1.描述:不连续存储的表,可以把链表看成一个数组,数组元素是一个个结构体,这些结构体之间通过指针连接

2.优点:
利用不连续的存储空间,提高内存使用效率
避免删除和插入的线性开销
对比数组,大小不固定,可以扩展
3. 缺点:查找效率低
4. 定义一个单向链表
1 struct Node 2 { 3 ElementType value; 4 Node *next; //next指针,指向下一个节点 5 };
5.检测链表是否为空
对于一个单向链表,链表为空即头节点为空
1 int IsEmpty(Node *head) //将链表传入函数,传入头指针即可 2 { 3 return head->next == NULL; //若为空编译器将提示异常 4 }
6.测试当前位置是否为链表末尾
1 int IsLast(Node *Pos) 2 { 3 return Pos->next == NULL; 4 }
7.遍历并打印链表
1 void Print(Node *head) 2 { 3 Node *p = head; //类似范围for循环 4 while (p != NULL) 5 { 6 cout << p->value << " "; 7 p = p->next; 8 } 9 cout << endl; 10 }
8.检索链表,找出匹配的节点
1 Node* Find(ElementType x, Node *head) 2 { 3 Node *Pos; 4 Pos = head->next; 5 while (Pos != NULL && Pos->value != x) 6 Pos = Pos->next; 7 8 return Pos; 9 }
9.检索匹配节点的前驱元
1 Node* FindPrevious(ElementType x, Node *head) 2 { 3 Node *Pos; 4 Pos = head; 5 while (Pos->next != NULL && Pos->next->value != x) 6 Pos = Pos->next; 7 8 return Pos; 9 }
10.删除节点
1 void Delete(ElementType x, Node *head) 2 { 3 Node *Pos, *temp; 4 Pos = FindPrevious(x, head); //对于单向链表来说,获取前驱元需要额外遍历一次,这里使用上面编写的(9)FindPrevious函数 5 if (!IsLast(Pos)) //(6)测试是否为链表末尾 6 { 7 temp = Pos->next; 8 Pos->next = temp->next; 9 //free(temp); //C语言释放内存 10 delete temp; 11 } 12 }
11.在链表任意位置插入节点
注意,如果当前链表为空,则需要先手动新建头节点
1 void Insert(ElementType x, Node *head, Node *Pos) 2 { 3 Node *temp = new Node; 4 temp->value = x; 5 temp->next = Pos->next; 6 Pos->next = temp; 7 }
12.删除链表
1 void DeleteNode(Node *head) 2 { 3 Node *Pos, *temp; //用临时变量temp储存被删除前的Pos 4 Pos = head->next; 5 head->next = NULL; 6 while (Pos != NULL) 7 { 8 temp = Pos->next; 9 delete Pos; 10 Pos = temp; 11 } 12 }
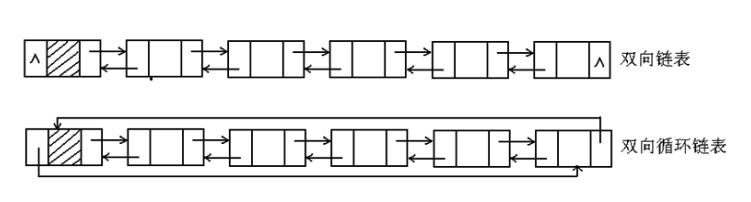
13.双向链表
1 struct Node 2 { 3 int value; 4 Node *next; 5 Node *pre; //添加一个pre指针指向上一个节点 6 };
14.循环链表
可以有表头,也可以没有表头
若有表头,则最后一个节点的next指向表头
循环链表可以与双向链表结合使用
15.链表的游标实现(freelist)
全局的结构体数组,用数组下标来代表地址
挖坑待填
参考资料:《数据结构与算法分析——C语言描述》 Mark Allen Weiss