目录
队列是一个能实现“先进先出”的一个存储结构。
队列分为链式队列和静态队列:静态队列一般用数组来实现,但此时队列必须是循环队列,否则会造成巨大的内存浪费。链式队列是用链表来实现队列的。
队列的顺序存储结构通常由一个一维数组和一个记录队列头元素位置的变量front以及一个记录队列尾元素位置的变量rear组成。
1 typedef struct _myqueue 2 { 3 char* _space; 4 int _len; 5 int _front; 6 int _rear; 7 }MyQueue;
- 普通队列和循环队列的对比
- 普通队列
对列初始化时,front和rear值都为0;
当队列不为空时,front指向队列的第一个元素,rear指向队列的最后一个元素的下一个位置;
当队列为空时,front和rear的值相等,但不一定为0;

由上普通队列入队出队的方式我们可以发现,当元素出队之后不能重复被使用,因此普通队列空间利用率是很低的,我们一般不推荐此种方式。
-
- 循环队列
为了解决普通队列存在的空间利用率低的问题,我们引入循环队列来解决这个问题。循环问题的关键就是判空和判满的问题

因此为了实现循环队列的判空和判满,我们牺牲一个存储单元来实现。
当其为空时,front==rear;
当其为满时,front=(rear+1)%len;
自己实现线性队列代码如下
typedef struct _myqueue { char* _space; int _len; int _front; int _rear; }MyQueue; //由于普通队列空间利用率过低,因此我们一般都使用循环队列 //初始化 void initQueue(MyQueue* s,int len) { s->_space = new char[len]; s->_len = len; s->_front = 0; s->_rear = 0; } //判空:当front==rear时为空 bool isQueueEmpty(MyQueue* s) { return s->_front == s->_rear; } //判满:循环队列,当(rear+1)%length==front时为满 bool isQueueFull(MyQueue* s) { return (s->_rear + 1) % s->_len == s->_front; } //入队 void enQueue(MyQueue* s,char ch) { s->_space[s->_rear] = ch; s->_rear = (s->_rear + 1) % s->_len;//不能直接加1是因为其是循环队列,有可能直接到达的队尾 } //出队 char deQueue(MyQueue* s) { char ch= s->_space[s->_front]; s->_front = (s->_front + 1) % s->_len; return ch; }
队列的链式存储结构也可以用一个单链表实现,插入和删除操作分别在链表的两头进行

链式存储结构
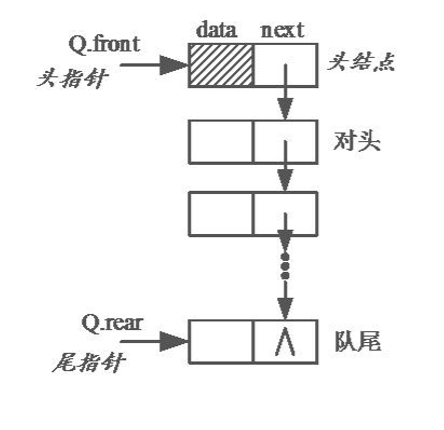
需要进行的操作为:初始化,判空,入队和出队,其中最难的是出队,分为两种情况:队列中只有两个节点和队列中有多个节点
队列中只有两个节点的情况
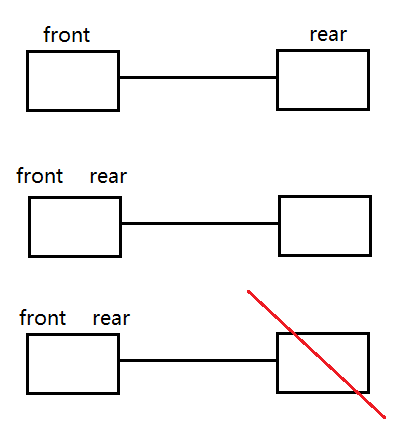
队列中有多个节点的情况
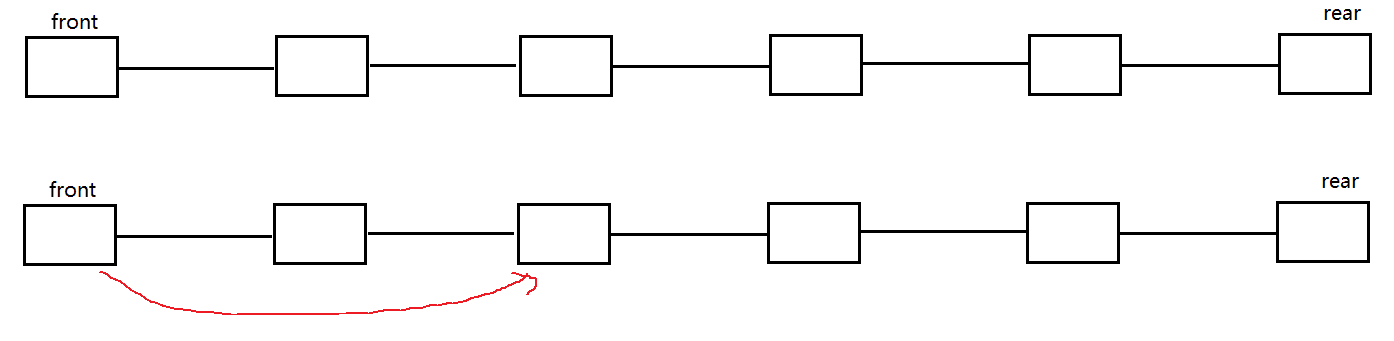
代码参考
1 typedef struct _node 2 { 3 char data; 4 struct _node* next; 5 }Node; 6 7 typedef struct _QueueList 8 { 9 Node* _front; 10 Node* _rear; 11 }QueueList; 12 13 //初始化 14 void initQueueList(QueueList* s) 15 { 16 s->_front = s->_rear = new Node[sizeof(Node)]; 17 s->_rear->next = nullptr; 18 } 19 20 //判空 21 bool isQueueListEmpty(QueueList* s) 22 { 23 return s->_front == s->_rear; 24 } 25 26 //入队:采用尾插法来实现入队 27 void enQueueList(QueueList* s, char ch) 28 { 29 Node* cur = new Node; 30 cur->data = ch; 31 cur->next = nullptr; 32 s->_rear->next = cur; 33 s->_rear = cur; 34 } 35 36 //出队:分为两种情况:队列中只剩下两个元素,和队列中剩余多个元素 37 //若队列中只剩下两个元素,即front->next==rear 38 char deQueueList(QueueList* s) 39 { 40 char ch = s->_front->next->data; 41 if (s->_front->next == s->_rear) 42 { 43 s->_rear = s->_front; 44 delete s->_front->next; 45 s->_front->next = nullptr; 46 } 47 else 48 { 49 Node* t = s->_front->next; 50 s->_front->next = t->next; 51 delete t; 52 } 53 return ch; 54 }
- 代码参考
myqueue.h
1 #pragma once 2 typedef struct _point 3 { 4 int _x; 5 int _y; 6 }Point; 7 8 9 typedef struct _node 10 { 11 Point data; 12 struct _node* next; 13 }Node; 14 15 typedef struct _queue 16 { 17 Node* _front; 18 Node* _rear; 19 }Queue; 20 21 //初始化 22 void initQueue(Queue* s); 23 //判空 24 bool isQueueEmpty(Queue* s); 25 //入队 26 void enQueue(Queue* s, Point data); 27 //出队 28 Point deQueue(Queue* s);
myqueue.cpp
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "myqueue.h" 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //初始化 7 void initQueue(Queue* s) 8 { 9 s->_front = s->_rear = new Node; 10 s->_front->next = nullptr; 11 } 12 //判空 13 bool isQueueEmpty(Queue* s) 14 { 15 return s->_front == s->_rear; 16 } 17 18 //入队 19 void enQueue(Queue* s, Point data) 20 { 21 Node* cur = new Node; 22 cur->data = data; 23 //cur->next = nullptr; 24 s->_rear->next = cur; 25 s->_rear = cur; 26 } 27 28 //出队 29 Point deQueue(Queue* s) 30 { 31 Point ch = s->_front->next->data; 32 if (s->_front->next == s->_rear) 33 { 34 s->_rear = s->_front; 35 delete s->_front->next; 36 s->_front->next = nullptr; 37 } 38 else 39 { 40 Node* t = s->_front->next; 41 s->_front->next = t->next; 42 delete t; 43 } 44 return ch; 45 }
main.cpp
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "myqueue.h" 3 4 #define MAXROW 10 5 #define MAXLINE 10 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 10 //1 代表墙,2 走过的路,0 代表路 11 int maze[MAXROW][MAXLINE] = 12 { 13 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1, 14 0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1, 15 1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1, 16 1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1, 17 1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1, 18 1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1, 19 1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1, 20 1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1, 21 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0, 22 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1, 23 }; 24 25 void displyMaze() 26 { 27 for (int i = 0; i < MAXROW; i++) 28 { 29 for (int j = 0; j < MAXLINE; j++) 30 { if (maze[i][j] == 1) 31 printf("%2s", " *"); 32 else if (maze[i][j] == 2) 33 printf("%2s", " #"); 34 else 35 printf("%2s", " "); 36 } 37 putchar(10); 38 } 39 printf(" ==================== "); 40 } 41 42 Queue q; 43 44 void visit(int x,int y) 45 { 46 Point p = { x,y }; 47 enQueue(&q, p); 48 } 49 50 51 int main() 52 { 53 displyMaze(); 54 Point sp = { 1,0 }; 55 Point ep = { 8,9 }; 56 enQueue(&q, sp); 57 bool flag = true; 58 while (!isQueueEmpty(&q)) 59 { 60 Point t = deQueue(&q); 61 maze[t._x][t._y] = 2; 62 system("cls"); 63 displyMaze(); 64 if (t._x - 1 >= 0 && maze[t._x - 1][t._y]==0) 65 visit(t._x - 1, t._y); 66 if (t._x + 1 <= 9 && maze[t._x + 1][t._y]==0) 67 visit(t._x + 1, t._y); 68 if (t._y - 1 >= 0 && maze[t._x][t._y - 1]==0) 69 visit(t._x, t._y - 1); 70 if (t._y + 1 <= 9 && maze[t._x][t._y + 1]==0) 71 visit(t._x, t._y + 1); 72 if (t._x == ep._x && t._y == ep._y) 73 flag = true; 74 } 75 if (flag) 76 cout << "find the path" << endl; 77 return 0; 78 }
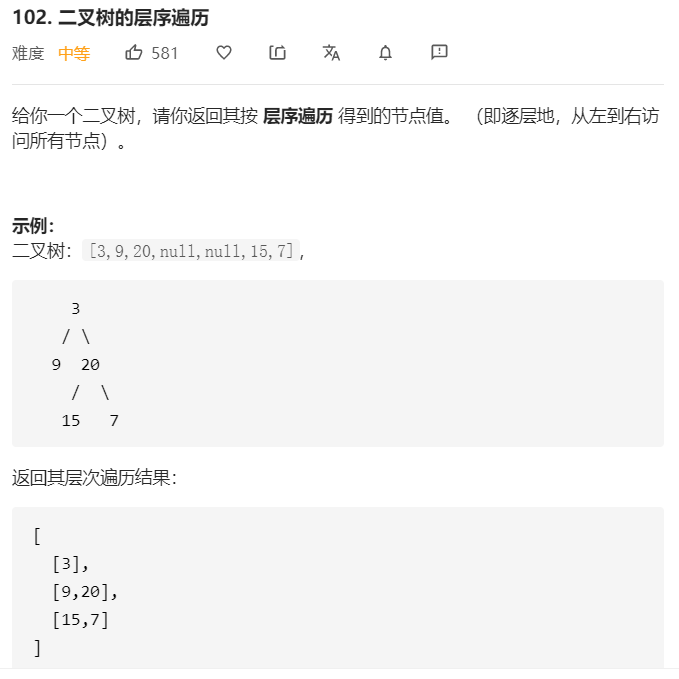
- 问题分析
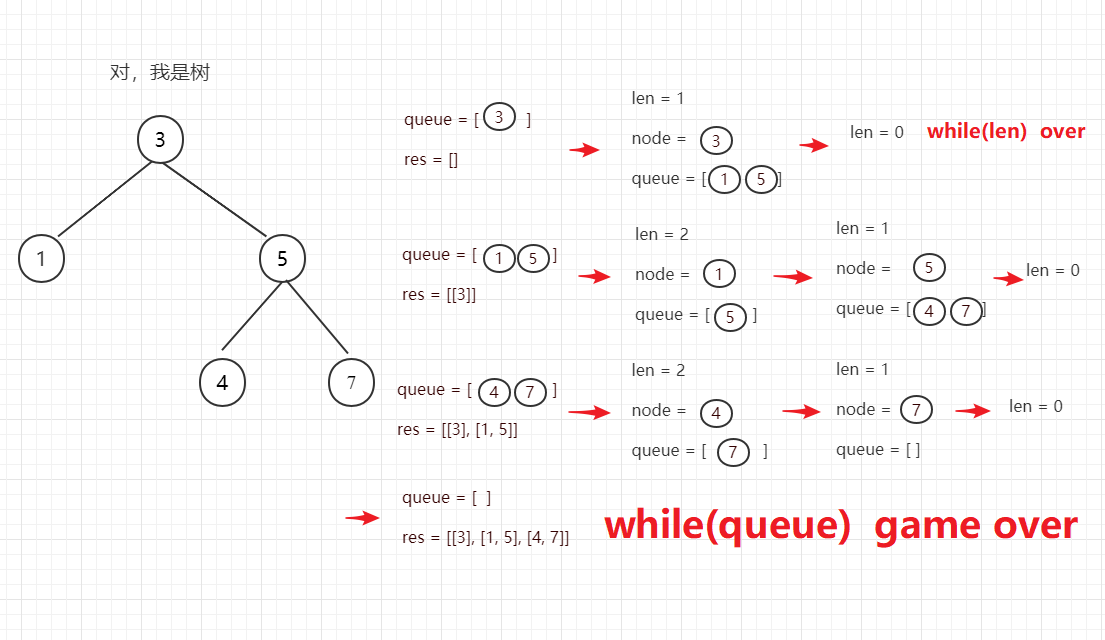
- 代码参考
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { 13 vector<vector<int>> B; 14 if(root==nullptr) 15 return B; 16 vector<int> line; 17 queue<TreeNode*> parent; 18 queue<TreeNode*> child; 19 parent.push(root); 20 while(!parent.empty()||!child.empty()) 21 { 22 TreeNode* t=parent.front(); 23 line.push_back(t->val); 24 parent.pop(); 25 if(t->left) 26 child.push(t->left); 27 if(t->right) 28 child.push(t->right); 29 if(parent.empty()) 30 { 31 B.push_back(line); 32 line.clear(); 33 while(!child.empty()) 34 { 35 parent.push(child.front()); 36 child.pop(); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 return B; 41 } 42 };
- 题目描述
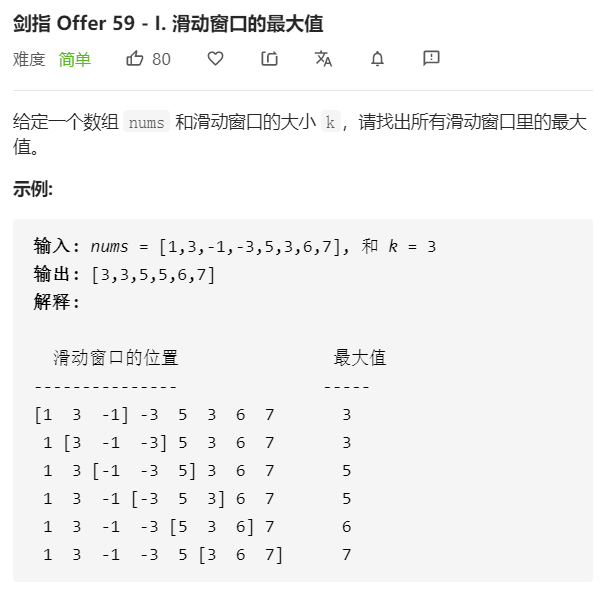
- 问题分析
将滑动窗口看成一个队列,窗口滑动时,处于窗口第一个数字被删除,同时在窗口的末尾添加一个新的数字,符合队列先进先出的原则。因此采用队列来存储滑动窗口。但我们不用队列来存储滑动窗口的所有值,而是存储滑动窗口中可能最大的值。从头到尾扫描整个数组,如果当前数组元素大于滑动窗口队列中的元素,则队列中的元素不可能成为滑动窗口的最大值,将其从队尾删除;如果当前数组元素小于滑动窗口队列中的元素,则当元素从滑动窗口队列头删除后,其可能成为滑动窗口最大元素,因此将元素入

- 代码参考
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) { 4 vector<int> maxInWindow; 5 if(nums.empty()||k<0||nums.size()<k) 6 return maxInWindow; 7 int len=nums.size(); 8 deque<int> index; 9 for(int i=0;i<k;++i) 10 { 11 while(!index.empty()&&nums[i]>nums[index.back()]) 12 index.pop_back(); 13 index.push_back(i); 14 } 15 16 //当滑动窗口中元素值等于滑动窗口的尺寸时,还要考虑滑动窗口中元素的个数问题 17 for(int i=k;i<len;++i) 18 { 19 maxInWindow.push_back(nums[index.front()]); 20 while(!index.empty()&&nums[i]>nums[index.back()]) 21 index.pop_back(); 22 while(!index.empty()&&(int)(i-index.front())>=k) 23 index.pop_front(); 24 index.push_back(i); 25 26 } 27 maxInWindow.push_back(nums[index.front()]); 28 return maxInWindow; 29 } 30 };

- 题目描述
为了解决上述问题,即定义一个函数得到队列中的最大值,则其可以参考上述滑动窗口的最大值来解决问题,刚开始可能思考,直接定义一个队列,每次入队操作时更新其最大值

但是出队后,这个方法会造成信息丢失,即当最大值出队后,我们无法知道队列里的下一个最大值

为了解决上述问题,我们只需记住当前最大值出队后,队列中的下一个最大值即可
具体方法是使用一个双端队列dequeue,在每次入队时。如果dequeue队尾元素小于即将入队的元素,则将小于value的全部元素出队后,再将value入队,否则直接入队
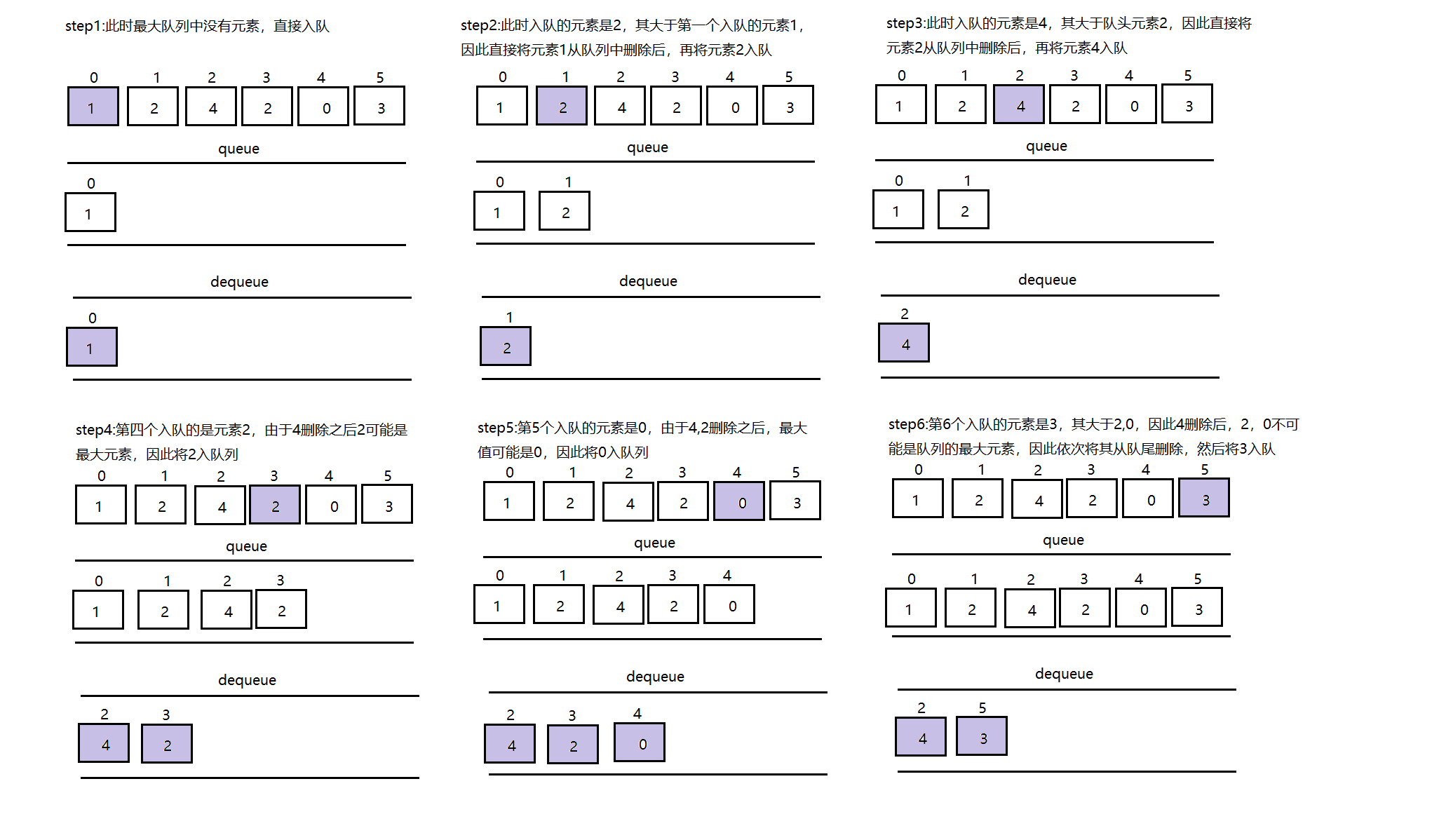
- 代码参考
1 class MaxQueue { 2 public: 3 MaxQueue() { 4 5 } 6 deque<int> data; 7 deque<int> maxinums; 8 int max_value() { 9 if(maxinums.empty()) 10 return -1; 11 return maxinums.front(); 12 } 13 14 void push_back(int value) { 15 data.push_back(value); 16 while(!maxinums.empty()&&value>maxinums.back()) 17 maxinums.pop_back(); 18 maxinums.push_back(value); 19 } 20 21 int pop_front() { 22 if(data.empty()) 23 return -1; 24 int ans=data.front(); 25 if(ans==maxinums.front()) 26 maxinums.pop_front(); 27 data.pop_front(); 28 return ans; 29 } 30 }; 31 32 /** 33 * Your MaxQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: 34 * MaxQueue* obj = new MaxQueue(); 35 * int param_1 = obj->max_value(); 36 * obj->push_back(value); 37 * int param_3 = obj->pop_front(); 38 */