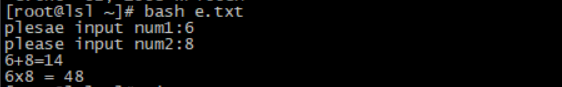if语句格式:
语句格式:
1、单分支语句:
if 条件;then
执行语句
fi
只有条件为真时,才会去执行后面的执行语句;
2、双分支语句:
if 条件;then
执行语句1
else
执行语句2
fi
3、多分支语句:
if 条件1;then
执行语句1
elif 条件2;then
执行语句2
elif 条件3;then
执行语句3
...
else
执行语句n
fi
实验部分:
1、判断/etc/inittab文件是否大于100行,如果大于,则显示”/etc/inittab is a big file.”否者显示”/etc/inittab is a small file.”
[root@lsl ~]vi 2.txt #!/bin/bash a=` wc -l /etc/inittab|cut -d ' ' -f1` if [ $a -gt 100 ];then echo '/etc/inittab is a big file.' else echo '/etc/inittab is small file.' fi

2、给定一个用户,来判断这个用户是什么用户,如果是管理员用户,则显示“该用户为管理员”,否则显示“该用户为普通用户”
[root@lsl ~]vi 6.txt #!/bin.bash #
read -p "please input a user:" user if id -u $1 &> /dev/null;then a=$(id -u $1) if [ $a -eq 0 ];then echo "$1 is a supper user" elif [ $a -ge 1 -a $a -lt 500 ];then echo "$1 is a system user" else echo "$1 is a ordinary user" fi else echo "$1 user not exist" fi

3、判断某个文件是否存在
[root@lsl ~]# vi 7.txt #!/bin/bash #
read -p "please input a file:" file if [ -e $1];then if [ -f $1];then echo "file exists" else echo "$1 is exists but not a file" fi else echo "$1 does not exists" f

4、判断当前系统上是否有用户的默认shell程序是否为bash程序,如果有,就显示有多个这类用户,否则就显示没有这类用户
[root@lsl~]vi 5.txt #!/bin/bash # grep "<nologin>" /etc/passwd &> /dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "cunzai user" echo "nologin user such as:" grep "<nologin>" /etc/passwd | cut -d":" -f1 echo "user total" grep "<nologin>" /etc/passwd | wc -l else echo "shell user not exist" fi


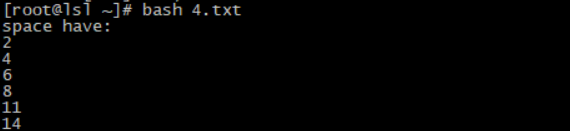
5、写出一个脚本程序,给定一个文件,比如:/etc/inittab a、判断这个文件中是否有空白行? b、如果有,则显示其空白行的行号,否则显示没有空白行
[root@lsl~]vi 4.txt #!/bin/bash # if [ -f $1 ];then grep "^[[:space:]]*$" /tmp/inittab.bak &> /dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "space have:" grep -n "^[[:space:]]*$" /tmp/inittab.bak | cut -d":" -f1 exit 0 else echo "no such:" exit 1 fi else echo "file not exits,or not a file!" exit 2 fi
6、写一个脚本程序,判断其UID与GID是否一样,如果一样,就显示该用户为“good boy”
[root@lsl ~]# vi 8.txt #!/bin/bash #
read -p "please input a user:" user ERNAME=user1 USERID=`id -u $USERNAME` GROUPID=`id -g $USERNAME ` if [ $USERID -eq $GROUPID ];then echo "good boy" else echo "bad boy" fi

7、写一个脚本程序,给定一个用户,获取其密码警告期限;然后判断用户最近一次修改密码的时间距离今天是否已经小于警告期限
[root@lsl ~]# vi 9.txt #!/bin/bash #
read -p "please input a user:" user W=`grep "student" /etc/shadow | cut -d: -f6` S=`date +%s` T=`expr $S/86400` L=`grep "^student" /etc/shadow | cut -d: -f5` N=`grep "^student" /etc/shadow | cut -d: -f3` SY=$[$L-$[$T-$N]] if [ $SY -lt $W ]; then echo 'Warning' else echo 'OK' fi
8、判断命令历史中历史命令的总条目是否大于1000,如果大于,则显示“some command will gone”,否则显示OK
[root@lsl ~]# vi b.txt #!/bin/bash # num=`history | wc -l` if [ $num -gt 1000 ];then echo "some command will gone" else echo "OK" fi

9、给定一个文件,如果是普通文件,就显示出来,如果是目录文件,也显示出来,否则就显示“无法识别”
[root@lsl ~]# vi c.txt #!/bin/bash # read -p "please input a file:" file if [ -f $file ];then echo "Ordinary file" elif [ -d $file ];then echo "Directory file" else echo "can not Distinguish" fi

10、写一个脚本,能接受一个参数(文件路径),判断这个参数如果是一个存在的文件就显示“ok”,否则显示“No such file"
[root@lsl ~]# vi d.txt #!/bin/bash # read -p "please input a pash:" route if [ -f $route ];then echo "ok" else echo "No such file" fi

11、写一个脚本,给脚本传递两个参数,显示两者之和和两者之积
[root@lsl ~]# vi e.txt #!/bin/bash # read -p "plesae input num1:" num1 read -p "please input num2:" num2 sum=$[$num1+$num2] product=$[$num1*$num2] echo "$num1+$num2=$sum" echo "$num1"x"$num2=$product"