一、选择排序的弊端
需要n^2。核心的耗时在每次寻找最大值。
public static void selectionSort(int[] list) {
for (int index = 0; index < list.length - 1; index++) {
int minIndex = findMinIndex(index, list);//寻找最小的index
int temp = list[index];
list[index] = list[minIndex];//把最小的值赋值到当前节点,完成一次排序
list[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
private static int findMinIndex(int startIndex, int[] list) {
int minData = list[startIndex];
int minIndex = startIndex;
for (int i = startIndex + 1; i < list.length; i++) {
if (minData > list[i]) {
minData = list[i];
minIndex = i;
}
}
return minIndex;
}
主要开销就是findMinIndex,这个方法的复杂度是O(n)。如果要进一步优化选择排序,就需要找到一个复杂度小于O(n)的findMinIndex的方法。
二、引入堆
采用堆数据结构,每次返回堆顶元素,就是最大值(从大到小排序。如果从小到大,使用小顶堆即可)。查找过程为log(n)。这样整个选择排序的整体算法时间复杂度从n^2降为nlog(n)。
但是这种算法最大的问题在于
- 额外引入了一个数组,空间复杂度为log(n)。
- 同时涉及到大量的数据的拷贝。
public static void advanceSelectionSort(Integer[] list) {
HeapStruct heapStruct = getHeapStruct(list);//创建堆
int[] tempList = new int[list.length];//额外的空间。
for (int index = 0; index < list.length - 1; index++) {
Integer maxValue = HeapUtil.deleteMax(heapStruct);//寻找最大的index
tempList[index] = maxValue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
list[i] = tempList[i];//大量的数据复制
}
}
三、堆排序
堆排序的引入:之前有文章介绍过如何把一个平衡二叉树调整为一个大顶堆,给定堆顶元素的index,从上往下找,一次循环结束后,index对应的元素(堆顶)便是最大值。
堆排序的核心就是利用大顶堆的调整方法,主要改进点便是,一次调整完成后把堆顶元素和数组的最后一个元素互换,同时把堆的规模缩小1。依次类推,一直到堆的规模为0即可。
3.1 演示
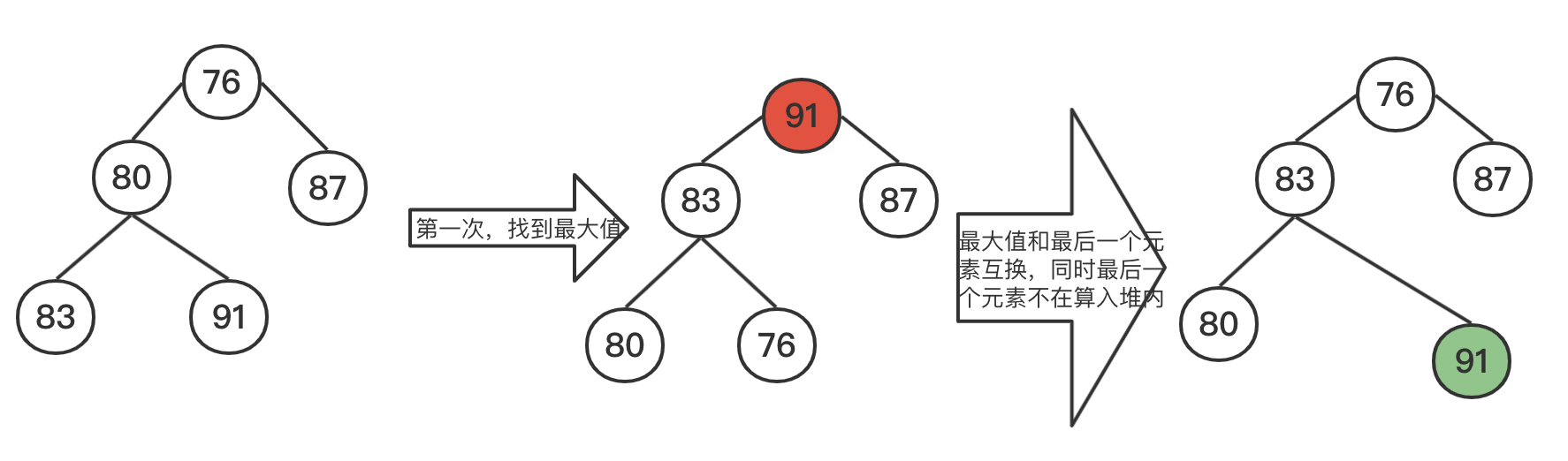
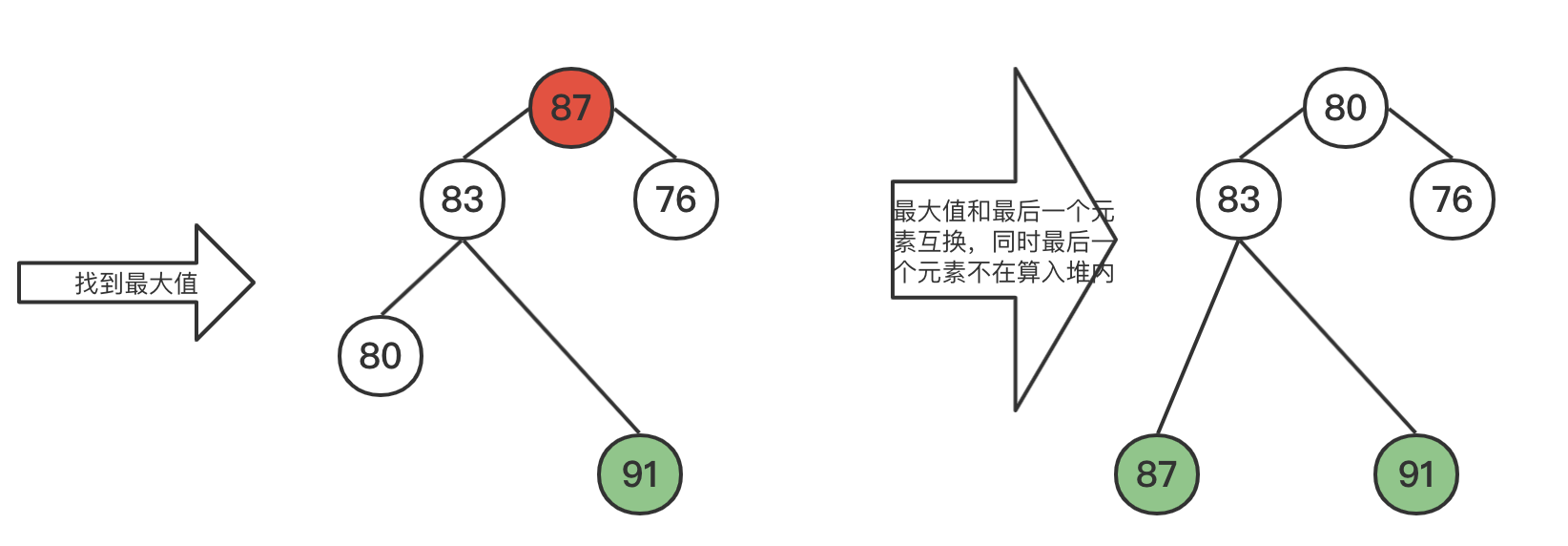
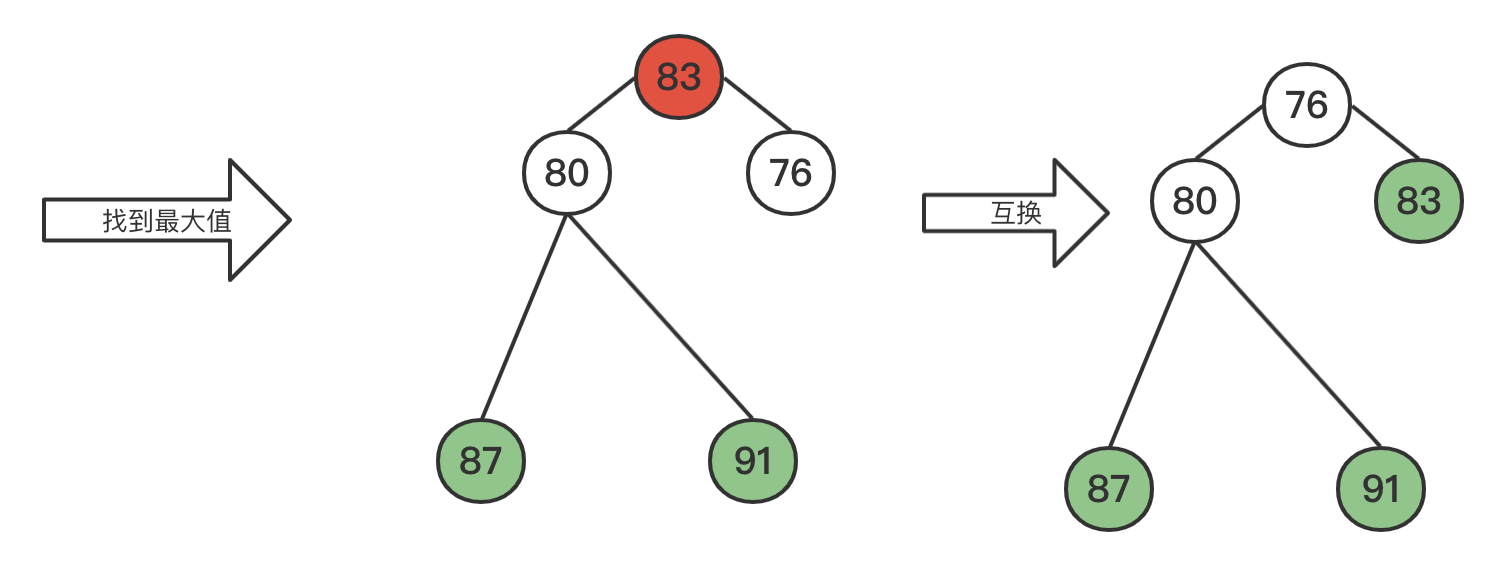


没有额外增加空间,同时利用了堆logn的时间复杂度。
3.2 代码
public static void heapSort(Integer[] list) {
HeapStruct heapStruct = getHeapStruct(list);//创建堆--此时,堆顶元素为最大值
for (int index = list.length - 1; index > 0; index++) {
Integer temp = list[0];
list[0] = list[index];
list[index] = temp;//把堆顶元素和最后一个元素互换
percDown(heapStruct, 0, index);//index每次减一,堆的规模慢慢变小,每次percDown结束,堆顶元素都是最大值
}
}
public static void percDown(HeapStruct heapStruct, int rootIndex, int heapSize) {
Integer[] elements = heapStruct.getElements();
Integer rootValue = elements[rootIndex];
int parentIndex = rootIndex;
while (parentIndex * 2 + 1 < heapSize) {
int childIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
if (childIndex < heapSize - 1 && elements[childIndex].compareTo(elements[childIndex + 1]) < 0) {
childIndex = childIndex + 1;
}
if (rootValue.compareTo(elements[childIndex]) > 0) {
break;
} else {
elements[parentIndex] = elements[childIndex];
parentIndex = childIndex;
}
}
elements[parentIndex] = rootValue;
}