1. SWI软中断
以ARMV7 A/R架构为例, SWI软中断和中断一样,内核空间处理始于异常向量表。Linux向量表默认地址0XFFFF0000,SWI向量偏移8字节为0xFFFF0008:
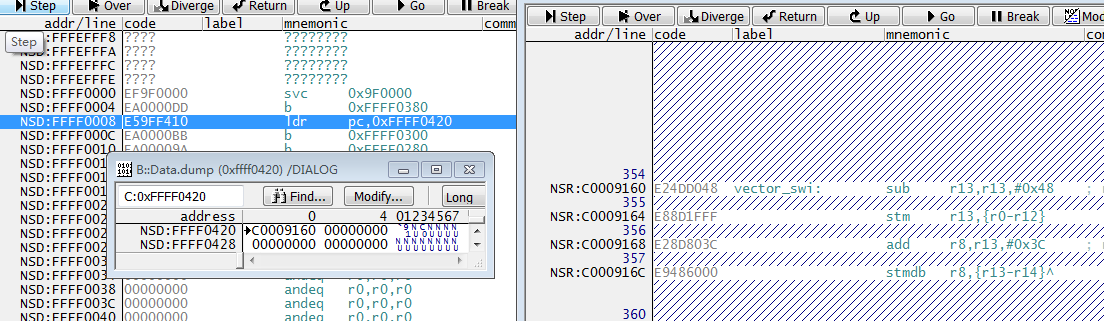
具体代码,位于 linux-3.4.xarcharmkernelentry-armv.S:
__vectors_start: ARM( swi SYS_ERROR0 ) THUMB( svc #0 ) THUMB( nop ) W(b) vector_und + stubs_offset W(ldr) pc, .LCvswi + stubs_offset W(b) vector_pabt + stubs_offset W(b) vector_dabt + stubs_offset W(b) vector_addrexcptn + stubs_offset W(b) vector_irq + stubs_offset W(b) vector_fiq + stubs_offset .globl __vectors_end __vectors_end: .LCvswi: .word vector_swi
vector_swi的具体实现,位于 linux-3.4.xarcharmkernelentry-common.S,vector_swi函数完成的工作:
1. 保存异常前的现场
1 ENTRY(vector_swi) 2 sub sp, sp, #S_FRAME_SIZE 3 stmia sp, {r0 - r12} @ Calling r0 - r12 4 ARM( add r8, sp, #S_PC ) 5 ARM( stmdb r8, {sp, lr}^ ) @ Calling sp, lr 6 THUMB( mov r8, sp ) 7 THUMB( store_user_sp_lr r8, r10, S_SP ) @ calling sp, lr 8 mrs r8, spsr @ called from non-FIQ mode, so ok. 9 str lr, [sp, #S_PC] @ Save calling PC 10 str r8, [sp, #S_PSR] @ Save CPSR 11 str r0, [sp, #S_OLD_R0] @ Save OLD_R0 12 zero_fp
保存现场大小为S_FRAME_SIZE,大小是一个完整的寄存器栈帧:
DEFINE(S_FRAME_SIZE, sizeof(struct pt_regs)); struct pt_regs { long uregs[18]; };
#define ARM_cpsr uregs[16]
#define ARM_pc uregs[15]
#define ARM_lr uregs[14]
#define ARM_sp uregs[13]
#define ARM_ip uregs[12]
#define ARM_fp uregs[11]
#define ARM_r10 uregs[10]
#define ARM_r9 uregs[9]
#define ARM_r8 uregs[8]
#define ARM_r7 uregs[7]
#define ARM_r6 uregs[6]
#define ARM_r5 uregs[5]
#define ARM_r4 uregs[4]
#define ARM_r3 uregs[3]
#define ARM_r2 uregs[2]
#define ARM_r1 uregs[1]
#define ARM_r0 uregs[0]
#define ARM_ORIG_r0 uregs[17]
从现场可以看出,每次用户空间向内核空间切换时,线程内核栈会保留一份完整的寄存器现场,保存地址在内核栈的(最高地址-8):
线程内核栈基地址:0xc288a000
线程内核栈最高地址:0xc288a000+8k = 0xc288c000
保存形式:
=============================低地址
R0 R1 R2 R3
R4 R5 R6 R7
R8 R9 R10 R11
R12 SP LR PC
CPSR R0_OLD X X
========================== kernel stack start(最高地址)

值得注意的是,arm-linux把内核栈的(最高地址-8)作为栈起始地址,详见 linux-3.4.xarcharmincludeasm hread_info.h
#define THREAD_SIZE 8192 #define THREAD_START_SP (THREAD_SIZE - 8)
原因:
https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/history/history.git/commit/?id=415395e19fd197ce4f248902dba54f4065af547c
Always leave 8 bytes free at the top of the kernel stack. This prevents the stack becoming completely empty when do_exit() is called from an exiting nfsd() thread, and causing the wrong pointer to be returned from current_thread_info()
[PATCH] ARM: Fix kernel stack offset calculations Various places in the ARM kernel implicitly assumed that kernel stacks are always 8K due to hard coded constants. Replace these constants with definitions. Correct the allowable range of kernel stack pointer values within the allocation. Arrange for the entire kernel stack to be zeroed, not just the upper 4K if CONFIG_DEBUG_STACK_USAGE is set. Signed-off-by: Russell King
2. 获取系统调用号
vector_swi函数中有两个重要的宏,分别为:
CONFIG_OABI_COMPAT
CONFIG_AEABI
OABI = Old application binary interface
EABI = Extended application binary interface
ABI = 应用程序二进制接口, OABI/EABI都是针对ARM处理器的接口,EABI也叫GNU EABI.
两者的区别:
1. 调用规则(参数传递,返回值传递)
2. 系统调用数目以及应用程序怎么做系统调用
3. 目标文件二进制个数
4. 结构体中填充和对齐
EABI的好处
1. 支持软件浮点/硬件浮点混用
2. 效率更高
3. 工具兼容
这两个宏可以在make menuconfig时进行配置
kernel features -->
[*] Use the ARM EABI to compile the kernel
[*] Allow old ABI binary to run this kernel
两个可以同时Yes, 也可以只选一个EABI或者都不选
OABI方式系统调用
SWI{cond} immed_24
immed_24: 24位立即数,指定了系统调用号,参数用通用寄存器传递
MOV R0,#34
SWI 12
EABI方式系统调用
MOV R7,#34
SWI 0X0
系统调用号由R7寄存器决定
在SWI异常处理程序中,得到系统调用号的方法:
- 如果定义了OABI,说明存在OABI方式的调用,需要从SWI指令中获得调用号:
- 首先确定软中断的SWI指令时ARM指令还是Thumb指令,这可通过对SPSR访问得到(前一步骤R8保存了SPSR);
- OABI方式无法使用Thumb指令实现SWI,因此下一步取得ARM指令中SWI操作的地址,这可通过访问(LR-4)得到(最后一条指令即SWI XXX);
- 接着读出指令,分解出立即数中低24位(这一步先保存整条指令在R10,待下一步骤分解);
#if defined(CONFIG_OABI_COMPAT) /* * If we have CONFIG_OABI_COMPAT then we need to look at the swi * value to determine if it is an EABI or an old ABI call. */ #ifdef CONFIG_ARM_THUMB tst r8, #PSR_T_BIT movne r10, #0 @ no thumb OABI emulation ldreq r10, [lr, #-4] @ get SWI instruction #else ldr r10, [lr, #-4] @ get SWI instruction #endif
- 如果没有定义OABI,但是定义了EABI,系此时统调用号只会存放在R7寄存器(即scno), 不需要做任何处理,:
#elif defined(CONFIG_AEABI) /* * Pure EABI user space always put syscall number into scno (r7). */
- 如果没有定义OABI/EABI,但是定义了CONFIG_ARM_THUMB:
#elif defined(CONFIG_ARM_THUMB) /* Legacy ABI only, possibly thumb mode. */ tst r8, #PSR_T_BIT @ this is SPSR from save_user_regs addne scno, r7, #__NR_SYSCALL_BASE @ put OS number in ldreq scno, [lr, #-4]
- 如果OABI/EABI/CONFIG_ARM_THUMB都没有定义,此时保存整条SWI指令在R7,待下一步骤分解:
#else /* Legacy ABI only. */ ldr scno, [lr, #-4] @ get SWI instruction #endif
3. 以系统调用号为索引查找系统调用表,然后调用相应的处理例程
- 首先打开中断,并把tbl变量赋值sys_call_table
enable_irq
get_thread_info tsk
adr tbl, sys_call_table @ load syscall table pointer
- 如果定义了OABI:
#if defined(CONFIG_OABI_COMPAT) /* * If the swi argument is zero, this is an EABI call and we do nothing. * * If this is an old ABI call, get the syscall number into scno and * get the old ABI syscall table address. */ bics r10, r10, #0xff000000 eorne scno, r10, #__NR_OABI_SYSCALL_BASE ldrne tbl, =sys_oabi_call_table
- 首先把R10(SWI指令)取低24位,得到系统调用号
- 然后检查该系统调用号是不是0,如果是0表明这是一个EABI系统调用,不做任何处理;如果不是0则把系统调用号与__NR_OABI_SYSCALL_BASE做异或处理,tbl赋值sys_oabi_call_table
- 如果OABI/EABI都没有定义,把R7(系统调用号)取低24位,并与__NR_OABI_SYSCALL_BASE做异或处理
#elif !defined(CONFIG_AEABI) bic scno, scno, #0xff000000 @ mask off SWI op-code eor scno, scno, #__NR_SYSCALL_BASE @ check OS number #endif
- 其他情况不做处理
- 然后根据转换后的系统调用号(都存在R7),在对应的调用跳转表(tbl)中进行偏移后,得到相应的调用函数
cmp scno, #NR_syscalls @ check upper syscall limit adr lr, BSYM(ret_fast_syscall) @ return address ldrcc pc, [tbl, scno, lsl #2] @ call sys_* routine
系统调用跳转表在vector_swi中有两份:
sys_call_table
sys_oabi_call_table
- 如果OABI和EABI都选择,应用程序使用OABI方式时调用sys_oabi_call_table,应用程序使用EABI时调用sys_call_table
- 如果只选择EABI,使用sys_call_table
- 如果都不选,使用sys_call_table
- 由于OABI对EABI有依赖关系,所以不能单独选择OABI
1 ENTRY(sys_call_table) 2 #include "calls.S" 3 #undef ABI 4 #undef OBSOLETE 5 6 /*============================================================================ 7 * Special system call wrappers 8 */ 9 @ r0 = syscall number 10 @ r8 = syscall table 11 sys_syscall: 12 bic scno, r0, #__NR_OABI_SYSCALL_BASE 13 cmp scno, #__NR_syscall - __NR_SYSCALL_BASE 14 cmpne scno, #NR_syscalls @ check range 15 stmloia sp, {r5, r6} @ shuffle args 16 movlo r0, r1 17 movlo r1, r2 18 movlo r2, r3 19 movlo r3, r4 20 ldrlo pc, [tbl, scno, lsl #2] 21 b sys_ni_syscall 22 ENDPROC(sys_syscall)