1、DecimalFormat格式化数字
package net.day0623;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class Text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double num1 = 2.5;
// 创建DecimalFormat对象
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.00");
// 调用df.format(num1)方法,传入参数
System.out.println("num1="+df.format(num1));
}
}
运行结果:
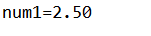
DecimalFormat("#.00")方法中,"#.00"为设置数字格式,# 表示只要有可能就把数字拉上这个位置。小数点后有两位数字,有几个0表示小数点后保留几位小数,不足用0补齐,如上程序,输入num1为2.5,设置保留两位小数,不够0补齐,所以输出num1=2.50.
2、字符串格式化-String.format()的使用
String类的format()方法用于创建格式化的字符串以及连接多个字符串对象
程序例子:
package net.day0623;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class Text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double num2 = 3.6;
// 调用df.format(num1)方法,传入参数
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", num2));
}
}
运行结果:
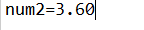
format()方法中的两个参数,format("%.2f", num2),例子中的第一个参数为数字格式,百分号表示小数点前的整数部分,“.”表示小数点,数字2表示保留小数位的个数,不足用0补齐,如上程序。“f”表示浮点类型,第二个参数为传入需要更改格式的参数。