
只有当严格递减的时候才会达到冒泡排序最坏时间复杂度
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,j,k) for(LL i=(j); i<(k); ++i)
#define pb push_back
#define PII pair<LL,LL>
#define PLL pair<long long, long long>
#define ini(a,j) memset(a,j,sizeof a)
#define rrep(i,j,k) for(LL i=j; i>=k; --i)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define LL long long
#define beg begin()
#define ed end()
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// #define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
freopen("1.dat","r",stdin);
#endif
LL _;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>_;
while(_--){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n);
rep(i,0,n) cin>>a[i];
vector<int> b = a;
sort(all(a), greater<int>());
bool flag = true;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
if(i&&a[i]==a[i-1])
flag = false;
if(a[i]!=b[i])
flag =false;
}
if(flag)
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
else
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

按照最高位进行分组然后统计答案就行了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,j,k) for(LL i=(j); i<(k); ++i)
#define pb push_back
#define PII pair<LL,LL>
#define PLL pair<long long, long long>
#define ini(a,j) memset(a,j,sizeof a)
#define rrep(i,j,k) for(LL i=j; i>=k; --i)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define LL long long
#define beg begin()
#define ed end()
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// #define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
freopen("1.dat","r",stdin);
#endif
LL _;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>_;
while(_--){
LL n;
cin>>n;
LL a;
map<LL, LL> cnt;
rep(i,0,n){
cin>>a;
LL k=0;
while(a>=(1LL<<k)){
k++;
}
cnt[k]++;
}
LL ans = 0;
for(auto e:cnt){
ans += (e.se*(e.se-1))/2;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

直接dp,记录前面为奇数长度和为偶数长的的最大值就可以了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,j,k) for(LL i=(j); i<(k); ++i)
#define pb push_back
#define PII pair<LL,LL>
#define PLL pair<long long, long long>
#define ini(a,j) memset(a,j,sizeof a)
#define rrep(i,j,k) for(LL i=j; i>=k; --i)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define LL long long
#define beg begin()
#define ed end()
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// #define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
freopen("1.dat","r",stdin);
#endif
LL _;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>_;
while(_--){
int n,q;
cin>>n>>q;
LL ans = 0LL;
vector<LL> a(n);
rep(i,0,n) {
cin>>a[i];
}
set<LL> odd, even;
odd.insert(a[0]);
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){
odd.insert(a[i]);
if(even.size()){
odd.insert(*(--even.end())+a[i]);
}
even.insert(*(--odd.end())-a[i]);
}
if(even.size())
ans = max(ans,*(--even.end()));
ans = max(ans,*(--odd.end()));
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

大佬给的思路,如果a[i]-a[i+1]大于零,那么这一组就要选
于是动态的更新就好了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int _;
cin>>_;
while(_--){
int n,q;
cin>>n>>q;
vector<int> a(n+10,0);
LL ans = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++){
ans += max(0, a[i]-a[i+1]);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
int x,y;
while(q--){
cin>>x>>y;
if(x==y){
cout<<ans<<endl;
continue;
}
ans -= max(a[x-1]-a[x], 0);
ans -= max(a[x]-a[x+1], 0);
ans -= max(a[y]-a[y+1], 0);
if(x+1!=y)
ans -= max(a[y-1]-a[y],0);
swap(a[x], a[y]);
ans += max(a[x-1]-a[x], 0);
ans += max(a[x]-a[x+1], 0);
ans += max(a[y]-a[y+1], 0);
if(x+1!=y)
ans += max(a[y-1]-a[y],0);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
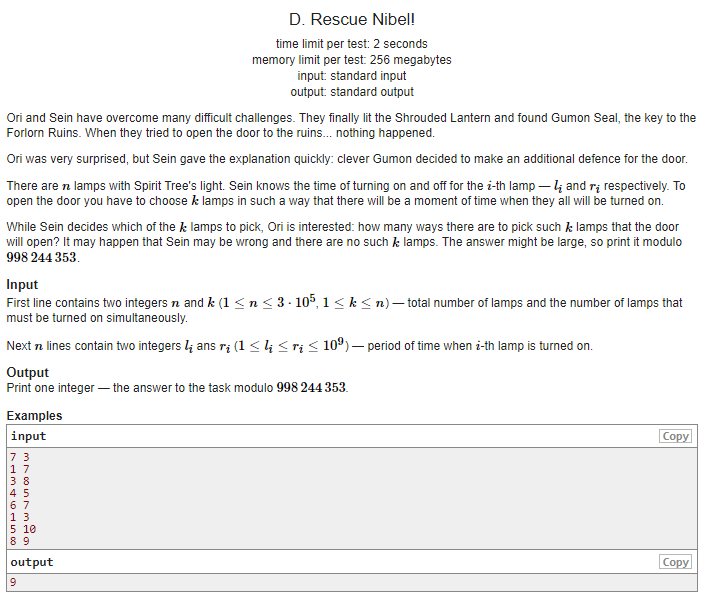
按照l从小到大排序之后
那么用优先队列维护r的值
对于每一个新的区间,抛弃掉优先队列里r小于a[i]的l的那些区间就可以
剩下就是求组合数了(学到了Lucas定理和小费马定理)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,j,k) for(LL i=(j); i<(k); ++i)
#define pb push_back
#define PII pair<LL,LL>
#define PLL pair<long long, long long>
#define ini(a,j) memset(a,j,sizeof a)
#define rrep(i,j,k) for(LL i=j; i>=k; --i)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define LL long long
#define beg begin()
#define ed end()
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
const int MAXN = 3e5+10;
LL mod = 998244353;
LL pre[MAXN];
LL qpow(LL x, LL n){
LL res = 1LL;
while(n){
if(n&1) res = (res*x)%mod;
n>>=1;
x = (x*x)%mod;
}
return res%mod;
}
LL C(LL n, LL k){
if(k==0) return 1;
return (pre[n]%mod*qpow((pre[k]*pre[n-k])%mod, mod-2)%mod)%mod;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
pre[0] = 1;
rep(i,1,MAXN){
pre[i] = (pre[i-1]*i)%mod;
}
vector<pair<int, int> > a(n);
rep(i, 0, n) cin>>a[i].fi>>a[i].se;
sort(all(a));
LL ans = 0LL;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > pq;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
while(pq.size()&&a[i].fi>pq.top()){
pq.pop();
}
if(pq.size()>=k-1){
ans = (ans+C(pq.size(), k-1));
}
pq.push(a[i].se);
}
cout<<ans%mod<<endl;
return 0;
}
我好菜啊