Print Article
Time Limit: 9000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 17335 Accepted Submission(s): 5310
Problem Description
Zero has an old printer that doesn't work well sometimes. As it is antique, he still like to use it to print articles. But it is too old to work for a long time and it will certainly wear and tear, so Zero use a cost to evaluate this degree.
One day Zero want to print an article which has N words, and each word i has a cost Ci to be printed. Also, Zero know that print k words in one line will cost
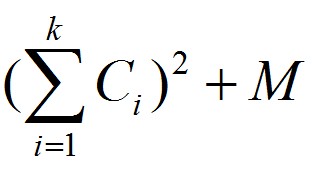
M is a const number.
Now Zero want to know the minimum cost in order to arrange the article perfectly.
One day Zero want to print an article which has N words, and each word i has a cost Ci to be printed. Also, Zero know that print k words in one line will cost
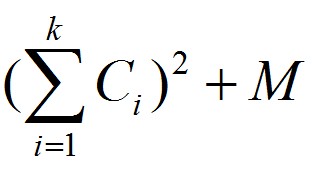
M is a const number.
Now Zero want to know the minimum cost in order to arrange the article perfectly.
Input
There are many test cases. For each test case, There are two numbers N and M in the first line (0 ≤ n ≤ 500000, 0 ≤ M ≤ 1000). Then, there are N numbers in the next 2 to N + 1 lines. Input are terminated by EOF.
Output
A single number, meaning the mininum cost to print the article.
一个本来朴素的想法是 dp[i] = min{dp[j] + m + (sum[i]-sum[j])^2} (1<=j<i)
然后这个方法是O(n^2的)
用斜率优化一下 (可以假设两个点 j,k 然后假设相应的 cost[j] <= cost[k] , 这样可以得到一个公式) 形如 f(k)-f(j) <= 2*f(i)*(sum[k] - sum[j])
接着就可以 用单调栈来维护和更新 复杂度就成O(n)的了
#include <iostream> #include <math.h> #include <algorithm> #include <string.h> #include <string> #define rep(i,l,r) for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N = 500000+10; int n, m, c[N]; ll sum[N], dp[N], Q[N]; void init() { memset(dp,0x3f,sizeof(dp)); } /* 朴素想法 void solve() { dp[1] = 1LL*c[1]*c[1] + m; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<i;j++) { dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[j] + m + 1LL*(sum[i]-sum[j])*(sum[i]-sum[j])); } } cout << dp[n] <<endl; } */ void solve() { dp[1] = 1LL*c[1]*c[1]+m; int st=0,ed=0; Q[ed++] = 0; dp[0]=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { while (st+1 < ed) { int j=Q[st], k=Q[st+1]; ll dx = sum[k] - sum[j]; ll dy = 1LL*(dp[k] + sum[k]*sum[k] - dp[j] - sum[j]*sum[j]); if(dy <= 1LL*2*dx*sum[i]) st++; else break; } int j=Q[st]; dp[i] = dp[j] + m + (sum[i]-sum[j])*(sum[i]-sum[j]); while (st+1 < ed) { int j=Q[ed-2],k=Q[ed-1]; ll dx1 = sum[i] - sum[k]; ll dx2 = sum[i] - sum[j]; ll dy1 = 1LL*(dp[i] + sum[i]*sum[i] -dp[k] - sum[k]*sum[k]); ll dy2 = 1LL*(dp[i] + sum[i]*sum[i] -dp[j] - sum[j]*sum[j]); if(dy1 * dx2 <= dy2 * dx1) ed--; else break; } Q[ed++]=i; } cout << dp[n] <<endl; } int main () { while (scanf("%d %d",&n, &m)==2) { init(); rep(i,1,n) scanf("%d", &c[i]),sum[i]=sum[i-1]+c[i]; solve(); } return 0; }