字体属性
font-weight:文字粗细
| 取值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| normal | 默认值,标准粗细 |
| bold | 粗体 |
| bolder | 更粗 |
| lighter | 更细 |
| 100~900 | 设置具体粗细,400等同于normal,而700等同于bold |
| inherit | 继承父元素字体的粗细值 |
font-style:文字风格
normal:正常,默认就是正常的
italic:倾斜
font-size:文字大小
一般是12、13或14px
注意:
1、通过font-size设置文字大小一定要带单位,即一定要写px
2、如果设置成inherit表示继承父元素的字体大小值
font-family:文字字体
font-family: "Microsoft Yahei", "微软雅黑", "Arial", sans-serif
常见字体:
serif 衬线字体
sans-serif 非衬线字体
中文:宋体,微软雅黑,黑体
注意:
1、设置的字体必须是用户电脑里已经安装的字体,浏览器会使用它可识别的第一个值。
2、如果取值为中文,需要用单或双引号括起来。
文字属性简写
/*font-weight: bolder;*/
/*font-style: italic;*/
/*font-size: 50px;*/
/*font-family: 'serif','微软雅黑';*/
简写为
font: bolder italic 50px 'serif','微软雅黑';
color:文字颜色
| 取值 | 格式 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
英文单词 |
color:red; | 大多数颜色都有对应的英文单词描述,但英文单词终究有其局限性:无法表示所有颜色 |
| rgb | color:rgb(255,0,0) | 什么是三原色? red,green,blue 什么是像素px? 对于光学显示器,一整个屏幕是有一个个点组成,每一个点称为一个像素 点,每个像素点都是由一个三元色的发光元件组成,该元件可以发出三种颜 色,red,green,blue。 发光元件协调三种颜色发光的明亮度可以调节出其他颜色 格式:rgb(255,0,0); 参数1控制红色显示的亮度 参数2控制绿色显示的亮度 参数3控制蓝色色显示的亮度 数字的范围0-255,0代表不发光,255代表发光,值越大越亮 红色:rgb(255,0,0) 绿色:rgb(0,255,0) 蓝色:rgb(0,0,255) 黑色:rgb(0,0,0) # 所有都不亮 白色:rgb(255,255,255) # 所有都最亮 灰色:只要让红色/绿色/蓝色的值都一样就是灰色,而且三个值越小,越偏 黑色,越大越偏白色 |
| rgba | color:rgba(255,0,0,0.1); | rgba到css3中才推出,比起rgb多了一个a,a代表透明度 a取值0-1,取值越小,越透明 |
| 十六进制 | color: #FF0000; | #FFEE00 其中FF代表R,EE代表G,00代表B 只要十六进制的颜色每两位都是一样的,那么就可以简写为一个, 例如#F00 等同于#FF0000 |
文本属性
text-align:规定元素中的文本水平对齐方式。
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| left | 左边对齐 默认值 |
| right | 右对齐 |
| center | 居中对齐 |
| justify | 两端对齐 |
text-decoration:文本装饰
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| none | 默认。定义标准的文本,通常用来去掉a标签的下划线 |
| underline | 定义文本下的一条线。 |
| overline | 定义文本上的一条线。 |
| line-through | 定义穿过文本下的一条线。 |
| inherit | 继承父元素的text-decoration属性的值。 |
text-indent:首行缩进
/*将段落的第一行缩进32像素,16px=1em*/
p {
text-indent: 32px;
}
line-height:行高
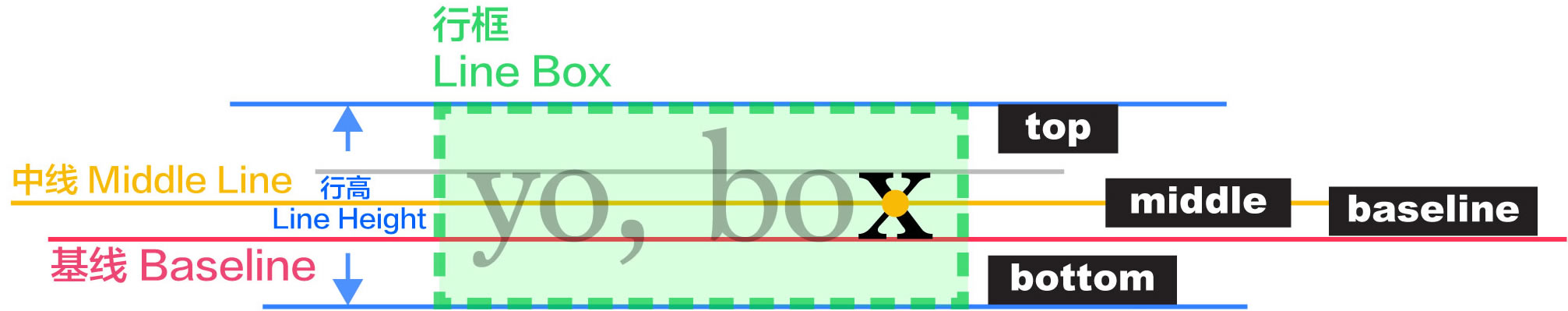
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>后代选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
p {
500px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: underline;
line-height: 200px;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>hello world</p>
<a href="#">点我啊</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
背景属性
注:没有宽高的标签,即便设置背景也无法显示
| 属性 | 描述 | 值 |
|---|---|---|
| background-color | 设置标签的背景颜色的 |
background-color: red; background-color: rgb(0,255,0); background-color: rgba(0,255,0,0.1); background-color: #00ffff; |
| background-image | 设置标签的背景图片 |
background-image: url("images/2.jpg"); background-image: url("图片网址"); 注意:如果图片的大小没有标签的大小大,那么会自动在水平和锤子方向平铺和填充 |
| background-size | 设置标签的背景图片的宽、高 |
background-size: 300px 300px; background-size: 100% 100%; |
| background-repeat | 设置标签的背景图片的平铺方式 |
background-repeat: repeat; #默认值,在垂直和水平方向都重复background-repeat: no-repeat; #不重复,背景图片将仅显示一次background-repeat: repeat-x; #背景图片将在水平方向平铺background-repeat: repeat-y; #背景图片将在垂直方向平铺应用:可以在服务端将一个大图片截成小图片,然后在客户端基于平铺属性将小图重复这样用户就以为是一张大图,如此,既节省了流量提升了速度,又不影响用户访问例如很多网站的导航条都是用这种手法制作的 |
| background-attachment | 设置标签的背景图片在标签中固定或随着页面滚动而滚动 |
background-attachment: scroll; #默认值,背景图片会随着滚动条的滚动而滚动background-attachment: fixed; #不会随着滚动条的滚动而滚动 |
| background-position | 前端的坐标系": *-------------------->x轴 | | | | | | y轴 *图片默认都是在盒子的左上角,background-position:属性,就是专门用于控制背景图片的位置 |
background-position:水平方向的值,垂直方向的值 1、具体的方位名词 *水平方向:left,center,right* *垂直方向:top,center,bottom* *如果只设置了一个关键词,那么第二个值就是"center"。*2、百分比 ***第一个值是水平位置,第二个值是垂直位置。* *左上角是 0% 0%。右下角是 100% 100%。* *如果只设置了一个值,另一个值就是50%。 *** 3、具体的像素(一定要加px单位) 例如:30px,50px等等 第一个值是水平位置,第二个值是垂直位置。 左上角是 0 0。单位是像素 (0px 0px) 或任何其他的 CSS 单位。 如果只设置了一个值,另一个值就是50%。 可以混合使用%和position值。 |
| inherit | 设置从父元素继承background属性值 |
以上背景属性的值均可以设置为inherit,代表从父元素继承background属性 |
| 背景缩写 | body { background: red url(xx.png) no-repeat fixed center/300px 300px; } |
背景属性缩写
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>后代选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
500px;
height: 500px;
/*background-color: red;*/
/*background-image: url("https://www.baidu.com/img/PCpad_012830ebaa7e4379ce9a9ed1b71f7507.png");*/
/*background-repeat: no-repeat;*/
/*background-position: right bottom;*/
/*background-size: 100px 100px;*/
background: red url("https://www.baidu.com/img/PCpad_012830ebaa7e4379ce9a9ed1b71f7507.png") no-repeat right bottom/100px 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
背景图片和插入图片的区别
- 1、背景图片仅仅只是一个装饰,不会占用位置,插入图片会占用位置。
- 2、背景图片可以有定位属性,可以很方便地控制图片的位置,而插入图片则不可以。
- 3、插入图片语义比背景图片的语义要强,所以在企业开发中如果图片想被搜索引擎收录,那么推荐使用插入图片。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>后代选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
background-image: url("https://www.baidu.com/img/PCpad_012830ebaa7e4379ce9a9ed1b71f7507.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right bottom;
}
.box2{
300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
1111111111111
</div>
<div class="box2">
22222222222222
<img src="https://www.baidu.com/img/PCpad_012830ebaa7e4379ce9a9ed1b71f7507.png" alt="">
</div>
</body>
</html>
背景图片居中显示:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>图片居中显示</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
height: 500px;
background-image: url("bg2.jpg");
background-position: top center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
图片拼接:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>图片拼接</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
height: 720px;
background-image: url("bg1.jpg");
}
.box2 {
background-image: url("ksyx.png");
background-position: bottom center;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
导航条:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>导航条</title>
<style type="text/css">
.navbar {
margin: 0 auto;
920px;
height: 50px;
background-image: url("dht.png");
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="navbar">
</div>
</body>
</html>
rgba与opacity
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.c1 {
200px;
height: 200px;
/*只能给背景设置透明度*/
/*background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.65);*/
background-color: rgb(0,0,0);
opacity: 0.65; /*改变整个标签的透明度*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c1">我是我啊啊啊啊</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.c1 {
height: 800px;
/*背景颜色不能与背景颜色同时使用,如果想给背景图片设置透明度,则必须使用opacity*/
background-image: url("https://images2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1036857/201805/1036857-20180516225809591-1990809146.jpg");
background-size:300px auto;
opacity: 0.55; /*改变整个标签的透明度*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c1"></div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.c1 {
200px;
height: 200px;
/*只能给背景设置透明度*/
/*background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.65);*/
background-color: rgb(0,0,0);
opacity: 0.65; /*改变整个标签的透明度*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c1">我是我啊啊啊啊</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.c1 {
height: 800px;
/*背景颜色不能与背景颜色同时使用,如果想给背景图片设置透明度,则必须使用opacity*/
background-image: url("https://images2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1036857/201805/1036857-20180516225809591-1990809146.jpg");
background-size:300px auto;
opacity: 0.55; /*改变整个标签的透明度*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c1"></div>
</body>
</html>
精灵图
精灵图是一种图像合成技术,一个网站可能有很多张图片,这就要求客户端发多次请求给服务端,但其实一次请求的带宽就足够容纳多张图片的大小。精灵图的作用就是用较少的请求次数,以降低服务器的处理压力。
精灵图需要配合背景图片和背景定位来使用。
切图需要用到frameworks软件,可以知道每个图片具体宽多少个像素高多少个像素,该软件与ps属于一个家族
在右面,图层-》位图-》出一把锁固定住图片 然后左侧,有一个切片工具,框住图片
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>导航条</title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
86px;
height: 28px;
background-image: url("https://images2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1036857/201805/1036857-20180510222513182-115432192.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: -425px -100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
</div>
</body>
</html>
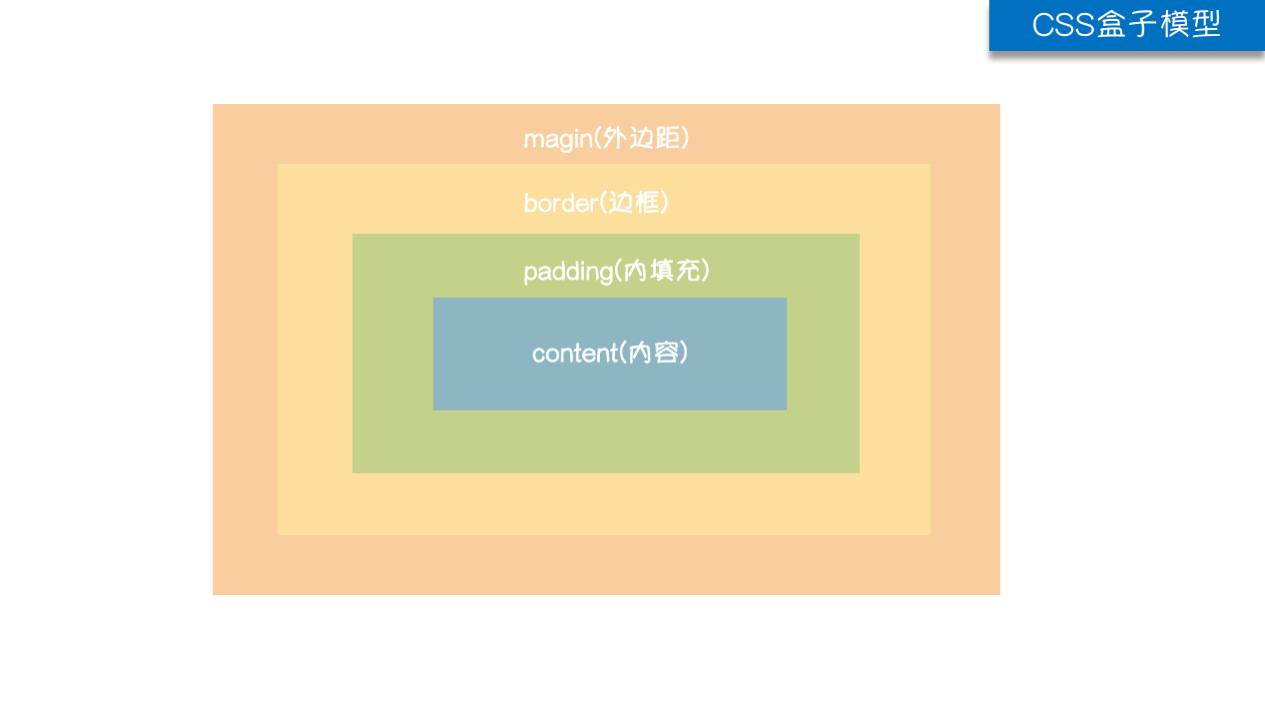
盒子模型
HTML文档中的每个元素都被比喻成矩形盒子,盒子模型通过四个边界来描述:margin(外边距),border(边框),padding(内填充),content(内容区域),如果把一个盒子比喻成一个壁挂相片,那么
- 外边距margin:一个相框与另外一个相框之间的距离
- 边框border:边框指的就是相框
- 内边距padding:内容/相片与边框的距离
- 宽度width/高度height:指定可以存放内容的区域
可以通过谷歌开发者工具查看盒子的各部分属性。
盒子模型的宽度和高度
#1、内容的宽度和高度
通过标签的width和height属性设置
#2、元素/盒子模型的宽度和高度
宽度= 左边框 + 左内边距 + width(内容的宽) + 右内边距 + 右边框高度
高度= 。。。。
#3、元素/盒子模型空间的宽度和高度
宽度= 左外边距 + 左边框 + 左内边距 + width(内容的宽) + 右内边距 + 右边框高度 + 右外边距
高度= 。。。。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>盒子模型宽度和高度</title>
<style>
span,a,b,strong {
display: inline-block;
100px;
height: 100px;
border: 6px solid #000;
padding: 20px;
margin: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>我是span</span>
<a href="#"> 我是超链接</a>
<b>我是加粗</b>
<strong>我是强调</strong>
</body>
</html>
为什么 height:100%;不起作用
如何让 height:100%起作用:你需要给这个元素的所有父元素的高度设定一个有效值。换句话说,你需要这样做:
现在你给div的高度为100%,它有两个父元素<body>和<html>。为了让你的div的百分比高度能起作用,你必须设定<body>和<html>的高度。
<html style="height: 100%;">
<body style="height: 100%;">
<div style="height: 100%;">
<p>
这样这个div的高度就会100%了
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
相似的例子:可以查看qq注册界面https://ssl.zc.qq.com/v3/index-chs.html
CSS显示模式:块级、行内、行内块级
在HTML中将所有标签分为两类:容器级和文本级。
在CSS中也将所有标签分为两类:块级元素和行内元素
HTML中容器级和文本级
容器级:可以嵌套其他的所有标签
div、h、ul>li、ol>li、dl>dt+dd
文本级标签:只能嵌套文字、图片、超链接
span、p、buis、strong、em、ins、del
CSS中块级与行内
块级:块级元素会独占一行,所有的容器类标签都是块级,文本标签中的p标签也是块级。
div、h、ul、ol、dl、li、dt、dd、p
行内:行内元素不会独占一行,所有除了p标签以外的文本标签都是行内。
span、buis、strong、em、ins、del
行内块级
img
块级和行内的区别:
1、块级元素block
- 独占一行,可以设置宽高,若没有设置宽度,那么默认和父元素一样宽,若没有设置宽高,那么就按照设置的来显示。
2、行内元素inline
- 不会独占一行,不可以设置宽高,盒子默认宽高默认和内容一样。
3、行内块级inline-block
- 不会独占一行,可以设置宽高
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
/*块级元素*/
div,p,h1 {
background-color: red;
200px;
height: 100px;
}
/*行内元素*/
span,b,strong {
background-color: blue;
200px;
height: 100px;
}
/*行内块级元素*/
img {
100px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--块级-->
<div>我是div</div>
<p>我是段落 </p>
<h1>我是标题</h1>
<hr>
<!--行内-->
<span>我是span</span>
<b>我是加粗</b>
<strong>我是强调</strong>
<hr>
<!--行内块级-->
<img src="../imags/1.png" alt="">
<img src="../imags/1.png" alt="">
</body>
</html>
CSS显示模式转化
| 属性 | 描述 | 值 |
|---|---|---|
display |
可以通过标签的display属性设置显示模式 |
none HTML文档中元素存在,但是在浏览器中不显示。一般用于配合JavaScript代码使用block 块级inline 行内inline-block 行内块级 |
**display:"none"与visibility:hidden的区别:** |
visibility:hidden: 可以隐藏某个元素,但隐藏的元素仍需占用与未隐藏之前一样的空间。也就是说,该元素虽然被隐藏了,但仍然会影响布局。 display:none: 可以隐藏某个元素,且隐藏的元素不会占用任何空间。也就是说,该元素不但被隐藏了,而且该元素原本占用的空间也会从页面布局中消失。 |
div与span
布局都是用块级元素,而行内元素是控制内容显示的。
div标签:一般用于配合CSS完成网页的基本布局
span标签:一般用于配合CSS修改网页中的一些局部信息,比如一行文字只为一部分加颜色<p>啊哈哈<span>呵呵呵</span></p>
区别:
- 1、div一般用于排版,span一般用于局部文字的样式
- 2、div是一个块级元素,独占一行,span是行内元素,不会独占一行
- 3、div是容器级标签,span是文本级标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>div与span标签</title>
<style>
.header {
margin: 0 auto;
980px;
height: 100px;
background: pink;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.content {
margin: 0 auto;
980px;
height: 500px;
background: #e9ca37;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.footer {
margin: 0 auto;
980px;
height: 100px;
background: #7e1487;
}
.logo {
200px;
height: 50px;
background: #bfccdb;
float: left;
margin: 20px;
}
.nav {
600px;
height: 50px;
background: palegreen;
float: right;
margin: 20px;
}
.aside {
250px;
height: 460px;
background: #cccccc;
float: left;
margin: 20px;
}
.article {
650px;
height: 460px;
background: green;
float: right;
margin: 20px;
}
span {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">
<div class="logo"></div>
<div class="nav"></div>
</div>
<div class="content">
<div class="aside">
<p>
君不见<span>黄河之水</span>,天上来<span>哈哈哈</span>
</p>
</div>
<div class="article"></div>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
</body>
</html>
盒子模型各部分详解
border边框
| 同时设置四条边的边框 | border:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色 |
|---|---|
| 分别设置四条边的边框 | border-left:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色border-top:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色border-right:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色border-bottom:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色 |
| 分别指定宽度、格式、颜色 | 1、连写:(分别设置四条边的边框)bord- 上 右 下 左border-style:上 右 下 左border-color:上 右 下 左2 、注意点: 1、这三个属性时按照顺时针,即上、右、下、左来赋值的 2、这三个属性的取值省略时的规律 省略右面,右面默认同左边 省略下部,下面默认跟上面一样 只留一个,那么其余三边都跟这一个一样 |
了解非连写 |
border-left- ;border-left-style: ;border-left-color: #000;border-top- ;border-top-style: ;border-top-color: #000;border-right- ;border-right-style: ;border-right-color: #000;border-bottom- ;border-bottom-style: ;border-bottom-color: #000;其他: http://www.w3school.com.cn/cssref/pr_border-style.asp |
| 边框的样式 | none 无边框。 dotted 点状虚线边框。 dashed 矩形虚线边框。 solid 实线边框。 |
| border-radius | /* 单独设置一个角:数值越大,弧度越大*/ border-top-left-radius: 20px;border-top-right-radius: 20px;border-bottom-left-radius: 20px;border-bottom-right-radius: 20px;/* 缩写设置 */border-radius: 20px;/* 所有角设置相同值 */border-radius: 20px 10px 10px 20px; /* 顺时针顺序:上左 上右 下左 下右*/ /* 百分比设置 */border-radius: 50%;/* 椭圆圆弧设置 */border-radius: 25%/50%; /* 前面一个值代表水平方向的半径占总宽度的,后面一个值代表垂直方向 */ |
同时设置四条边的边框
border:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色
分别设置四条边的边框
border-left:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色
border-top:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色
border-right:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色
border-bottom:边框的宽度 边框的样式 边框的颜色
分别指定宽度、格式、颜色
1、连写:(分别设置四条边的边框)
bord- 上 右 下 左
border-style:上 右 下 左
border-color:上 右 下 左
2 、注意点:
1、这三个属性时按照顺时针,即上、右、下、左来赋值的
2、这三个属性的取值省略时的规律
省略右面,右面默认同左边
省略下部,下面默认跟上面一样
只留一个,那么其余三边都跟这一个一样
了解非连写
border-left- ;
border-left-style: ;
border-left-color: #000;
border-top- ;
border-top-style: ;
border-top-color: #000;
border-right- ;
border-right-style: ;
border-right-color: #000;
border-bottom- ;
border-bottom-style: ;
border-bottom-color: #000;
其他:
http://www.w3school.com.cn/cssref/pr_border-style.asp
边框的样式
none 无边框。
dotted 点状虚线边框。
dashed 矩形虚线边框。
solid 实线边框。
border-radius
/* 单独设置一个角:数值越大,弧度越大*/
border-top-left-radius: 20px;
border-top-right-radius: 20px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 20px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 20px;
/* 缩写设置 */
border-radius: 20px;/* 所有角设置相同值 */
border-radius: 20px 10px 10px 20px; /* 顺时针顺序:上左 上右 下左 下右*/
/* 百分比设置 */
border-radius: 50%;
/* 椭圆圆弧设置 */
border-radius: 25%/50%; /* 前面一个值代表水平方向的半径占总宽度的,后面一个值代表垂直方向 */
border-radius练习1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
margin: 0 auto;
height: 100px;
920px;
border-radius: 5px 5px 0px 0px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
border-radius练习
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
img {
185px;
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="https://images2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1036857/201805/1036857-20180511163924274-1737036731.png" alt="">
</body>
</html>
padding内边距:边框与内容的距离就是内边距
| 非连写 | padding-top:20px;padding-right:20px;padding-bottom:20px;padding-left:20px; |
|---|---|
| 连写 | padding:上 右 下 左; |
| 注意 | 给标签设置内边距后,标签内容占有的宽度和高度会发生变化,设置padding之后标签内容的宽高是在原宽高的基础上加上padding值。如果不想改变实际大小,那就在用宽高减掉padding对应方向的值2 padding是添加给父级的,改变的是父级包含的内容的位置 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>内边距属性</title>
<style>
div {
100px;
height: 110px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
.box1 {
padding-top: 30px;
}
.box2 {
padding-right: 40px;
}
.box3 {
padding-bottom: 50px;
}
.box4 {
padding-left: 60px;
}
.box5 {
/*只留一个。全都相等*/
padding: 70px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字
</div>
<hr>
<div class="box2">
我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字
</div>
<hr>
<div class="box3">
我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字
</div>
<hr>
<div class="box4">
我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字
</div>
<hr>
<div class="box5">
我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字
</div>
</body>
</html>
添加边框与padding后保持盒子大小不变:方式一做减法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
/* 100px;*/
/*height: 100px;*/
background-color: red;
border: 10px solid #000;
padding: 10px;
60px;
height: 60px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">我是文字</div>
</body>
</html>
添加边框与padding后保持盒子大小不变:方式二box-sizing
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
border: 10px solid #000;
padding: 10px;
/*本质原理就是做减法*/
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">我是文字</div>
</body>
</html>
外边距:标签与标签之间的距离就是外边距
| 非连写 | margin-top:20px;margin-right:20px;margin-bottom:20px;margin-left:20px; |
|---|---|
| 连写 | margin:上 右 下 左; |
| 注意 | 外边距的那一部分是没有背景颜色的2、外边距合并现象 在默认布局的水平方向上,默认两个盒子的外边距会叠加 而在垂直方向上,默认情况下两个盒子的外边距是不会叠加的,会出现合并现象,谁的外边距比较大,就听谁的 |
外边距合并现象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>外边距合并现象
</title>
<style>
span {
display: inline-block;
100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
div {
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
/*水平方向上。外边距会叠加*/
.hezi1 {
margin-right: 50px;
}
.hezi2 {
margin-left: 100px;
}
/*垂直方向上。外边距不会叠加,会合并成一个,谁比较大就听谁的*/
.box1 {
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.box2 {
margin-top: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
快捷创建
span.hezi${我是span}*2
-->
<span class="hezi1">我是span</span><span class="hezi2">我是span</span>
<div class="box1">我是div</div>
<div class="box2">我是div</div>
</body>
</html>
margin-top塌陷
两个嵌套的盒子,内层盒子设置margin-top后会将外层盒子一起顶下来,解决方法如下:
1、外部盒子设置一个边框
2、外部盒子设置 overflow: hidden; 当子元素的尺寸超过父元素的尺寸时,内容会被修剪,并且其余内容是不可见的,此属性还有清除浮动、清除margin-top塌陷的功能。
3、使用伪元素类:
.clearfix:before{
content: '';
display:table;
}
#示范
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>盒子模型宽度和高度</title>
<style>
.outter {
background-color: green;
300px;
height: 300px;
/*方式一*/
/*border: 1px solid #000;*/
/*方式二*/
/*overflow: hidden;*/
}
.inner {
background-color: red;
200px;
height: 200px;
margin-top: 100px;
}
/*方式三*/
.clearfix:before {
display: table;
content: "";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outter clearfix">
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
内边距vs外边距
- 1、在企业开发中,一般情况下如果需要控制嵌套关系盒子之间的距离,应该首先考虑padding,其次再考虑margin。margin本质上适用于控制兄弟直接的关系的,padding本质才是控制父子关系的关系
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.egon {
300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
padding: 50px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.alex {
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
}
.linhaifeng {
300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: purple;
padding: 50px;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin-top: 100px;
}
.liuqingzheng {
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="egon">
<div class="alex"></div>
</div>
<div class="linhaifeng">
<div class="liuqingzheng"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- 2、如果两个盒子是嵌套关系,并且设置了里面一个盒子顶部的外边距,那么外面一个盒子也会被顶下来。如果外面的盒子不想被顶下来,那么可以给外面的盒子设置一个边框属性。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.egon {
300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.alex {
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
margin-top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="egon">
<div class="alex"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
盒子居中与内容居中
内容居中
1、让一行内容在盒子中水平且垂直居中
/*水平居中*/
text-align: center;
/*垂直居中*/
line-height: 500px;
2、让多行内容在盒子中垂直居中(水平居中与单行内容一样)
让行高与盒子高度一样,只能让一行内容垂直居中,如果想让多行内容垂直居中,
比如下面这种,想让div中的多行内容垂直居中,一看div中的文字是两行,每一行
的行高为20,加起来就是40,80-40=40,需要让文字距离顶部pading为20,底部padding为20
*/
height: 80px;
line-height: 20px;
padding-top: 20px;
padding-bottom: 20px;
box-sizing: border-box;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>盒子居中和内容居中</title>
<style>
div {
300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: red;
/*多行内容水平居中与单行一样*/
text-align: center;
/*多行内容垂直居中*/
line-height: 30px;
padding-top: 120px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字
</div>
</body>
</html>
盒子居中
text-align center;只能让盒子中存储的文字、图片水平居中
如果想让盒子自己相对于父元素水平居中,需要用到
margin: 0 auto;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>盒子居中和内容居中</title>
<style>
.son {
300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: red;
/*多行内容水平居中与单行一样*/
text-align: center;
/*多行内容垂直居中*/
line-height: 30px;
padding-top: 120px;
box-sizing: border-box;
/*盒子本身水平居中*/
margin: 0 auto;
}
.father {
500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">
我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字我是文字
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
防止文字溢出word-break:break-all;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>欢迎界面</title>
<style type="text/css">
div {
200px;
height: 200px;
/*字母、数字溢出,可以用下列属性控制自动换行:允许在单词内换行。
http://www.w3school.com.cn/cssref/pr_word-break.asp
*/
word-break: break-all;
}
.box1 {
background-color: red;
}
.box2 {
background-color: green;
}
.box3 {
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<p>asdfasdfsadfasdfasdfasdfad sfasdfsadasDSfafsafaasdfasdfasfdqwerqwerwqersdfqerwrsdf你好我的啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊</p>
</div>
<div class="box2">一行白鹭上青天两个黄鹂鸣翠柳啊哈哈哈
</div>
<div class="box3">我是12312312312312312312312312312312312312312312312312312312312我
</div>
</body>
</html>
清除默认边距
#1、为什么要清空默认边距(外边距和内边距)
浏览器会自动附加边距,在企业开发中为了更好的控制盒子的宽高和计算盒子的宽高等等
编写代码之前的第一件事情就是清空默认的边距
#2、如何清空默认的边距
* {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
#3、注意点:
通配符选择器会找到(遍历)当前界面中所有的标签,所以性能不好,参考:https://yuilibrary.com/yui/docs/cssreset/
拷贝代码:
body,div,dl,dt,dd,ul,ol,li,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,pre,code,form,fieldset,legend,input,textarea,p,blockquote,th,td{margin:0;padding:0}
可以查看京东,bat主页也是这么做的,在企业开发中也应该像上面这么写
实例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>清除默认边距</title>
<style>
/*
* {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
*/
body,div,dl,dt,dd,ul,ol,li,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,pre,code,form,fieldset,legend,input,textarea,p,blockquote,th,td{margin:0;padding:0}
.box1 {
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
}
.box2 {
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.box3 {
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>