源代码:
<div class="out"> <div class="in">Content here</div> </div>
.out{ width: 300px; height: 400px; margin: 20px auto 0; background:red; } .in{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: blue; line-height: 100px; }
运行图:
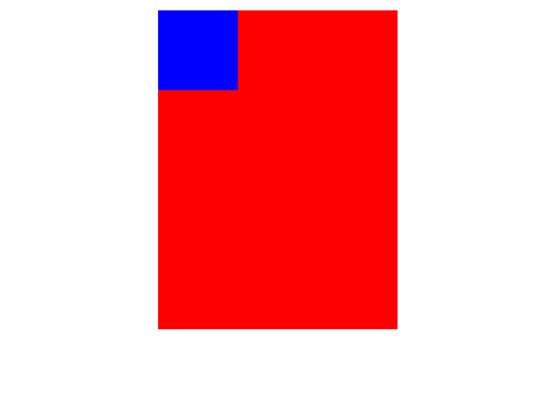
1.使用表格法:
运行图:
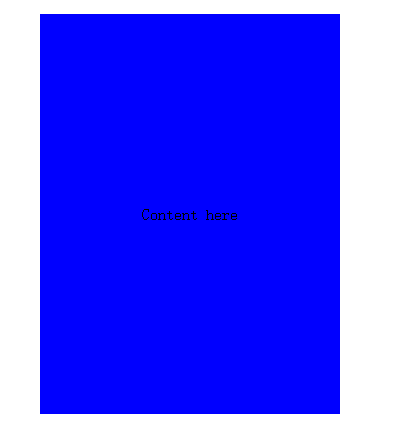
.out{ display: table; text-align: center; } .in{ display: table-cell; vertical-align: middle; }
缺点:子元素的会撑满父元素。
2.绝对定位计算:对子元素使用绝对定位,并分别移动上左50%,再分别margin-top:-50%height px,margin-left:-50%width px;
运行图:
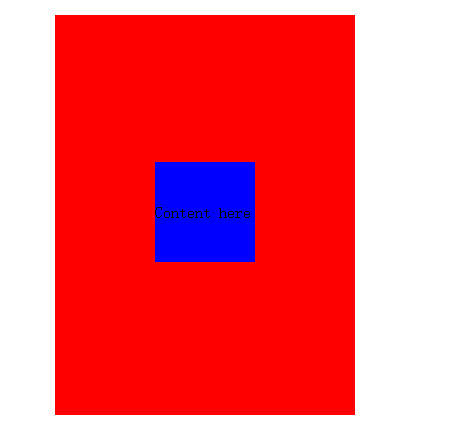
.in{ position: absolute; top: 50%; left: 50%; margin-left: -50px; margin-top: -50px; }
缺点:需要对子元素的宽高固定,并且绝对定位容易影响布局。
3. 利用绝对定位和translate。
同上,先左上各自移动50%,再使用transform: translate(-50%, -50%);translate是基于自身元素的宽高为基准进行移动的。
运行图同上。
.in{ position: absolute; top: 50%; left: 50%; transform: translate(-50%, -50%); }
缺点:需要绝对定位。
4. 基于Flex.
运行图同上。
.out{ display: flex; } .in{ margin: auto; }
优点:代码简单。
缺点:兼容性差。