1 class C1 2 { 3 private int num; 4 public C1(int num) 5 { 6 this.num=num; 7 } 8 } 9 public class Text_001 10 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) 12 { 13 C1 t1=new C1(100); 14 C1 t2=new C1(100); 15 System.out.println(t1==t2); 16 C1 t3=t1; 17 System.out.println(t1==t3); 18 t2=t1; 19 System.out.println(t1==t2); 20 } 21 }
结果:
false
true
true
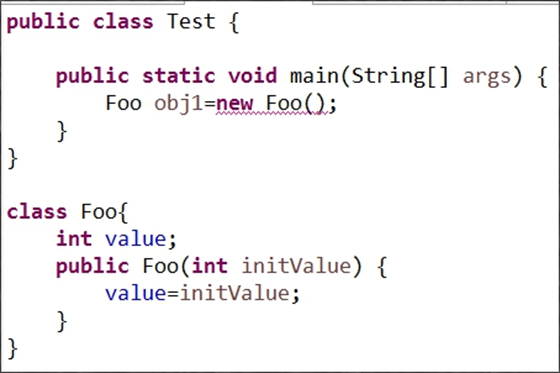
对象在定义的时候调用了没有参数的构造函数,但是该类并不含有对应的构造函数
public class InitializeBlockDemo { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { InitializeBlockClass obj=new InitializeBlockClass(); System.out.println(obj.field); obj=new InitializeBlockClass(300); System.out.println(obj.field); } } class InitializeBlockClass{ //下面这句在初始化块之前与之后,会影响到field字段的初始值 //public int field=100; { field=200; } public int field=100; public InitializeBlockClass(int value){ this.field=value; } public InitializeBlockClass(){ } }
结果:
100
300
在同时有初始化块和构造方法的情况下,构造方法优先。
1 public class Text_002 2 { 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) 5 { 6 int i=100; 7 C1 t1=new C1(); 8 t1.setNum(i);//静态方法访问没有附加static的变量 9 } 10 11 } 12 class C1 13 { 14 private int num; 15 public void setNum(int num) 16 { 17 this.num=num; 18 } 19 }
1 public class HowManyClassYouHaveCreated 2 { 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) 5 { 6 int f=1; 7 Hello h1=new Hello(); 8 Hello h2=new Hello(); 9 Hello h3=new Hello(); 10 Hello h4=new Hello(); 11 Hello h5=new Hello(); 12 Hello h6=new Hello(); 13 Hello h7=new Hello(); 14 System.out.println("HowManyClassYouHaveCreated?"); 15 System.out.println(h7.getNum()); 16 17 } 18 19 } 20 class Hello 21 { 22 static private int num=0; 23 public Hello() 24 { 25 System.out.println("Hello"); 26 num++; 27 } 28 public int getNum() 29 { 30 return num; 31 } 32 }