In some country there are exactly n cities and m bidirectional roads connecting the cities. Cities are numbered with integers from 1 to n. If cities a and b are connected by a road, then in an hour you can go along this road either from city a to city b, or from city b to city a. The road network is such that from any city you can get to any other one by moving along the roads.
You want to destroy the largest possible number of roads in the country so that the remaining roads would allow you to get from city s1 to city t1 in at most l1 hours and get from city s2 to city t2 in at most l2 hours.
Determine what maximum number of roads you need to destroy in order to meet the condition of your plan. If it is impossible to reach the desired result, print -1.
The first line contains two integers n, m (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000, 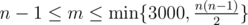 ) — the number of cities and roads in the country, respectively.
) — the number of cities and roads in the country, respectively.
Next m lines contain the descriptions of the roads as pairs of integers ai, bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n, ai ≠ bi). It is guaranteed that the roads that are given in the description can transport you from any city to any other one. It is guaranteed that each pair of cities has at most one road between them.
The last two lines contains three integers each, s1, t1, l1 and s2, t2, l2, respectively (1 ≤ si, ti ≤ n, 0 ≤ li ≤ n).
Print a single number — the answer to the problem. If the it is impossible to meet the conditions, print -1.
5 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
1 3 2
3 5 2
0
5 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
1 3 2
2 4 2
1
5 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
1 3 2
3 5 1
-1
转化题意:我们要留下最少的道路使得s1->t1距离<=l1, s2->t2距离<=l2.
我们考虑最后留下的路的形态, 无非有两种状态:
1.只有从s1->t1, s2->t2的道路。
2.存在两个(或一个)点u, v, 最后留下的边为
(s1, u), (s2, u), (u, v), (v, t1), (v, t2)或者
(s1, u), (t2, v), (u, v), (v, t1), (v, s2)的五元组。
我们根据以上的情况, 先bfs求出每两个点之间的距离, 然后按状态2的两种情况分别找最优解。
然后最后再考虑第一种情况。
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <queue> #include <cstring> using namespace std; #define int long long inline int read(){ int res = 0;char ch=getchar();bool fl = 0; while(!isdigit(ch)){if(ch=='-')fl=1;ch=getchar();} while(isdigit(ch)){res=(res<<3)+(res<<1)+(ch^48);ch=getchar();} return fl?-res:res; } const int N = 3005, M = 6005; int n, m; struct edge{ int nxt, to; }ed[M]; int head[N], cnt; inline void add(int x, int y){ ed[++cnt] = (edge){head[x], y}; head[x] = cnt; } int s1, s2, t1, t2, l1, l2; int dis[N][N]; bool ex[N]; int ans = 1e9; inline void bfs(int cur) { queue <int> q; memset(dis[cur], 0x3f, sizeof dis[cur]); memset(ex, 0, sizeof ex); dis[cur][cur] = 0; q.push(cur);ex[cur] = 1; while(!q.empty()){ int x = q.front(); q.pop(); ex[x] = 0; for (register int i = head[x] ; i ; i = ed[i].nxt){ int to = ed[i].to; if (dis[cur][to] > dis[cur][x] + 1) { dis[cur][to] = dis[cur][x] + 1; if (!ex[to]){ ex[to] = 1, q.push(to); } } } } } signed main() { n = read(), m = read(); for (register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++){ int x = read(), y = read(); add(x, y), add(y, x); } s1 = read(), t1 = read(), l1 = read(); s2 = read(), t2 = read(), l2 = read(); for (register int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) bfs(i); for (register int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){ for (register int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++){ int res1 = dis[s1][i] + dis[i][j] + dis[j][t1]; int res2 = dis[s2][i] + dis[i][j] + dis[j][t2]; if (res1 <= l1 and res2 <= l2) ans = min(ans, dis[s1][i] + dis[i][j] + dis[j][t1] + dis[s2][i] + dis[j][t2]); res1 = dis[s1][i] + dis[i][j] + dis[j][t1]; res2 = dis[s2][j] + dis[i][j] + dis[i][t2]; if (res1 <= l1 and res2 <= l2) ans = min(ans, dis[s1][i] + dis[i][j] + dis[j][t1] + dis[s2][j] + dis[i][t2]); } } if (dis[s1][t1] <= l1 and dis[s2][t2] <= l2) ans = min(ans, dis[s1][t1] + dis[s2][t2]); if (ans == 1e9) return puts("-1"), 0; cout << m - ans; return 0; }