简介
( extbf{01trie}) 就是把整数的二进制表达式当作字符串,按照从高位到低位的顺序,挂载在字典树上,每个节点有两个孩子,分别是 (0, 1),从而形成一棵二叉树,常用来处理异或问题
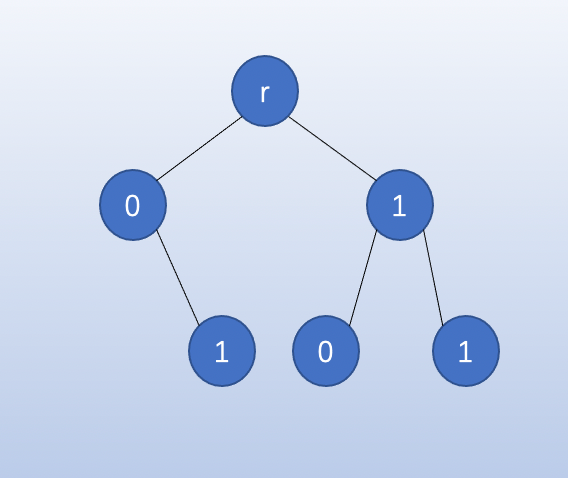
例如将一个数组 ([1, 2, 3]) 挂在 ( extbf{01trie}) 上,便得到如下所示的一棵二叉树
性质
由于 ( extbf{01trie}) 是一棵二叉树,且最大深度取决于挂载值的大小,设挂载最大值为 (n),那么一次查询前缀的过程便可以在 (O(log n)) 时间完成
例题
力扣 421. 数组中两个数的最大异或值
给定 (n) 个正整数的数组 (a),计算 (a_{i} oplus a_{j}) 的最大值
数据规定
(1leq nleq 2cdot 10^4)
(1leq a_{i}leq 2^{31} - 1)
题解
将数组中所有正整数的二进制表示,按照从高位到低位的顺序,当作字符串挂载在字典树上,形成 (01) 字典树,该字典树为一棵二叉树
对于正整数 (t),为了寻找数组中的 (s),使得 (xoplus t) 最大,我们只要每次贪心走与当前位相反的路即可
具体来讲,如果当前位为 (1),我们走 (0) 子树,反之走 (1) 子树,当然,如果不存在对应的子树,我们还是得走存在的子树
这样可以保证异或后的高位尽可能为 (1),在二进制表示中,高位为 (1),即使剩下的全 (0),结果也要比高位为 (0),剩下的全 (1) 结果大,直观的感受,((100)_{2} > (011)_{2}),这便证明了贪心的正确性
时间复杂度为 (O(nlog L)),其中 (L = 2^{31} - 1)
// cpp
const int N = 2e4;
const int M = 31;
class Solution {
public:
int node[N * M][2], cnt = 0;
void insert(int x)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; --i) {
int idx = 1 & (x >> i);
if (!node[p][idx]) node[p][idx] = ++cnt;
p = node[p][idx];
}
}
int query(int x)
{
int p = 0;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; --i) {
int idx = 1 & (x >> i);
if (node[p][idx ^ 1]) {
ans *= 2, ans += 1;
p = node[p][idx ^ 1];
}
else {
ans *= 2, ans += 0;
p = node[p][idx];
}
}
return ans;
}
int findMaximumXOR(vector<int>& nums) {
for (auto &i: nums) insert(i);
int ans = 0;
for (auto &i: nums) ans = max(ans, query(i));
return ans;
}
};
力扣 1707. 与数组中元素的最大异或值
给定 (n) 个正整数的数组 (a),给定 (q) 个询问,每个询问包含两个正整数 (x_{i}, m_{i})
对于每一个询问,在 (a) 中所有不大于 (m_{i}) 的数中选一个 (y),使得 (x_{i}oplus y) 最大,返回这个最大值
数据规定
(1leq n, qleq 10^5)
(1leq a_{i}, x_{i}, m_{i}leq 10^9)
题解
离线查询,对 (a) 从小到大排序,对 (q) 按照 (m_{i}) 从小到大排序
根据单调性,使用双指针,将 (a) 中符合条件的正整数 (a_{i}) 挂载到字典树上,进行查询即可
时间复杂度为 (O((q + n)cdot log L + qlog q + nlog n)),其中 (L = 10^9)
// cpp
#define pb push_back
const int N = 1e5;
const int M = 30;
class Solution {
public:
int node[N * M][2], cnt = 0;
void insert(int x)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; --i) {
int idx = 1 & (x >> i);
if (!node[p][idx]) node[p][idx] = ++cnt;
p = node[p][idx];
}
}
int query(int x)
{
int p = 0;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; --i) {
int idx = 1 & (x >> i);
if (node[p][idx ^ 1]) {
ans *= 2, ans += 1;
p = node[p][idx ^ 1];
}
else {
ans *= 2, ans += 0;
p = node[p][idx];
}
}
return ans;
}
vector<int> maximizeXor(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {
int idx = 0;
for (auto &i: q) i.pb(idx++);
sort(q.begin(), q.end(), [&](const vector<int> &x, const vector<int> &y){
return x[1] < y[1];
});
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int n = q.size();
vector<int> ans(n);
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while (j < nums.size() && nums[j] <= q[i][1])
insert(nums[j++]);
if (!j) ans[q[i][2]] = -1;
else ans[q[i][2]] = query(q[i][0]);
}
return ans;
}
};
力扣 1938. 查询最大基因差
给定一棵 (n) 个节点的树,每个节点的编号 (i) 即为其权值 (v_{i})
给定 (q) 个查询,每个查询包含树上一个点的编号 (i) 和目标值 (t)
对于每一个查询,你需要选一个从根到 (i) 的节点 (j),要求使得 (j oplus i) 值最大,返回这个最大值
数据规定
(1leq nleq 10^5)
(1leq qleq 3cdot 10^4)
(1leq v_{i}leq 2cdot 10^5)
题解
离线查询,维护每个节点的所有查询
我们需要维护一个从根到当前节点的路径,因此考虑 dfs
具体来讲,深搜到当前点 (i) 时,将 (v_{i}) 挂载在 01 trie 上,同时进行一次查询,计算出最大的异或值,继续向下深搜,等到回溯的时候,将当前节点的权值从字典树上删除
计算最大异或值时,每次贪心选择与当前位相反的节点即可
时间复杂度为 (O((n + q)cdot log L)),其中 (L = 2cdot 10^5)
// cpp
#define pii pair< int, int >
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
const int N = 2e5;
const int M = 18;
int node[N * M][2], bucket[N * M][2], cnt = 0;
void insert(int x)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; --i) {
int idx = 1 & (x >> i);
if (!node[p][idx]) node[p][idx] = ++cnt;
bucket[p][idx]++;
p = node[p][idx];
}
}
void del(int x)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; --i) {
int idx = 1 & (x >> i);
int next = node[p][idx];
if (bucket[p][idx] == 1) node[p][idx] = 0;
bucket[p][idx]--;
p = next;
}
}
int query(int x)
{
int p = 0;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = M; i >= 0; --i) {
int idx = 1 & (x >> i);
if (node[p][idx ^ 1]) {
ans *= 2, ans += 1;
p = node[p][idx ^ 1];
}
else {
ans *= 2, ans += 0;
p = node[p][idx];
}
}
return ans;
}
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map< int, vector< pii > > mp;
vector< int > son[N];
void dfs(int u, vector< int > &ans)
{
insert(u);
for (auto &i : mp[u]) ans[i.se] = query(i.fi);
for (auto &i : son[u]) dfs(i, ans);
del(u);
}
vector< int > maxGeneticDifference(vector< int > &p, vector< vector< int > > &q)
{
int root = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); ++i) {
if (p[i] != -1)
son[p[i]].push_back(i);
else
root = i;
}
int n = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
q[i].pb(i);
mp[q[i][0]].pb({ q[i][1], q[i][2] });
}
vector< int > ans(n);
dfs(root, ans);
return ans;
}
};