在17年校招中3道题目AC却无缘华为面试,大概是华为和东华互不待见吧!分享一道华为笔试原题,共同进步!
***************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
题目描述:
LISP语言唯一的语法就是括号要匹配。
形如(OP P1 P2 …),括号内元素由单个空格分割。
其中第一个元素OP为操作符,后续元素均为其参数,参数个数取决于操作符类型
注意:参数P1,P2也有可能是另外一个嵌套的(OP P1 P2 …)
其中OP类型为add/sub/mul/div(全小写),分别代表整数的加减乘除法
其中add/mul参数个数2或以上,sub/div参数个数为2
举例:
-输入:(mul 3 -7) 输出:-21
-输入:(add1 2 3) 输出:6
-输入:(sub (mul 2 4) (div 9 3)) 输出:5
-输入:(div 1 0) 输出:error
题目涉及数字均为整数,可能为负;不考虑32位溢出翻转
除零错误时,输出"error",除法遇除不尽,取整,即3/2=1
输入描述:
合法C字符串,字符串长度不超过512;用例保证了无语法错误
输出描述:
合法C字符串,字符包括'0'-'9'及负号'-'或者'error'
示例
输入 (add 1 2 3) 输出 6
*********************************************************
这是数据结构中括号匹配问题的变形。在检验括号是否匹配的方法中,可用“期待的急迫程度”这个概念来描述。在算法中设置了一个栈,每读入一个括号,若是右括号,则或者使置于栈顶的最急迫的期待得以消解,或者是不合法的情况;若是左括号,则作为一个新的更急迫的期待压入栈中,自然使原有的在栈中的所有未消解的期待的急迫性降了一级。另外,在算法的开始和结束时,栈都应该是空的。
同样的道理,针对LISP的括号匹配,我们不仅需要一个符号栈opstack去保存每一个括号里的操作符OP,还需要一个栈strstack去保存括号里的参数P1、P2及符号位。
从头到尾对输入的C字符串进行遍历,当遇到左括号"("时,将"("压入strstack中,其后的操作符压入opstack栈中;当遇到参数P时,通过字符串分割,放入strstack中;当遇到右括号")"时,在strstack栈中依次弹出参数,压入tmps栈,直到遇到"("为止,那么tmps中为一个不包含子括号参数列表,运算符为opstack的栈顶元素,其中根据操作符和参数可以进行加减乘除运运算,这部分不讨论。注意,运算结果需要在压入strstack栈中作为参数P。
如下图所示,以(sub (mul 2 4) (div 9 3))为例,在遇到第一个")"时,strstack中分别为{(,(,2,4},opstack中分别为{sub ,mul},则strstack中依次弹出4,2,(,运算符为opstack的栈顶元素mul,可以得到结果为8,其中运算结果再压入strstack中作为参数。
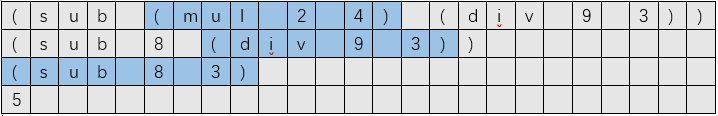
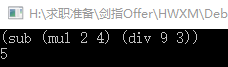
程序输入输出,运行结果示意图:
源码分享:
代码同步更新于 https://github.com/wylloong/TinyPrograms/blob/master/Coding%20Interviews/LISPGenerateParentheses.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <cstdio> #include <stdlib.h> #include <cstring> using namespace std; int main() { char chs[512]; bool error = false; gets_s(chs); //gets(chs); //old version std::string str(chs); std::stack<std::string> opstack; // operations std::stack<std::string> strstack; // divided strings for (int i = 0; i < str.size();) { if (str[i] == ' ') { i = i + 1; continue; } if (str[i] == '(') { strstack.push(std::string("(")); int spaceIndex = str.find(' ', i); std::string tmp = str.substr(i + 1, spaceIndex - i - 1); opstack.push(tmp); // operation i = spaceIndex; } else if (str[i] == ')') { std::string curOp = opstack.top(); opstack.pop(); std::vector<std::string> tmps; // strs temp while (strstack.top() != "(") { tmps.push_back(strstack.top()); strstack.pop(); } strstack.pop(); // add if (curOp == "add") { int temp = 0; for (int i = 0; i<=tmps.size() - 1; ++i) { temp += atoi(tmps[i].c_str()); } strstack.push(to_string(temp)); } // sub else if (curOp == "sub") { int temp = 0; if (tmps.size() > 0) temp = atoi(tmps[tmps.size() - 1].c_str()); for (int i = tmps.size() - 2; i >= 0; --i) { temp -= atoi(tmps[i].c_str()); } strstack.push(to_string(temp)); } // mul else if (curOp == "mul") { int temp = 0; if (tmps.size() > 0) temp = atoi(tmps[tmps.size() - 1].c_str()); for (int i = tmps.size() - 2; i >= 0; --i) { temp *= atoi(tmps[i].c_str()); } strstack.push(to_string(temp)); } // div else if (curOp == "div") { int temp = 0; if (tmps.size() > 0) temp = atoi(tmps[tmps.size() - 1].c_str()); for (int i = tmps.size() - 2; i >= 0; --i) { int data1 = atoi(tmps[i].c_str()); if (data1 == 0) { error = true; break; } else temp /= data1; } if (error) break; else strstack.push(to_string(temp)); } ++i; } else // substrs { // get substring by ' ' or ')' auto index = str.find(' ', i); auto index2= str.find(')', i); if (index < index2) { strstack.push(str.substr(i, index - i)); i = index; } else { strstack.push(str.substr(i, index2 - i)); i = index2; } } } if (error) cout << "error"; else cout << atoi(strstack.top().c_str()); return 0; }