Http Basic Authentication是HTTP协议中定义的Web系统中的验证方式。参考wiki
主要的实现机制如下:
1. 用户通过浏览器匿名访问web资源。
2. web服务器检测到web资源是需要已验证的用户才能访问。向浏览器返回Response(状态码401)。该response会携带如下Header:
WWW-Authenticate: {authentication schema} realm="{The realm of the resource}"
对于该header的value:
authentication schema是表示资源采用的验证方式,Http Basic Authentication对应的值为Basic
realm是对web资源进行的逻辑划分。以方便对不同分类的资源进行不同的验证方式.这个可自行定义
3. web浏览器收到Response后会弹出对话框来让用户输入用户名及密码。然后重新发送对web资源的请求。并将用户输入的验证信息包含在Authorization头中。
Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpPcGVuU2VzYW1l
这里的Basic为验证方式,而后面接着的字符串是将用户输入的用户名和密码以特定格式组合(username:name)得到的字符串进行base64编码后得到的字符串。
4. web服务器收到新的request后会对Authorization头进行解码并验证,如果验证通过则将资源返回。否则返回401
下面通过ASP.NET Core来演示Basic验证的实现:
首先我们假设已经有一个web api(GET http://localhost/api/values),我们需要对它实现Basic验证。
1. 我们添加一个负责验证的Authentication Middleware
public class AuthenticateMiddleware { private readonly RequestDelegate _next; public AuthenticateMiddleware(RequestDelegate next) { _next = next; } public Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context) { if (context == null) { throw new System.ArgumentNullException(nameof(context)); } if(!context.Request.Headers.ContainsKey("Authorization")){ context.Response.StatusCode = 401; context.Response.Headers["WWW-Authenticate"] = "Basic realm='My Realm'"; return Task.FromResult<object>(null); } return _next.Invoke(context); } }
2. 将middleware添加到pipeline中
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } else { app.UseHsts(); } //注册middleware app.UseMiddleware<AuthenticateMiddleware>(); app.UseHttpsRedirection(); app.UseMvc(); }
这样我们的所有资源就被保护起来了。不过用户输入任何内容均可通过验证^_^。此处仅作为演示
看看效果:
当我们访问资源时,浏览器会提示我们输入用户名和密码。输入后,浏览器再次发送请求。并带上Authorization头:
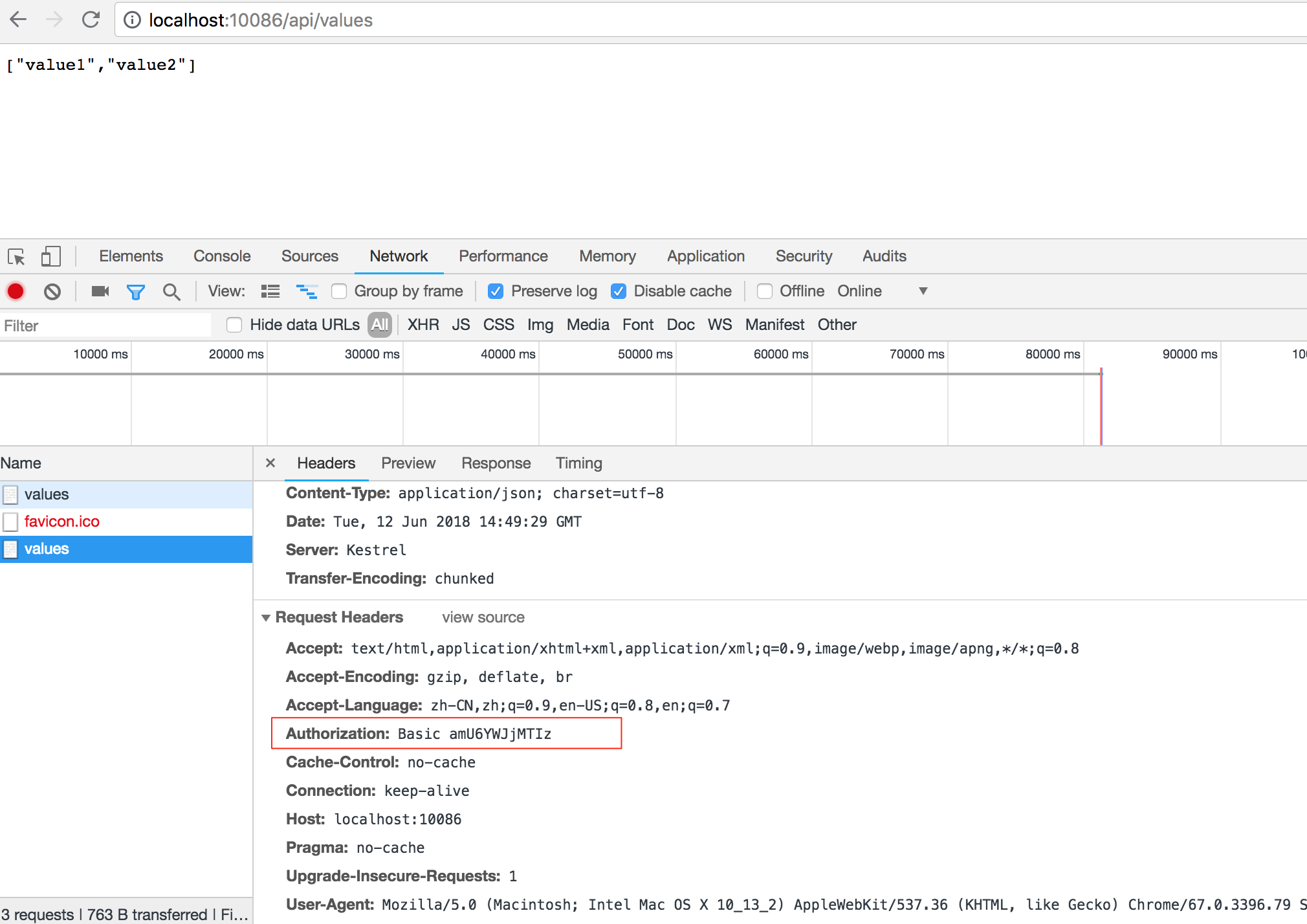
然后我们就能看到所访问资源的数据了。浏览器会将Authorization的值缓存一段时间(各个浏览器实现不一样),然后在后续的请求中携带。
Basic验证其实是很不安全的,Authorization的值仅仅做了base64编码,但安全度很低,可以直接被反编码。所以Basic验证最好是于https一起使用来保证安全性。