转自:https://blog.csdn.net/hanjing_csdn/article/details/79922660
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/44435521
1.介绍
当我们需要在程序中使用字符串和数字数据互相转换的时候,可以使用stringstream类,
- 通过运算符 ”<<“ 将数据传递给 stringstream 对象;
- 通过调用stringstream 类的函数str() 将对象所包含的内容赋给一个string对象;
- 可以方便的以流运算符<<将数值以各种数据(字串、数值)写入stringstream对象,且不用担心写越界等问题;
2.使用
#include <iostream> #include <sstream> int main() { // default constructor (input/output stream) std::stringstream buf1; buf1 << 7;//将int转换为stringstream对象 int n = 0; buf1 >> n; std::cout << "buf1 = " << buf1.str() << " n = " << n << '\n'; // input stream std::istringstream inbuf("-10"); inbuf >> n;//可以将stringstream对象转换为int std::cout << "n = " << n << '\n'; // output stream in append mode (C++11) std::ostringstream buf2("test", std::ios_base::ate);//如果不设置第二个参数的话,就会变为1est buf2 << '1'; std::cout << buf2.str() << '\n'; }
输出:
buf1 = 7 n = 7 n = -10 test1
转换过程:
- 数字 -> stringstream对象 -> string
- string -> stringstream对象 -> 数字
#include <sstream> #include <iostream> int main() { int n; std::istringstream in; // could also use in("1 2") in.str("1 2"); in >> n; std::cout << "after reading the first int from \"1 2\", the int is " << n << ", str() = \"" << in.str() << "\"\n"; std::ostringstream out("1 2"); out << 3; std::cout << "after writing the int '3' to output stream \"1 2\"" << ", str() = \"" << out.str() << "\"\n"; out << 4; std::cout << "after writing the int '4' to output stream \"1 2\"" << ", str() = \"" << out.str() << "\"\n"; out << 5; std::cout << "after writing the int '5' to output stream \"1 2\"" << ", str() = \"" << out.str() << "\"\n"; std::ostringstream ate("1 2", std::ios_base::ate); ate << 3; std::cout << "after writing the int '3' to append stream \"1 2\"" << ", str() = \"" << ate.str() << "\"\n"; return 0; }
输出为:
after reading the first int from "1 2", the int is 1, str() = "1 2" after writing the int '3' to output stream "1 2", str() = "3 2"//插入时如果不设置,默认从头开始插入 after writing the int '4' to output stream "1 2", str() = "342" after writing the int '5' to output stream "1 2", str() = "345" after writing the int '3' to append stream "1 2", str() = "1 23"
>>操作也默认从头开始输出,<<默认从头开始输入。(感觉好反直觉。。)
3.效率
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/mijichui2153/article/details/118154341
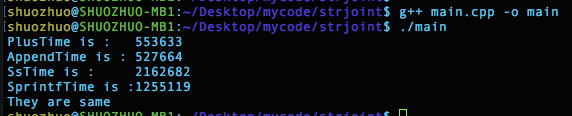
此链接的实验中,+=和append操作,效率都高,但是stringstream由于是类,频繁地创建和销毁代价较高,涉及到内存分配、对象构造和销毁。如果循环中需要频繁使用stringstream对象的话,可以共用一个,在使用中clear和清空:
void* test_stringstream(void * arg) { stringstream oss; for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) { oss.clear();这仅仅置流标记 oss.str("");/这是才是真正清空操作 oss << i; } }
stringstream不会主动释放内存,stream.str("")清除缓冲。