网络流、最大流、费用流
(1.) 网络流概念
(1.1) 网络
网络指的是有向图 (G(V, E))
每条边 ((u, v)in E) 都有一个权值 (w(u, v)),称之为容量
两个特殊的点为源点 (s) 和汇点 (t)
(1.2) 流
定义 (f(u, v)) 为流经边 ((u, v)) 的流量
流量满足
- 正反流量互为相反数,即 (f(u, v) = -f(v, u))
- 流量限制,即 (f(u, v)leq w(u, v))
- 流量守恒,即流出点的流量和流入该点的流量相等
- 若边 ((u, v)) 流过一个大小为 (f(u, v)) 的流,那么该边剩余的容量为 (w(u, v) - f(u, v))
可行流指的就是能从源点 (s) 汇入汇点 (t) 的一个流量
最大流指的就是可行流的最大值
(1.3) 残余网络
网络上所有边的容量减去可行流的大小,得到的新的网络被称为残余网络
(1.4) 增广路
网络中能使可行流增加的一条路径被称为增广路
(1.5) 反悔边
经典图如下
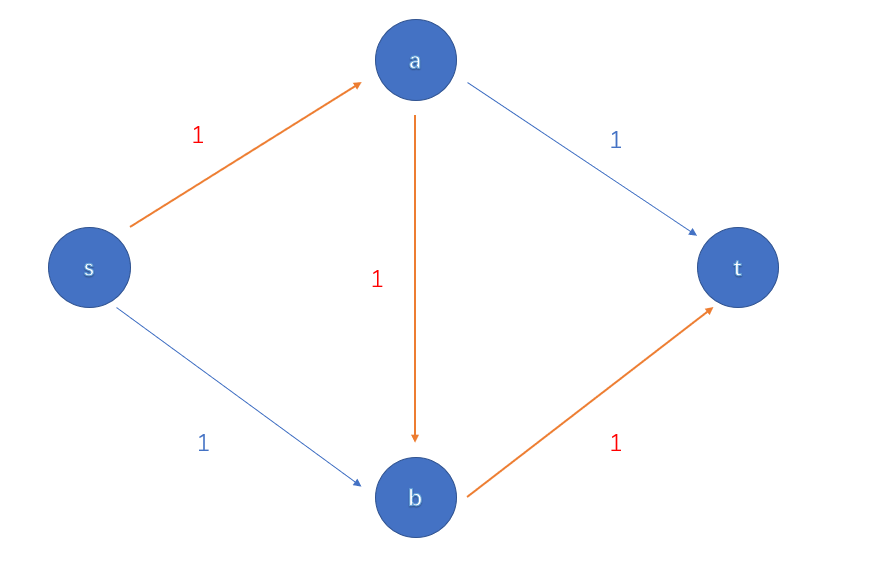
走红线标注的路显然不是流量最大
考虑引入反悔边
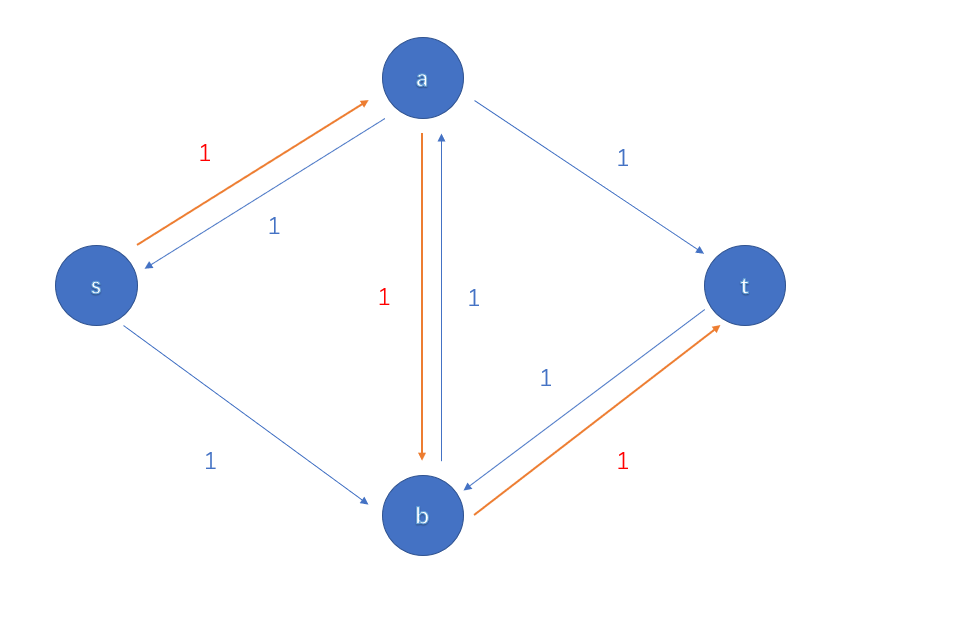
反悔可以认为是决策的重构,边 ((a, b)) 的流量对答案的贡献并没有变化,所以这是正确的
不得不说,反悔边真是一个天才的想法
(1.6) 最大流算法
不断寻找增广路,同时建立反悔边
当无法找到增广路时,流量达到最大值
(2. Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm)
(2.1) (FF) 算法概括
- 用 (dfs) 寻找增广路
- 建立反悔边
- 重复上述过程
(2.2) (FF code)
/*FF Algorithm*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define arrayDebug(a, l, r) for(int i = l; i <= r; ++i) printf("%d%c", a[i], "
"[i == r])
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int DX[] = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 1, 1};
const int DY[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1};
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double EPS = 1e-6;
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
char c = getchar();
int ans = 0, f = 1;
while(!isdigit(c)) {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();}
while(isdigit(c)) {ans = ans * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar();}
return ans * f;
}
int n, m, s, t, cnt, head[N], vis[N];
struct edge
{
int fr, to, next, w;
}e[N];
void addedge(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[cnt].fr = a;//第一条边标为 1
e[cnt].to = b;
e[cnt].w = c;
e[cnt].next = head[a];
head[a] = cnt++;
}
int dfs(int u = s, int flow = inf)
{
if(u == t) return flow;
vis[u] = 1;
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next){
int v = e[i].to;
if(e[i].w == 0 || vis[v]) continue;
int res = dfs(v, min(flow, e[i].w));
if(res > 0) {
e[i].w -= res;
e[i ^ 1].w += res;
return res;
}
}
return 0;
}
int FF()
{
int res = dfs(), ans = 0;
while(res > 0) {
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
ans += res;
res = dfs();
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &n, &m, &s, &t);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
addedge(a, b, c);
addedge(b, a, 0);
}
printf("%d
", FF());
return 0;
}
(2.3) (FF) 时间复杂度及瓶颈
每次增广,至少增加 (1) 的流量
每次增广,最多流经 (m) 条边
所以理论复杂度为 (O(CM)),其中 (C) 为流量,(M) 为边数
如果流量特别大,那么这样的复杂度显然是不够优秀的
如下所示

(3. Edmond-Karp Algorithm)
(3.1) (EK) 算法概括
- (bfs) 找最近的增广路
- 建立反边
- 重复上述过程
(3.2) (EK code)
/*EK Algorithm*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define arrayDebug(a, l, r) for(int i = l; i <= r; ++i) printf("%d%c", a[i], "
"[i == r])
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int DX[] = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 1, 1};
const int DY[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1};
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double EPS = 1e-6;
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
char c = getchar();
int ans = 0, f = 1;
while(!isdigit(c)) {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();}
while(isdigit(c)) {ans = ans * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar();}
return ans * f;
}
int n, m, s, t, cnt, head[N], vis[N], pre[N];
struct edge
{
int fr, to, next, w;
}e[N];
void addedge(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[cnt].fr = a;//第一条边标为 1
e[cnt].to = b;
e[cnt].w = c;
e[cnt].next = head[a];
head[a] = cnt++;
}
int bfs(int u = s)
{
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre));
vis[u] = 1;
queue<int> q;
q.push(u);
while(!q.empty()) {
int temp = q.front(); q.pop();
if(temp == t) break;
for(int i = head[temp]; ~i; i = e[i].next) {
if(vis[e[i].to] || e[i].w == 0) continue;
vis[e[i].to] = 1;
pre[e[i].to] = i; //记录点 x 的前驱边的序号
q.push(e[i].to);
}
}
int flow = inf;
for(int i = pre[t]; ~i; i = pre[e[i].fr]) //找出流量
flow = min(flow, e[i].w);
if(flow == inf) return 0;
for(int i = pre[t]; ~i; i = pre[e[i].fr]) { //建立反边
e[i].w -= flow;
e[i ^ 1].w += flow;
}
return flow;
}
int EK()
{
int res = bfs(), ans = 0;
while(res > 0) {
ans += res;
res = bfs();
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &n, &m, &s, &t);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
addedge(a, b, c);
addedge(b, a, 0);
}
printf("%d
", EK());
return 0;
}
/*
4 5 4 3
4 2 30
4 3 20
2 3 20
2 1 30
1 3 40
*/
(3.3) (EK) 时间复杂度及瓶颈
(O(NM^2)),其中 (N) 为顶点数,(M) 为边数
当边数 (M) 特别大时,这样的复杂度是不够优秀的
(4. Dinic Algorithm)
(4.1) (Dinic) 算法概述
- 先用 (bfs) 对网络图分层,即预处理出每个点相对于源点的距离
- 然后用 (dfs) 多路增广,同时建立反边,直到当前图没有流量为止
- 重复上述过程
多路增广的含义是,不是找到一个流量就返回,而是要穷尽当前网络的所有流量才返回
(4.2) (Dinic) 的特点以及其他优化
(4.2.1) 多路增广
相较于传统 (dfs) 寻找增广路,多路增广实际上找出了一个增广路网
(4.2.2) 分层图
设立分层图的本质就是预处理每个点相对于源点的距离
这样流量在流动时避免“绕路”,而是直接流向更远的点


(4.2.3) 可行性剪枝
若当前点流出的剩余流量为零,那么无法继续向下传输流量
所以直接退出循环,回溯到上一层
(4.2.4) 当前弧优化
多路增广时,已经增广的路径可能会被再次访问
用 (cur) 数组记录点 (u) 已经被增广的出边,下次直接从未被增广的出边开始增广
for(int &i = cur[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next) {
...
}
注意到这里的引用取值
随着 (i) 增加,(cur[i]) 也会增加,于是起到了记录的作用
值得一提的是,当前弧优化的优化效果相当不错
(4.3) (Dinic code)
/*Dinic Algorithm*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define arrayDebug(a, l, r) for(int i = l; i <= r; ++i) printf("%d%c", a[i], "
"[i == r])
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int DX[] = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 1, 1};
const int DY[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1};
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double EPS = 1e-6;
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
char c = getchar();
int ans = 0, f = 1;
while(!isdigit(c)) {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();}
while(isdigit(c)) {ans = ans * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar();}
return ans * f;
}
int n, m, s, t, cnt, head[N], dep[N], cur[N];
struct edge
{
int fr, to, next, w;
}e[N];
void addedge(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[cnt].fr = a;//第一条边标为 0,对应反边为 1
e[cnt].to = b;
e[cnt].w = c;
e[cnt].next = head[a];
head[a] = cnt++;
}
void debug()
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
cout<<i<<": ";
for(int j = head[i]; ~j; j = e[j].next)
printf("(%d, %d, %d)", e[j].fr, e[j].to, e[j].w);
puts("");
cout<<dep[i]<<endl;
}
puts("");
}
bool bfs()
{
memset(dep, 0, sizeof(dep)); //dep 有标记,则可以访问到该点
queue<int> q; q.push(s);
dep[s] = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].to, cost = e[i].w;
if(cost && !dep[v]) dep[v] = dep[u] + 1, q.push(v);
}
}
return dep[t];
}
int dfs(int u = s, int flow = inf)
{
if(u == t) return flow;
int ans = 0;
for(int &i = cur[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].to, cost = e[i].w;
if(dep[v] == dep[u] + 1 && cost) {
int res = dfs(v, min(flow, cost));
if(res > 0) {
e[i].w -= res, e[i ^ 1].w += res; //建立反边
flow -= res; //可以流通的流量减少
ans += res; //答案的贡献增加
if(!flow) break; //没有可以流通的流量,直接退出循环
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int Dcnic()
{
int ans = 0;
while(bfs()) {
memcpy(cur, head, sizeof(head));
ans += dfs();
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
n = read(), m = read(), s = read(), t = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int a, b, c;
a = read(), b = read(), c = read();
addedge(a, b, c);
addedge(b, a, 0);
}
printf("%d
", Dcnic());
return 0;
}
/*
4 5 4 3
4 2 30
4 3 20
2 3 20
2 1 30
1 3 40
*/
(4.4) (Dinic) 时间复杂度
(O(N^2M)),其中 (N) 为顶点数,(M) 为边数