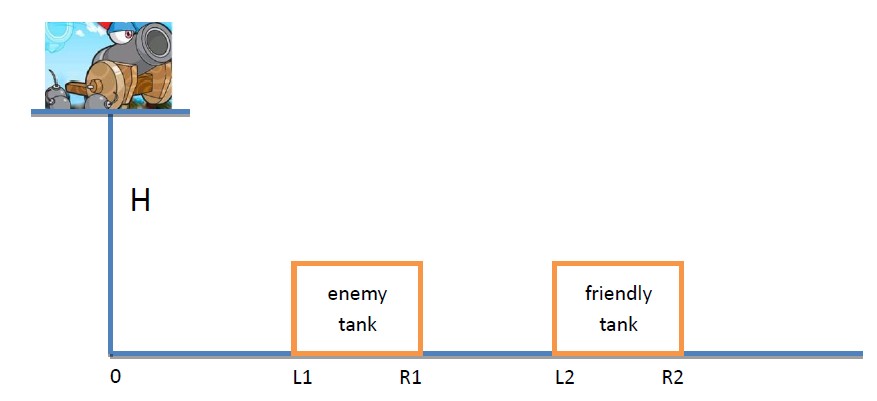
Now you’re controlling the tank Laotu on a platform which is H meters above the ground. Laotu is so old that you can only choose a shoot angle(all the angle is available) before game start and then any adjusting is not allowed. You need to launch N cannonballs and you know that the i-th cannonball’s initial speed is Vi.
On the right side of Laotu There is an enemy tank on the ground with coordination(L1, R1) and a friendly tank with coordination(L2, R2). A cannonball is considered hitting enemy tank if it lands on the ground between [L1,R1] (two ends are included). As the same reason, it will be considered hitting friendly tank if it lands between [L2, R2]. Laotu's horizontal coordination is 0.
The goal of the game is to maximize the number of cannonballs which hit the enemy tank under the condition that no cannonball hits friendly tank.
The g equals to 9.8.

Now you’re controlling the tank Laotu on a platform which is H meters above the ground. Laotu is so old that you can only choose a shoot angle(all the angle is available) before game start and then any adjusting is not allowed. You need to launch N cannonballs and you know that the i-th cannonball’s initial speed is Vi.
On the right side of Laotu There is an enemy tank on the ground with coordination(L1, R1) and a friendly tank with coordination(L2, R2). A cannonball is considered hitting enemy tank if it lands on the ground between [L1,R1] (two ends are included). As the same reason, it will be considered hitting friendly tank if it lands between [L2, R2]. Laotu's horizontal coordination is 0.
The goal of the game is to maximize the number of cannonballs which hit the enemy tank under the condition that no cannonball hits friendly tank.
The g equals to 9.8.
Input
There are multiple test case.
Each test case contains 3 lines.
The first line contains an integer N(0≤N≤200), indicating the number of cannonballs to be launched.
The second line contains 5 float number H(1≤H≤100000), L1, R1(0<L1<R1<100000) and L2, R2(0<L2<R2<100000). Indicating the height of the platform, the enemy tank coordinate and the friendly tank coordinate. Two tanks may overlap.
The third line contains N float number. The i-th number indicates the initial speed of i-th cannonball.
The input ends with N=0.
Each test case contains 3 lines.
The first line contains an integer N(0≤N≤200), indicating the number of cannonballs to be launched.
The second line contains 5 float number H(1≤H≤100000), L1, R1(0<L1<R1<100000) and L2, R2(0<L2<R2<100000). Indicating the height of the platform, the enemy tank coordinate and the friendly tank coordinate. Two tanks may overlap.
The third line contains N float number. The i-th number indicates the initial speed of i-th cannonball.
The input ends with N=0.
Output
For each test case, you should output an integer in a single line which indicates the max number of cannonballs hit the enemy tank under the condition that no cannonball hits friendly tank.
Sample Input
2
10 10 15 30 35
10.0
20.0
2
10 35 40 2 30
10.0
20.0
0
Sample Output
1
0
Hint
In the first case one of the best choices is that shoot the cannonballs parallelly to the horizontal line, then the first
cannonball lands on 14.3 and the second lands on 28.6.
In the second there is no shoot angle to make any cannonball land between [35,40] on the condition that no
cannonball lands between [2,30].
Source
Recommend
zhuyuanchen520
/* * Author: * Created Time: 2013/10/17 14:45:31 * File Name: B.cpp * solve: B.cpp */ #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<map> #include<stack> #include<set> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<queue> //ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); //#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000") using namespace std; #define sz(v) ((int)(v).size()) #define rep(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i < (b); ++i) #define repf(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); ++i) #define repd(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); --i) #define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x)) #define clrs( x , y ) memset(x,y,sizeof(x)) #define out(x) printf(#x" %d ", x) #define sqr(x) ((x) * (x)) typedef long long LL; const int INF = 1000000000; const double eps = 1e-6; const int maxn = 30000; int sgn(const double &x) { return (x > eps) - (x < -eps); } const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double G = 9.8; double v[maxn]; int n; int h,l1,l2,r1,r2; int dcmp(double x) { if(fabs(x)<eps) { return 0; }else { return x<0 ? -1 : 1 ; } } int b; int solve(double L,double R) { double unit = (R - L)/1000.0; int ans = 0; repf(i,0,1000) { int sum = 0; double angle = L + i*unit; if(dcmp(angle - PI/2) <= 0) { repf(j,1,n) { double vr = v[j]*sin(angle); double vd = v[j]*cos(angle); double t = (sqrt(vd*vd + 2*h*G) - vd)/G; double len = vr*t; if(dcmp(len - l2) >= 0 && dcmp(len - r2) <= 0){ sum = 0; break; } if(dcmp(len - l1) >= 0 && dcmp(len - r1) <= 0){ sum++; } } if(sum > ans) { ans = sum; b = i; } }else { repf(j,1,n) { double vu = v[j]*sin(angle - PI/2); double vr = v[j]*cos(angle - PI/2); double t1 = vu/G; double s1 = vu*t1 - 0.5*G*t1*t1; double s = s1 + h; double t2 = sqrt(2*s/(G)); double t = t1 + t2; double len = vr*t; if(dcmp(len - l2) >= 0 && dcmp(len - r2) <= 0) { sum = 0; break; } if(dcmp(len - l1) >= 0 && dcmp(len - r1) <= 0) { sum++; } } if(sum > ans) { ans = sum; b = i; } } } return ans; } int main() { //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); while(scanf("%d",&n) == 1 && n) { scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&h,&l1,&r1,&l2,&r2); repf(i,1,n) scanf("%lf",&v[i]); cout<<solve(0,PI)<<endl; } return 0; }