题目链接
A题
题目

题意
给你两个正整数(n)和(m),然后你可以进行无数次操作(每次操作可以将(n)扩大两倍,或者扩大三倍),问你是否能够得到(m)。
代码实现如下
n, m = map(int, input().split())
if m % n == 0:
num = 0
m //= n
while(m % 2 == 0):
m //= 2
num = num + 1
while(m % 3 == 0):
m //= 3
num = num + 1
if(m == 1):
print(num)
else:
print(-1)
else:
print(-1)
B题
题目


题意
给你一个长度为(n)的(01)串进行无限循环,问你连续最长的(1)有多长。
思路
将这个(01)串复制一次,然后找连续最长的(1)就行。
代码实现如下
n = eval(input())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
a.extend(a)
cnt = 0
l = -1
for i in range(2*n):
if(a[i] == 1):
if(l == -1):
l = i
cnt = max(cnt, 1)
else:
cnt = max(cnt, i - l + 1)
else:
l = -1
print(cnt)
C题
题目

题意
有一个长为(1~n)的排列(a_i),现在给你相邻两项的差(p_i),要你重新构造这个排列。
思路
我们通过计算可以发现(a_2=a_1+p_1,a_3=a_1+p_1+p_2,a_n=a_1+p_1+p_2+...+p_{n-1}),然后我们知道(sum_{i=1}^{k}p_i)最大对应的那个(a_i)一定是(n),因此我们一减就可以得到(a_1),然后剩下的也都可以通过前面说的那些等式构造出来~
代码实现如下
n = eval(input())
a = list(map(int,input().split()))
p = [0]
for i in range(0,n-1):
p.append(p[-1]+a[i])
mx = max(p)
ans = []
ans.append(n-mx)
for i in range(1,n):
ans.append(ans[0]+p[i])
if set(range(1,n+1))==set(ans):
print(*ans)
else:
print(-1)
D题
题目

题意
给你两个字符串(s)和(t),问这两个字符串的最大匹配度是多少。
匹配规则为:
1.相同字母进行匹配;
2.字符和'?'进行匹配。
代码实现如下
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> piL;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
#define name2str(name) (#name)
#define bug printf("*********
")
#define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl
#define FIN freopen("in","r",stdin)
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 150000 + 7;
const double pi = acos(-1);
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
int n;
char s[maxn], t[maxn];
vector<int> l[30], r[30], lp, rp;
vector<pii> ans;
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN;
#endif
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%s%s", s, t);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(s[i] == '?') {
lp.push_back(i+1);
} else {
int x = s[i] - 'a';
l[x].push_back(i+1);
}
if(t[i] == '?') {
rp.push_back(i+1);
} else {
int x = t[i] - 'a';
r[x].push_back(i+1);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
int lsz = (int)l[i].size(), rsz = (int)r[i].size();
int lpsz = (int)lp.size(), rpsz = (int)rp.size();
while(lsz >= 1 && rsz >= 1) {
ans.push_back({l[i][lsz-1], r[i][rsz-1]});
l[i].pop_back();
r[i].pop_back();
lsz--, rsz--;
}
while(lsz >= 1 && rpsz >= 1) {
ans.push_back({l[i][lsz-1], rp[rpsz-1]});
l[i].pop_back();
rp.pop_back();
lsz--, rpsz--;
}
while(rsz >= 1 && lpsz >= 1) {
ans.push_back({lp[lpsz-1], r[i][rsz-1]});
r[i].pop_back();
lp.pop_back();
rsz--, lpsz--;
}
}
int lpsz = (int)lp.size(), rpsz = (int)rp.size();
while(lpsz && rpsz) {
ans.push_back({lp[lpsz-1], rp[rpsz-1]});
lp.pop_back();
rp.pop_back();
lpsz--, rpsz--;
}
printf("%d
", (int)ans.size());
for(auto x : ans) {
printf("%d %d
", x.first, x.second);
}
return 0;
}
E题
题目

题意
有一只血量为(H)的怪物,每一轮有(n)个回合,每一回合血量的变化为(d_i),每一轮的变化情况都和上一轮一样,问怪物在第几回合死亡。
思路
暴力,不太擅长这种题……
代码实现如下
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> piL;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
#define name2str(name) (#name)
#define bug printf("*********
")
#define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl
#define FIN freopen("in","r",stdin)
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 7;
const double pi = acos(-1);
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
int n;
int d[maxn];
LL H, sum;
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN;
#endif
scanf("%lld%d", &H, &n);
LL mx = inf;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &d[i]);
sum += d[i];
if(sum < 0) mx = min(mx, sum);
}
if(sum >= 0) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
H += d[i];
if(H <= 0) {
printf("%d
", i);
return 0;
}
}
printf("-1
");
} else {
LL ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
H += d[i];
if(H <= 0) {
printf("%d
", i);
return 0;
}
}
ans += n;
sum = -sum;
ans += H / sum * n;
H %= sum;
if(mx != inf) {
mx = -mx;
ans -= (mx + sum - 1) / sum * n;
H += (mx + sum - 1) / sum * sum;
}
while(H > 0) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
H += d[i];
if(H <= 0) {
ans += i;
break;
}
}
if(H > 0) ans += n;
}
printf("%lld
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
F题
题目


题意
给你(n)个数,要你选择不相交的(k)个区间,使得这(k)个区间的和相同,最大化k。
思路
由于(n)很小,我们可以先暴力以(i)为左端点(j)为右端点这段区间的和,然后用一个(vector)来存下这个和对应的所有区间,然后对每个和的所有区间进行贪心取即可(贪心入门经典题)。
代码实现如下
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> piL;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define x first
#define y second
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
#define name2str(name) (#name)
#define bug printf("*********
")
#define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl
#define FIN freopen("in","r",stdin)
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 7;
const double pi = acos(-1);
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
int n;
int a[maxn], vis[maxn];
LL sum[maxn];
vector<LL> s;
vector<pii> v[maxn], seg;
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN;
#endif
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
sum[i] = sum[i-1] + a[i];
for(int j = 1; j <= i; ++j) {
s.push_back(sum[i] - sum[j-1]);
}
}
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
s.erase(unique(s.begin(), s.end()), s.end());
int sz = s.size();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j <= i; ++j) {
int x = sum[i] - sum[j-1];
int p = lower_bound(s.begin(), s.end(), x) - s.begin();
v[p].push_back({i, j});
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) sort(v[i].begin(), v[i].end());
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
int las = 0, cnt = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < v[i].size(); ++j) vis[j] = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < v[i].size(); ++j) {
if(v[i][j].y > las) {
cnt++;
vis[j] = 1;
las = v[i][j].x;
}
}
if(cnt > ans) {
seg.clear();
ans = cnt;
for(int j = 0; j < v[i].size(); ++j) {
if(vis[j]) {
seg.push_back({v[i][j]});
}
}
}
}
printf("%d
", ans);
for(auto x : seg) {
printf("%d %d
", x.y, x.x);
}
return 0;
}
G题
题目
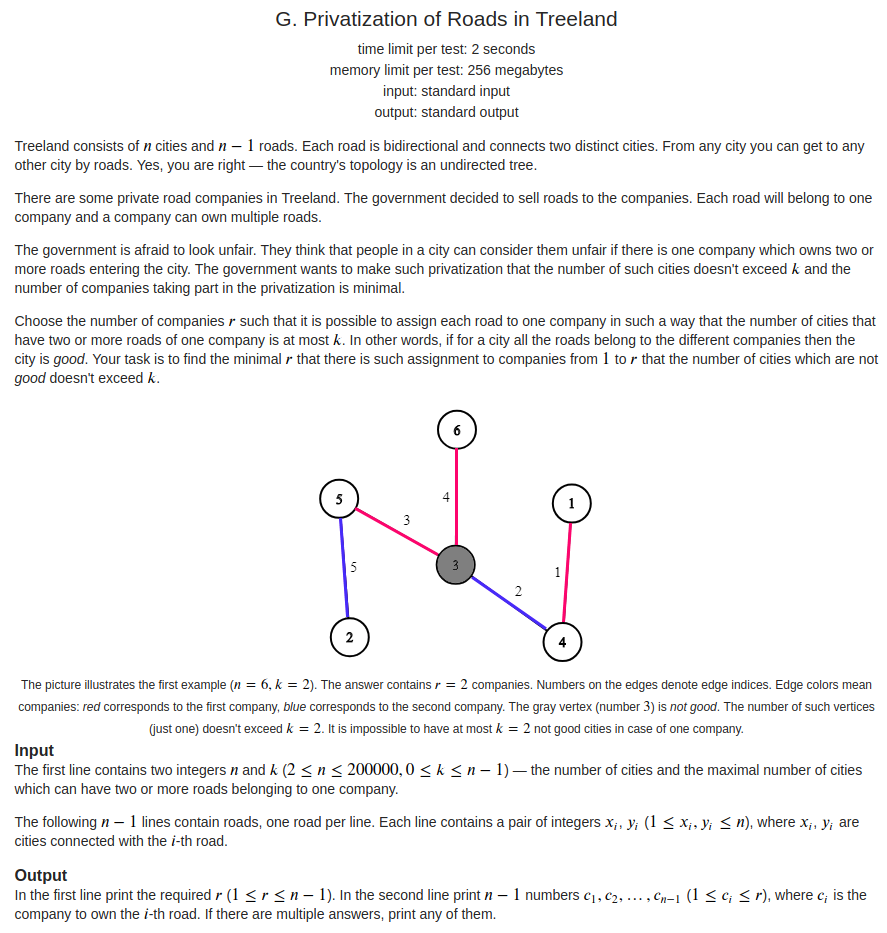

题意
给你一棵树,需要将树进行染色,可以有(k)个结点(称为特殊点)使得它所连接的边颜色相同,其他的(n-k)个结点连接的边的颜色不能相同,要你最小化颜色数。
思路
要使得颜色数最少,我们很容易可以知道度最大的(k)个结点是特殊点(我们可以知道颜色数(equiv)非特殊点中度最大的结点的度,因此要想最小化颜色数,就要最小化非特殊点中度最大的结点的度),剩下的dfs进行染色即可。
代码实现如下
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
typedef pair<int, LL> piL;;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
#define lson rt<<1
#define rson rt<<1|1
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
#define name2str(name) (#name)
#define bug printf("*********
")
#define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl
#define FIN freopen("in","r",stdin)
#define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 7;
const double pi = acos(-1);
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
int n, k, tot, ans;
int in[maxn], head[maxn], vis[maxn], c[maxn];
struct edge {
int v, next;
}ed[maxn];
void add(int u, int v) {
ed[tot].v = v;
ed[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
}
void dfs(int u, int p, int pp) {
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = ed[i].next) {
int v = ed[i].v;
if(v == p) continue;
if(vis[u]) c[i] = (pp == 0 ? 1 : pp);
else {
cnt++;
if(cnt == pp) cnt++;
c[i] = cnt;
}
dfs(v, u, c[i]);
}
ans = max(ans, max(1, cnt));
}
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
FIN;
#endif
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
int u, v;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) head[i] = -1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add(u, v); add(v, u);
in[u]++, in[v]++;
}
priority_queue<pii> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
q.push({in[i], i});
}
int cnt = 0;
while(cnt < k) {
vis[q.top().second] = 1;
q.pop();
cnt++;
}
dfs(1, 0, 0);
printf("%d
", ans);
for(int i = 0; i < tot; ++i) {
if(c[i] == 0) continue;
printf("%d ", c[i]);
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}