tensorflow学习笔记(2)-反向传播
反向传播是为了训练模型参数,在所有参数上使用梯度下降,让NN模型在的损失函数最小
损失函数:学过机器学习logistic回归都知道损失函数-就是预测值和真实值得差距,比如sigmod或者cross-entropy
均方误差:tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_))很好理解,假如在欧式空间只有两个点的的话就是两点间距离的平方,多点就是多点误差的平方和除以对比点个数
学习率:决定了参数每次更新的幅度
反向传播训练方法:为了减小loss的值为优化目标
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat May 26 18:42:08 2018
@author: Administrator
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
BATCH_SIZE=8
seed=23455
#基于seed产生随机数
rng=np.random.RandomState(seed)
#随机返回32行2列的矩阵 作为数据集输入
X=rng.rand(32,2)
#从X这个32行2列的矩阵中取出一行 判断如果和小于1 给Y赋值1 如果和不小于1 给Y赋值0
#Y作为训练集的标签
Y=[[int((x0+x1)<1)] for(x0,x1) in X]
print(X)
print(Y)
#定义输入,参数和输出
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=(None,2))
y_=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=(None,1))
#2是特征值 3是隐藏层 1是输出
w1=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2,3],stddev=1,seed=1))
w2=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,1],stddev=1,seed=1))
a=tf.matmul(x,w1)
y=tf.matmul(a,w2)
#定义损失函数以及反向传播方法
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_))
train_step=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
#会话训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
#输出未训练的参数值
print(sess.run(w1))
print(sess.run(w2))
#训练3000次
STEPS=10000
for i in range(STEPS):
start=(i*BATCH_SIZE)%32
end=BATCH_SIZE+start
#每次训练抽取start到end的数据
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:X[start:end],y_:Y[start:end]})
#每500次打印一次参数
if i%500==0:
total_loss=sess.run(loss,feed_dict={x:X,y_:Y})
print("在第%d次训练,损失为%g"%(i,total_loss))
#输出训练后的参数
print("
")
print(sess.run(w1))
print(sess.run(w2))
这是输出的内容
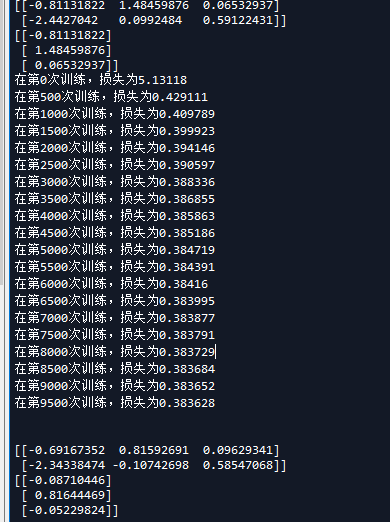
我们现在稍微改下参数比较下,首先是学习速率
当学习速率为0.1时候 当学习速率为0.01

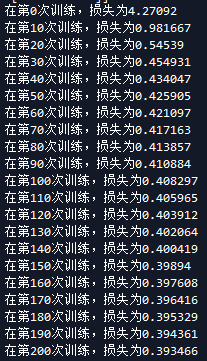
可以看出来学习速率越大梯度下降越块。
再来看看隐藏层
首先是隐藏层为4时候 隐藏层为3时候

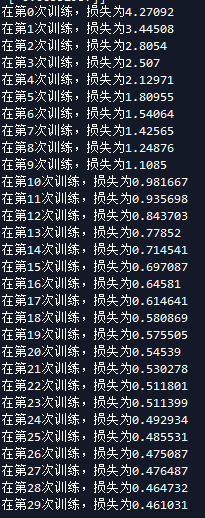
现在还不知道隐藏层怎么定义,知道以后再补上
问了群里老哥:老哥回答
