昨晚打得小号,虽然很菜,可是还是涨了些rating
Arpa is researching the Mexican wave.
There are n spectators in the stadium, labeled from 1 to n. They start the Mexican wave at time 0.
- At time 1, the first spectator stands.
- At time 2, the second spectator stands.
- ...
- At time k, the k-th spectator stands.
- At time k + 1, the (k + 1)-th spectator stands and the first spectator sits.
- At time k + 2, the (k + 2)-th spectator stands and the second spectator sits.
- ...
- At time n, the n-th spectator stands and the (n - k)-th spectator sits.
- At time n + 1, the (n + 1 - k)-th spectator sits.
- ...
- At time n + k, the n-th spectator sits.
Arpa wants to know how many spectators are standing at time t.
The first line contains three integers n, k, t (1 ≤ n ≤ 109, 1 ≤ k ≤ n, 1 ≤ t < n + k).
Print single integer: how many spectators are standing at time t.
10 5 3
3
10 5 7
5
10 5 12
3
In the following a sitting spectator is represented as -, a standing spectator is represented as ^.
- At t = 0 ----------
 number of standing spectators = 0.
number of standing spectators = 0. - At t = 1 ^---------
 number of standing spectators = 1.
number of standing spectators = 1. - At t = 2 ^^--------
 number of standing spectators = 2.
number of standing spectators = 2. - At t = 3 ^^^-------
 number of standing spectators = 3.
number of standing spectators = 3. - At t = 4 ^^^^------
 number of standing spectators = 4.
number of standing spectators = 4. - At t = 5 ^^^^^-----
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 6 -^^^^^----
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 7 --^^^^^---
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 8 ---^^^^^--
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 9 ----^^^^^-
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 10 -----^^^^^
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 11 ------^^^^
 number of standing spectators = 4.
number of standing spectators = 4. - At t = 12 -------^^^
 number of standing spectators = 3.
number of standing spectators = 3. - At t = 13 --------^^
 number of standing spectators = 2.
number of standing spectators = 2. - At t = 14 ---------^
 number of standing spectators = 1.
number of standing spectators = 1. - At t = 15 ----------
 number of standing spectators = 0.
number of standing spectators = 0.
这个题我还看了两三分钟,发现就是个分段函数,结论很明显
不过我竟脑残打错了字母,wa了一发
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { long long n,k,t; cin>>n>>k>>t; if(t<=k) cout<<t<<endl; else if(t>=n) cout<<n+k-t<<endl; else cout<<k<<endl; return 0; }
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { long long ax,ay,bx,by,cx,cy; cin>>ax>>ay>>bx>>by>>cx>>cy; long long a=(ax-bx)*(ax-bx)+(ay-by)*(ay-by); long long b=(cx-bx)*(cx-bx)+(cy-by)*(cy-by); if(a==b&&(cx+ax!=2*bx||cy+ay!=2*by)) puts("Yes"); else puts("No"); return 0; }
我现在发现是我斜率公式交换的时候写错了啊,改了字母就过了。我好菜啊
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { long long ax,ay,bx,by,cx,cy; cin>>ax>>ay>>bx>>by>>cx>>cy; if((ax-bx)*(ax-bx)+(ay-by)*(ay-by)==(cx-bx)*(cx-bx)+(cy-by)*(cy-by)&&(cy-ay)*(bx-ax)!=(by-ay)*(cx-ax)) puts("Yes"); else puts("No"); return 0; }
You are given set of n points in 5-dimensional space. The points are labeled from 1 to n. No two points coincide.
We will call point a bad if there are different points b and c, not equal to a, from the given set such that angle between vectors 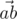 and
and 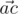 is acute (i.e. strictly less than
is acute (i.e. strictly less than 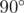 ). Otherwise, the point is called good.
). Otherwise, the point is called good.
The angle between vectors 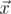 and
and 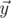 in 5-dimensional space is defined as
in 5-dimensional space is defined as 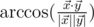 , where
, where 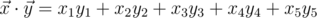 is the scalar product and
is the scalar product and 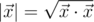 is length of
is length of 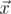 .
.
Given the list of points, print the indices of the good points in ascending order.
The first line of input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 103) — the number of points.
The next n lines of input contain five integers ai, bi, ci, di, ei (|ai|, |bi|, |ci|, |di|, |ei| ≤ 103) — the coordinates of the i-th point. All points are distinct.
First, print a single integer k — the number of good points.
Then, print k integers, each on their own line — the indices of the good points in ascending order.
6
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1
1
1
3
0 0 1 2 0
0 0 9 2 0
0 0 5 9 0
0
In the first sample, the first point forms exactly a 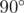 angle with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
angle with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
In the second sample, along the cd plane, we can see the points look as follows:
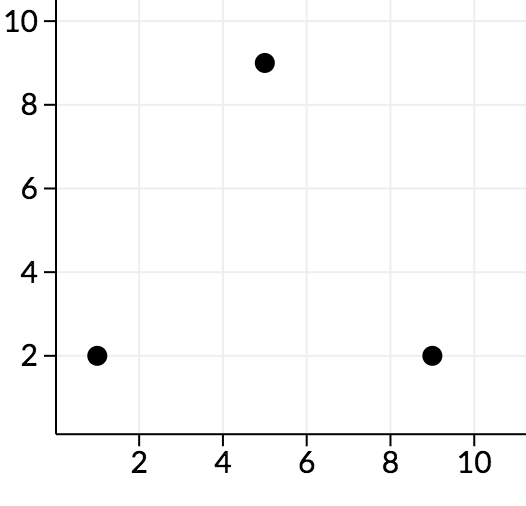
We can see that all angles here are acute, so no points are good.
给了五维坐标系,拿出了累似二维的东西,但是1e9可以跑下来么,这时候qls给了一个243的结论牛逼啊
这个题自己写错了break条件导致写了太久了,虽然中途还看了B,但是这个题分数已经掉光了
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N=1e3+5; double PI=acos(0.0); struct Point { int a,b,c,d,e; } f[250]; int main() { int n; scanf("%d",&n); if(n>500) printf("0 "); else { for(int i=0; i<n; i++) scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&f[i].a,&f[i].b,&f[i].c,&f[i].d,&f[i].e); vector<int>V; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { int ff=0; for(int j=0; j<n; j++) { Point x; if(j==i)continue; x.a=f[j].a-f[i].a; x.b=f[j].b-f[i].b; x.c=f[j].c-f[i].c; x.d=f[j].d-f[i].d; x.e=f[j].e-f[i].e; for(int k=0; k<n; k++) { Point y; if(j==i||k==j)continue; y.a=f[k].a-f[i].a; y.b=f[k].b-f[i].b; y.c=f[k].c-f[i].c; y.d=f[k].d-f[i].d; y.e=f[k].e-f[i].e; int z=y.a*x.a+y.b*x.b+y.c*x.c +y.d*x.d+y.e*x.e; if(z>0) { ff=1; break; } } if(ff)break; } if(!ff) V.push_back(i+1); } printf("%d ",(int)V.size()); for(int i=0; i<(int)V.size(); i++) printf("%d ",V[i]); } return 0; }
 .
.