前言:
最近再项目当中使用的ApachShiro安全框架,对于权限和服务器资源的保护都有一个很好的管理。前期主要参考的文章有
项目中设计密码的加盐处理以及二次加密问题,跟着断点 一步步揭开Apach Shiro 的神秘面纱
数据库:

这里我们就用最简单的admin + 123456(加密前的密码) 来做测试
ShiroConfig 配置
/** * 凭证匹配器 告诉 * @return */ @Bean public HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher() { HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher(); hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5");// 散列算法:这里使用MD5算法; hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(2);// 散列的次数,比如散列两次,相当于 md5(md5("")); return hashedCredentialsMatcher; }
这里我摘取了一段shiro 配置类当中的一个Bean注入对象,这里是告诉ApachShiro 我用的加密方式是MD5 散列次数是两次,后面你把传上来的用户名和密码交给Shiro校验的时候,它会按照你传入的凭证匹配器去校验用户名和密码是否正确
继承 AuthorizingRealm 重写 doGetAuthenticationInfo(校验)
@Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("MyShiroRealm.doGetAuthenticationInfo()"); // 获取用户的输入的账号. String username = (String) token.getPrincipal(); System.out.println(token.getCredentials()); // 通过username从数据库中查找 User对象,如果找到,没找到. // 实际项目中,这里可以根据实际情况做缓存,如果不做,Shiro自己也是有时间间隔机制,2分钟内不会重复执行该方法 UserInfo userInfo = userInfoService.findByUsername(username); System.out.println("----->>userInfo=" + userInfo); if (userInfo == null) { return null; } SimpleAuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(userInfo, // 用户名 userInfo.getPassword(), // 密码 ByteSource.Util.bytes(userInfo.getCredentialsSalt()), // salt=username+salt getName() // realm name ); return authenticationInfo; }
这个方法最后返回一个 AuthenticationInfo (身份验证信息)需要传入这样几个参数,principal(当前需要校验的用户)hashedCredentials (已经加密后密码) credentialsSalt(密码加盐)realmName(特定安全的 DAO名称)
public SimpleAuthenticationInfo(Object principal, Object hashedCredentials, ByteSource credentialsSalt, String realmName) { this.principals = new SimplePrincipalCollection(principal, realmName); this.credentials = hashedCredentials; this.credentialsSalt = credentialsSalt; }

构建校验对象
SimpleAuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(userInfo, // 用户名 userInfo.getPassword(), // 密码 ByteSource.Util.bytes(userInfo.getCredentialsSalt()), // salt=username+salt getName() // realm name );
我们在这里把从数据库查出来的userInfo对象传入,全局作为唯一
第二个参数依然是传入用户被MD5加盐加密后的密码 d3c59d25033dbf980d29554025c23a75
第三个参数传入盐值 (这里的盐值是用户名+盐值)再用 ByteSource进行一次编码 YWRtaW44ZDc4ODY5ZjQ3MDk1MTMzMjk1OTU4MDQyNGQ0YmY0Zg==
最后一个参数当然就是本次Realm的名字

断点跟进,进入一个getAuthenticationInfo核心方法
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { AuthenticationInfo info = this.getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token); if (info == null) {
//从自定义的Realm中拿出一个包装好的对象 ,和token传过来的进行一个比较 info = this.doGetAuthenticationInfo(token); log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info); if (token != null && info != null) { this.cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info); } } else { log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info); } if (info != null) { this.assertCredentialsMatch(token, info); } else { log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token); } return info; }
注意:
1.方法传入的AuthenticationToken token 保存了当前传入过来的用户名 密码
继续用断点进行跟进 进入这样一个方法 cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible()
private void cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
//isAuthenticationCachingEnabled 首选检查是否启用缓存 我这里没有启用 返回的是false 直接跳出这个方法
if (!this.isAuthenticationCachingEnabled(token, info)) { log.debug("AuthenticationInfo caching is disabled for info [{}]. Submitted token: [{}].", info, token); } else { Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> cache = this.getAvailableAuthenticationCache(); if (cache != null) { Object key = this.getAuthenticationCacheKey(token); cache.put(key, info); log.trace("Cached AuthenticationInfo for continued authentication. key=[{}], value=[{}].", key, info); } } }
跳出来回到上面的 getAuthenticationInfo 核心方法 ,这里才是身份验证的主要位置
if (info != null) {
//凭证匹配器,提交的凭证和存储的凭证进行匹配比较 this.assertCredentialsMatch(token, info); } else { log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token); }
进入这个 assertCredentialsMatch(token,info)
protected void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) throws AuthenticationException {
//取出我们配置的凭证管理器 这里当然是MD5 CredentialsMatcher cm = this.getCredentialsMatcher(); if (cm != null) { if (!cm.doCredentialsMatch(token, info)) { String msg = "Submitted credentials for token [" + token + "] did not match the expected credentials."; throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(msg); } } else { throw new AuthenticationException("A CredentialsMatcher must be configured in order to verify credentials during authentication. If you do not wish for credentials to be examined, you can configure an " + AllowAllCredentialsMatcher.class.getName() + " instance."); } }
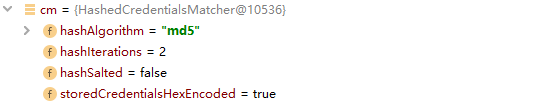
引用:
返回设定的凭证匹配器(匹配规则),包含了hashAlgorithmName(加密方式名如md5)、hashIterations(加密次数)、
storedCredentialsHexEncoded(密文进行16进制存储)、hashSalted(默认值false)、passwordRetryCache(密码重试缓存)5个属性。
凭证管理器 CredentialsMatcher
public interface CredentialsMatcher { boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken var1, AuthenticationInfo var2); }
凭证管理器定义为一个接口,我们在注入凭证管理器的时候,我们选择的是 Hash加密方法
HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
所以跳到 HashedCredentialsMatcher 类下面的校验方法
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
//把前台传过来的token明文密码进行加密 Object tokenHashedCredentials = this.hashProvidedCredentials(token, info);
//数据库查出来的已经加密过的密码 Object accountCredentials = this.getCredentials(info);
//进行比较 return this.equals(tokenHashedCredentials, accountCredentials); }
继续断点跟进,这里是要给取出盐值的操作 判断info的类型是否是 SaltedAuthenticationInfo
protected Object hashProvidedCredentials(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) { Object salt = null; if (info instanceof SaltedAuthenticationInfo) { salt = ((SaltedAuthenticationInfo)info).getCredentialsSalt(); } else if (this.isHashSalted()) { salt = this.getSalt(token); } return this.hashProvidedCredentials(token.getCredentials(), salt, this.getHashIterations()); }
拿到盐值后 传给hashProvidedCredentials方法 传入明文密码 盐值 以及 加密散列的次数
protected Hash hashProvidedCredentials(Object credentials, Object salt, int hashIterations) { String hashAlgorithmName = this.assertHashAlgorithmName(); return new SimpleHash(hashAlgorithmName, credentials, salt, hashIterations); }
最后使用 SimpleHash构造器构造出加密后的对象
两个 SimpleHash 进行比较的方法
protected boolean equals(Object tokenCredentials, Object accountCredentials) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Performing credentials equality check for tokenCredentials of type [" + tokenCredentials.getClass().getName() + " and accountCredentials of type [" + accountCredentials.getClass().getName() + "]"); } if (this.isByteSource(tokenCredentials) && this.isByteSource(accountCredentials)) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Both credentials arguments can be easily converted to byte arrays. Performing array equals comparison"); } byte[] tokenBytes = this.toBytes(tokenCredentials); byte[] accountBytes = this.toBytes(accountCredentials); return MessageDigest.isEqual(tokenBytes, accountBytes); } else { return accountCredentials.equals(tokenCredentials); } }
得知这些以后 ,我们自然而然的知道了密码加密的过程 ,我们在创建用户的时候 按照同样的方式,对密码进行一个加密 ,这样解密一点毛病也没有了
密码生成过程
@Test public void contextLoads() { String password = "123456"; String salt = "admin8d78869f470951332959580424d4bf4f"; int hashIterations = 2; SimpleHash simpleHash = new SimpleHash("md5",password, ByteSource.Util.bytes(salt),hashIterations); System.out.println(simpleHash.toHex());
// 结果 : d3c59d25033dbf980d29554025c23a75 }

比较数据库的密码 发现一致