发现了大学时候写的计算器小程序,还有个图形界面,能够图形化展示表达式语法树,哈哈;)
只有200行Java代码,不但能够计算加减乘除,还能够匹配小括号~
代码点评:
从朴素的界面配色到简单易懂错误提示,无不体现了“用户体验”至上的设计理念;代码异常处理全面合理、滴水不漏,代码缩进优雅大方,变量命名直观易懂;再结合长度适中简单明了的注释,程序整体给人一种清新脱俗之感。背后不难看出作者对学习的热爱以及对设计的苛求,工匠精神可见一斑,真可谓是大学数据结构学以致用的典范!
关于数据结构的干货,可参考博主的《深入理解Java集合框架》系列文章,一定不让你失望。
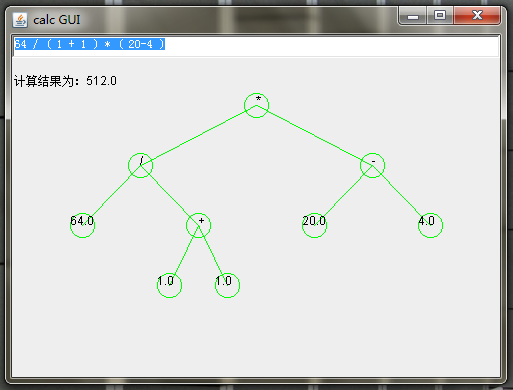
实现算法参考严蔚敏的《数据结构(C语言版)》第三章“栈和队列”,3.2.5节“表达式求值”。
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Point;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.util.Stack;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
/**
* 图形界面的计算器程序,只能计算加减乘除,
* 算式中可以有小括号。数字可以是小数
*/
public class CalcGUI extends JFrame{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private TreeNode resultTree;
private String textFieldString;
private boolean calcSuccess = true;
private char ops[][] = {
{'>', '>', '<', '<', '<', '>', '>'},
{'>', '>', '<', '<', '<', '>', '>'},
{'>', '>', '>', '>', '<', '>', '>'},
{'>', '>', '>', '>', '<', '>', '>'},
{'<', '<', '<', '<', '<', '=', 'E'},
{'E', 'E', 'E', 'E', 'E', 'E', 'E'},
{'<', '<', '<', '<', '<', 'E', '='},
};
Stack<TreeNode> nodesStack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
Stack<Character> opsStack = new Stack<Character>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
CalcGUI gui = new CalcGUI();
gui.userGUI();
}
public void userGUI(){
this.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
TextField tf = new TextField("请输入表达式,按Enter开始计算~", 40);
tf.selectAll();
tf.getText();
tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter(){
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e){
if(e.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.VK_ENTER){
textFieldString = ((TextField)e.getComponent()).getText();
calcSuccess = true;
resultTree = null;
try{
resultTree = calc(textFieldString + "#");
}catch(Exception e1){
calcSuccess = false;
}
CalcGUI.this.repaint();
}
}
});
this.add(tf, BorderLayout.NORTH);
this.setSize(500, 500);
this.setTitle("calc GUI");
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setResizable(true);
this.setVisible(true);
}
private int levelHeight = 60;
private int diameter = 25;
public void paint(Graphics g){
super.paint(g);
if(calcSuccess){
if(resultTree != null){
g.drawString("计算结果为:" + resultTree.value, 10, 80);
int rootBeginX = this.getWidth() / 2;
int rootBeginY = 100;
Point p = new Point(rootBeginX, rootBeginY);
drawTree(g, resultTree, p, this.getWidth() / 2 - 20, p);
}
}else{
g.setColor(Color.RED);
g.drawString("表达式语法有误!", 10, 80);
}
}
private void drawCircle(Graphics g, Point p, int r){
g.drawOval(p.x - r, p.y - r, r * 2, r * 2);
}
private void drawTree(Graphics g, TreeNode node, Point pme, int width, Point pfather){
if(node == null) return;
// System.out.println("in drawTree, node.value=" + node.value + ",node.op=" + node.op);
g.setColor(Color.GREEN);
this.drawCircle(g, pme, diameter / 2);
g.drawLine(pme.x, pme.y, pfather.x, pfather.y);
if(node.op != 'E'){
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g.drawString(String.valueOf(node.op), pme.x, pme.y);
}else{
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g.drawString(String.valueOf(node.value), pme.x - diameter / 2, pme.y);
}
drawTree(g, node.lft, new Point(pme.x - width / 2, pme.y + levelHeight), width / 2, pme);
drawTree(g, node.rt, new Point(pme.x + width / 2, pme.y + levelHeight), width / 2, pme);
}
public TreeNode calc(String inStr) throws Exception{
opsStack.push('#');
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
int i = 0;
while(i < inStr.length()){
if(Character.isDigit(inStr.charAt(i)) || inStr.charAt(i) == '.'){// number
buf.delete(0, buf.length());
while(i < inStr.length() &&
(Character.isDigit(inStr.charAt(i)) || inStr.charAt(i) == '.'))
buf.append(inStr.charAt(i++));
Double number = Double.parseDouble(buf.toString());
nodesStack.push(new TreeNode(number));
}else if(inStr.charAt(i) == ' '){
i++;
continue;
}else{// operation
char op = inStr.charAt(i);
int subNew = getSub(op);
boolean goOn = true;
while(goOn){
if(opsStack.isEmpty())
throw new Exception("运算符太少!");
char opFormer = opsStack.peek();
int subFormer = getSub(opFormer);
switch(ops[subFormer][subNew]){
case '=':
goOn = false;
opsStack.pop();
break;
case '<':
goOn = false;
opsStack.push(op);
break;
case '>':
goOn = true;
TreeNode n1 = nodesStack.pop();
TreeNode n0 = nodesStack.pop();
double rs = doOperate(n0.value, n1.value, opFormer);
nodesStack.push(new TreeNode(rs, opFormer, n0, n1));
opsStack.pop();
break;
default:
throw new Exception("没有匹配的操作符:" + op);
}
}
i++;
}
}
return nodesStack.pop();
}
private double doOperate(double n0, double n1, char op) throws Exception{
switch(op){
case '+': return n0 + n1;
case '-': return n0 - n1;
case '*': return n0 * n1;
case '/': return n0 / n1;
default: throw new Exception("非法操作符:" + op);
}
}
private int getSub(char c){
switch(c){
case '+': return 0;
case '-': return 1;
case '*': return 2;
case '/': return 3;
case '(': return 4;
case ')': return 5;
case '#': return 6;
default : return -1;
}
}
}
class TreeNode{
public double value;
public char op = 'E';
public TreeNode lft;
public TreeNode rt;
public TreeNode(double value){
this.value = value;
}
public TreeNode(double value, char op, TreeNode lft, TreeNode rt){
this.value = value;
this.op = op;
this.lft = lft;
this.rt = rt;
}
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
public String toString(){
out(this);
return buf.toString();
}
private void out(TreeNode node){
if(node == null) return;
out(node.lft);
if(node.op != 'E')
buf.append(node.op);
else
buf.append(node.value);
out(node.rt);
}
}