PathGeometry可以创建任意的2D图形形状。
其内部通过PathSegment集合来实现
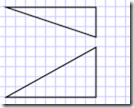
如画2个三角形
<Path Stroke="Black" StrokeThickness="1"> <Path.Data> <PathGeometry> <PathGeometry.Figures> <PathFigureCollection> <PathFigure IsClosed="True" StartPoint="10,100"> <PathFigure.Segments> <PathSegmentCollection> <LineSegment Point="100,100" /> <LineSegment Point="100,50" /> </PathSegmentCollection> </PathFigure.Segments> </PathFigure> <PathFigure IsClosed="True" StartPoint="10,10"> <PathFigure.Segments> <PathSegmentCollection> <LineSegment Point="100,10" /> <LineSegment Point="100,40" /> </PathSegmentCollection> </PathFigure.Segments> </PathFigure> </PathFigureCollection> </PathGeometry.Figures> </PathGeometry> </Path.Data> </Path>
外边框和笔刷均由Path提供,Geometry只负责绘制形状
为简化上面xaml,wpf提供了路径语法解析器,由
<Path Stroke="Black" StrokeThickness="1" Data="M 10,100 L 100,100 100,50 Z M 10,10 100,10 100,40 Z" />
孰能生巧而已,用多了就自然会了。
性能更好的StreamGeometry
不管Shape,Geometry还是Segment,其提供的熟悉均是依赖属性,所以其提供了依赖属性相关的特性,绑定和动画.
若Shape不用xaml表示,而是提供一个画图的DrawRectangle等方法,提供参数传递,那么可能就没必要提供依赖属性提供支持了.这样就回归到原始画法,从而了提高了性能
如下示例,StreamGeometryContext 提供了所有Segment的方法,可以猜测StreamGeometryContext 也是对Segment对象属性的一种封装,直接调用方法则省去了Segment集合的对象以及Segment内部的依赖属性来提供性能.
var g = new StreamGeometry(); using (StreamGeometryContext context = g.Open()) { context.BeginFigure(new Point(100,100), false, false); context.LineTo(new Point(200, 100), true, false); context.LineTo(new Point(200, 200), true, false); context.LineTo(new Point(100, 100), true, false); context.BeginFigure(new Point(300, 200), false, false); context.LineTo(new Point(400, 200), true, false); //context.LineTo(new Point(500, 200), true, false); //context.LineTo(new Point(200, 100), true, false); }
看来WPF还是以减少整体对象来提升性能的.
真正绘图的对象
FrameworkElement并不提供任何绘制图形的能力,其只是为绘图提供了必要的数据.即自上而下的封装.
Rectangle=>Create RectangleGeometry=>调用DrawingContext的DrawRoundedRectangle
若不提供Geometry,DrawingContext内部则会再次创建Geometry.
WPF的元素就是通过一个个FrameworkElement结合DrawingContext为基础,结合WPF各项特性搭积木而成,所以性能不好的时候就请查看visual tree的数量吧.