单例设计模式
知识点
-
1.模式定义/应用场景/类图分析
-
2.字节码知识/字节码指令重排序
-
3.类加载机制
-
4.JVM序列化机制
-
5.单机模式在Spring框架 & JDK源码中的应用
懒加载模式
延迟加载,只有在真正使用的时候,才开始实列化。
-
线程安全问题
-
double check 加锁优化
-
编译器(JIT) CPU有可能对指令进行重排序,导致使用道尚未初始化的实列,可以通过添加volatile关键字进行修饰,对于volatile修饰的段,可以防止指令重排。
什么是指令重排,这里我们用javap -v xxx.class查看new 一个对象的过程。

class LazySingletonClass {
private static volatile LazySingletonClass instance;
private LazySingletonClass() {
}
public static LazySingletonClass getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (LazySingletonClass.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new LazySingletonClass();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
饿汉模式
基于JVM的类加载模,保证实例的唯一性
类的加载过程:
-
1.加载二进制数据道内存中,生成对应的Class数据结构
-
2.连接: a.验证,b-准备(给类的静态成员变量赋默认值),c-解析
-
3.初始化:给类的静态变量赋初值
只有在真正使用对应的类时,才会触发初始化 如直接进行new操作,访问静态属性,访问静态方法,用反射访问类,初始化一个类的子类等
class HungrySingleton {
private static HungrySingleton instance = new HungrySingleton();
private HungrySingleton() { }
public static HungrySingleton getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
内部类加载模式
class InnerSingletonClass {
private static class InnerSingletonHolderClass {
private static InnerSingletonClass instance = new InnerSingletonClass();
}
private InnerSingletonClass() {
}
public static InnerSingletonClass getInstance() {
return InnerSingletonHolderClass.instance;
}
}
调用getInstance()方法时,才调用这个内部类。本质上也是一种懒加载的一种形式
反射调用
在以上三种中,不做任何措施,时没有做到单例的用途。以懒加载模式为例如:
Constructor<LazySingletonClass> declaredConstructors = LazySingletonClass.class.getDeclaredConstructor();
declaredConstructors.setAccessible(true);
LazySingletonClass lazySingletonClass = declaredConstructors.newInstance();
InnerSingletonClass instance = InnerSingletonClass.getInstance();
System.out.println(lazySingletonClass);
System.out.println(instance);
结果为:
org.example.singleton.LazySingletonClass@1540e19d
org.example.singleton.InnerSingletonClass@677327b6
明显不是同一个实列。在以类的静态实列一起加载的模式,如内部类,在初始化时,即可以在私有的构造方法中加入一个判断。
private InnerSingletonClass() {
if(InnerSingletonHolderClass.instance != null){
throw new RuntimeException("单例不允许多个实例");
}
}
单例模式的应用
Runtime
饿汉模式
public class Runtime {
private static Runtime currentRuntime = new Runtime();
/**
* Returns the runtime object associated with the current Java application.
* Most of the methods of class <code>Runtime</code> are instance
* methods and must be invoked with respect to the current runtime object.
*
* @return the <code>Runtime</code> object associated with the current
* Java application.
*/
public static Runtime getRuntime() {
return currentRuntime;
}
/** Don't let anyone else instantiate this class */
private Runtime() {}
}
Currency
序列化,的处理方式,它也是提供了readResolve方法。
/**
* Resolves instances being deserialized to a single instance per currency.
*/
private Object readResolve() {
return getInstance(currencyCode);
}
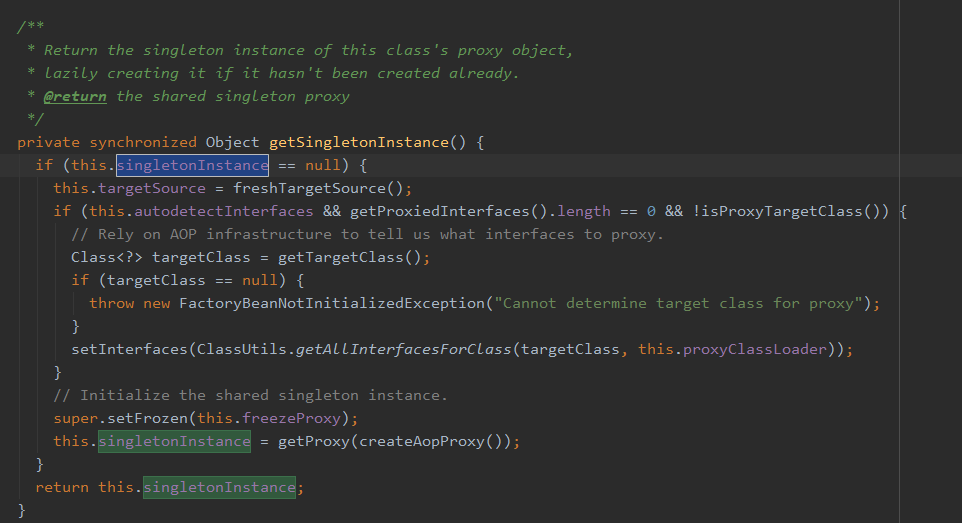
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry

ReactiveAdapterRegistry
public static ReactiveAdapterRegistry getSharedInstance() {
ReactiveAdapterRegistry registry = sharedInstance;
if (registry == null) {
synchronized (ReactiveAdapterRegistry.class) {
registry = sharedInstance;
if (registry == null) {
registry = new ReactiveAdapterRegistry();
sharedInstance = registry;
}
}
}
return registry;
}
ProxyFactoryBean