ACM计算几何总结
1 几何基础
#include <cstdio> #include <cmath> using namespace std; const double pi = acos(-1.0); const double inf = 1e100; const double eps = 1e-6; int sgn(double d){ if(fabs(d) < eps) return 0; if(d > 0) return 1; return -1; } int dcmp(double x, double y){ if(fabs(x - y) < eps) return 0; if(x > y) return 1; return -1; } int main() { double x = 1.49999; int fx = floor(x);//向下取整函数 int cx = ceil(x);//向上取整函数 int rx = round(x);//四舍五入函数 printf("%f %d %d %d ", x, fx, cx, rx); //输出结果 1.499990 1 2 1 return 0 ; }
3 点与向量
2.1 手动实现
点积: Dot
a·b的几何意义为a在b上的投影长度乘以b的模长
a·b=|a||b|cosθ,其中θ为a,b之间的夹角
坐标表示
a=(x1,y1) b=(x2,y2)
a·b=x1*x2+y1*y2;
点积的应用: Angle
(1)判断两个向量是否垂直 a⊥b <=> a·b=0
(2)求两个向量的夹角,点积<0为钝角,点积>0为锐角
求模长:Length
法向量:与单位向量垂直的向量称为单位法向量Normal
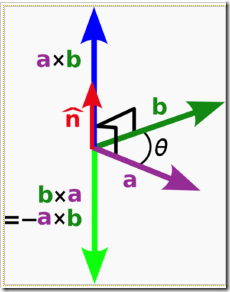
二维叉积Cross
两个向量a和b的叉积写作a×b(有时也被写成a∧b,避免和字母x混淆)
两个向量的叉积是一个标量,a×b的几何意义为他们所形成的平行四边形的有向面积
坐标表示a=(x1,y1) b=(x2,y2)
a×b=x1y2-x2y1
直观理解,假如b在a的左边,则有向面积为正,假如在右边则为负。假如b,a共线,则叉积为0,。
所以叉积可以用来判断平行。
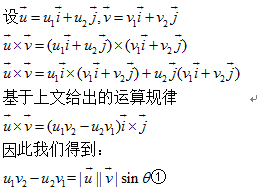
向量的旋转Rotate
a=(x,y)可以看成是x*(1,0)+y1*(0,1)
分别旋转两个单位向量,则变成x*(cosθ,sinθ)+y1*(-sinθ,cosθ)
struct Point{ double x, y; Point(double x = 0, double y = 0):x(x),y(y){} }; typedef Point Vector; Vector operator + (Vector A, Vector B){ return Vector(A.x+B.x, A.y+B.y); } Vector operator - (Point A, Point B){ return Vector(A.x-B.x, A.y-B.y); } Vector operator * (Vector A, double p){ return Vector(A.x*p, A.y*p); } Vector operator / (Vector A, double p){ return Vector(A.x/p, A.y/p); } bool operator < (const Point& a, const Point& b){ if(a.x == b.x) return a.y < b.y; return a.x < b.x; } const double eps = 1e-6; int sgn(double x){ if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0; if(x < 0) return -1; return 1; } bool operator == (const Point& a, const Point& b){ if(sgn(a.x-b.x) == 0 && sgn(a.y-b.y) == 0) return true; return false; } double Dot(Vector A, Vector B){ return A.x*B.x + A.y*B.y; } double Length(Vector A){ return sqrt(Dot(A, A)); } double Angle(Vector A, Vector B){ return acos(Dot(A, B)/Length(A)/Length(B)); } double Cross(Vector A, Vector B){ return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x; } double Area2(Point A, Point B, Point C){ return Cross(B-A, C-A); } Vector Rotate(Vector A, double rad){//rad为弧度 且为逆时针旋转的角 return Vector(A.x*cos(rad)-A.y*sin(rad), A.x*sin(rad)+A.y*cos(rad)); } Vector Normal(Vector A){//向量A左转90°的单位法向量 double L = Length(A); return Vector(-A.y/L, A.x/L); } bool ToLeftTest(Point a, Point b, Point c){ return Cross(b - a, c - b) > 0; }
2.2 复数黑科技
#include <complex> using namespace std; typedef complex<double> Point; typedef Point Vector;//复数定义向量后,自动拥有构造函数、加减法和数量积 const double eps = 1e-9; int sgn(double x){ if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0; if(x < 0) return -1; return 1; } double Length(Vector A){ return abs(A); } double Dot(Vector A, Vector B){//conj(a+bi)返回共轭复数a-bi return real(conj(A)*B); } double Cross(Vector A, Vector B){ return imag(conj(A)*B); } Vector Rotate(Vector A, double rad){ return A*exp(Point(0, rad));//exp(p)返回以e为底复数的指数 }
3 点与线
3.1 直线定义
struct Line{//直线定义 Point v, p; Line(Point v, Point p):v(v), p(p) {} Point point(double t){//返回点P = v + (p - v)*t return v + (p - v)*t; } };
3.2 求两直线交点
//调用前需保证 Cross(v, w) != 0 Point GetLineIntersection(Point P, Vector v, Point Q, Vector w){ Vector u = P-Q; double t = Cross(w, u)/Cross(v, w); return P+v*t; }
3.3 求点到直线距离
利用叉积求面积,然后除以平行四边形的底边长,得到平行四边形的高即点到直线的距离
//点P到直线AB距离 double DistanceToLine(Point P, Point A, Point B){ Vector v1 = B-A, v2 = P-A; return fabs(Cross(v1, v2)/Length(v1)); }//不去绝对值,得到的是有向距离
3.4 求点到线段距离
比点到直线的距离稍微复杂。因为是线段,所以如果平行四边形的高在区域之外的话就不合理,这时候需要计算点到距离较近的端点的距离。
矢量算法过程清晰,如果具有一定的空间几何基础,则是解决此类问题时应优先考虑的方法。当需要计算的数据量很大时,这种方式优势明显。
由于矢量具有方向性,故一些方向的判断直接根据其正负号就可以得知,使得其中的一些问题得以很简单的解决。用此方法考虑,
我们只需要找到向量 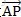
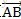
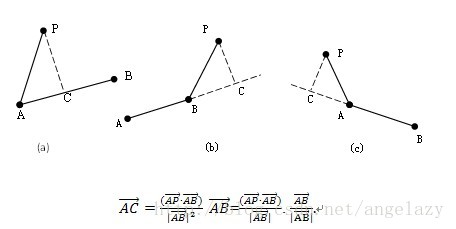
上面的 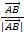
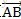
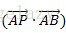
且 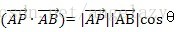
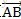
那么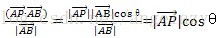
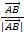
有方向的新向量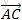
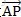
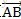
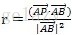
故根据r值的不同,最短距离
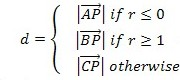
//点P到线段AB距离公式 double DistanceToSegment(Point P, Point A, Point B){ if(A == B) return Length(P-A); Vector v1 = B-A, v2 = P-A, v3 = P-B; if(dcmp(Dot(v1, v2)) < 0) return Length(v2); if(dcmp(Dot(v1, v3)) > 0) return Length(v3); return DistanceToLine(P, A, B); }
3.5 求点在直线上的投影点
//点P在直线AB上的投影点 Point GetLineProjection(Point P, Point A, Point B){ Vector v = B-A; return A+v*(Dot(v, P-A)/Dot(v, v)); }
3.6 判断点是否在线段上
//判断p点是否在线段a1a2上 bool OnSegment(Point p, Point a1, Point a2){ return dcmp(Cross(a1-p, a2-p)) == 0 && dcmp(Dot(a1-p, a2-p)) < 0; }
3.7 判断两线段是否相交
//判断两线段是否相交 bool SegmentProperIntersection(Point a1, Point a2, Point b1, Point b2){ double c1 = Cross(a2-a1, b1-a1), c2 = Cross(a2-a1, b2-a1); double c3 = Cross(b2-b1, a1-b1), c4 = Cross(b2-b1, a2-b1); //if判断控制是否允许线段在端点处相交,根据需要添加 if(!sgn(c1) || !sgn(c2) || !sgn(c3) || !sgn(c4)){ bool f1 = OnSegment(b1, a1, a2); bool f2 = OnSegment(b2, a1, a2); bool f3 = OnSegment(a1, b1, b2); bool f4 = OnSegment(a2, b1, b2); bool f = (f1|f2|f3|f4); return f; } return (sgn(c1)*sgn(c2) < 0 && sgn(c3)*sgn(c4) < 0); }
4 三角形
4.1求三角形外心
struct Point { double x, y; }; struct Line{ Point a, b; }; Point Intersection(Line u, Line v){ Point ret = u.a; double t1 = (u.a.x - v.a.x)*(v.a.y - v.b.y) - (u.a.y - v.a.y)*(v.a.x - v.b.x); double t2 = (u.a.x - u.b.x)*(v.a.y - v.b.y) - (u.a.y - u.b.y)*(v.a.x - v.b.x); double t = t1/t2; ret.x += (u.b.x - u.a.x)*t; ret.y += (u.b.y - u.a.y)*t; return ret; } //外心 Point Circumcenter(Point a, Point b, Point c){ Line u, v; u.a.x = (a.x + b.x)/2; u.a.y = (a.y + b.y)/2; u.b.x = u.a.x - a.y + b.y; u.b.y = u.a.y + a.x - b.x; v.a.x = (a.x + c.x)/2; v.a.y = (a.y + c.y)/2; v.b.x = v.a.x - a.y + c.y; v.b.y = v.a.y + a.x - c.x; return Intersection(u, v); }
4.1 求三角形内心
struct Point { double x, y; }; struct Line{ Point a, b; }; Point Intersection(Line u, Line v){ Point ret = u.a; double t1 = (u.a.x - v.a.x)*(v.a.y - v.b.y) - (u.a.y - v.a.y)*(v.a.x - v.b.x); double t2 = (u.a.x - u.b.x)*(v.a.y - v.b.y) - (u.a.y - u.b.y)*(v.a.x - v.b.x); double t = t1/t2; ret.x += (u.b.x - u.a.x)*t; ret.y += (u.b.y - u.a.y)*t; return ret; } //三角形内心 Point Incenter(Point a, Point b, Point c){ Line u, v; double m, n; u.a = a; m = atan2(b.y - a.y, b.x - a.x); n = atan2(c.y - a.y, c.x - a.x); u.b.x = u.a.x + cos((m + n)/2); u.b.y = u.a.y + sin((m + n)/2); v.a = b; m = atan2(a.y - b.y, a.x - b.x); n = atan2(c.y - b.y, c.x - b.x); v.b.x = v.a.x + cos((m + n)/2); v.b.y = v.a.y + sin((m + n)/2); return Intersection(u, v); }
4.2 求三角形垂心
struct Point { double x, y; }; struct Line{ Point a, b; }; Point Intersection(Line u, Line v){ Point ret = u.a; double t1 = (u.a.x - v.a.x)*(v.a.y - v.b.y) - (u.a.y - v.a.y)*(v.a.x - v.b.x); double t2 = (u.a.x - u.b.x)*(v.a.y - v.b.y) - (u.a.y - u.b.y)*(v.a.x - v.b.x); double t = t1/t2; ret.x += (u.b.x - u.a.x)*t; ret.y += (u.b.y - u.a.y)*t; return ret; } //三角形垂心 Point Perpencenter(Point a, Point b, Point c){ Line u, v; u.a = c; u.b.x = u.a.x - a.y + b.y; u.b.y = u.a.y + a.x - b.x; v.a = b; v.b.x = v.a.x - a.y + c.y; v.b.y = v.a.y + a.x - c.x; return Intersection(u, v); }
4.3 求三角形重心
struct Point { double x, y; }; struct Line{ Point a, b; }; Point Intersection(Line u, Line v){ Point ret = u.a; double t1 = (u.a.x - v.a.x)*(v.a.y - v.b.y) - (u.a.y - v.a.y)*(v.a.x - v.b.x); double t2 = (u.a.x - u.b.x)*(v.a.y - v.b.y) - (u.a.y - u.b.y)*(v.a.x - v.b.x); double t = t1/t2; ret.x += (u.b.x - u.a.x)*t; ret.y += (u.b.y - u.a.y)*t; return ret; } //三角形重心 //到三角形三顶点距离的平方和最小的点 //三角形内到三边距离之积最大的点 Point barycenter(Point a, Point b, Point c){ Line u, v; u.a.x = (a.x + b.x)/2; u.a.y = (a.y + b.y)/2; u.b = c; v.a.x = (a.x + c.x)/2; v.a.y = (a.y + c.y)/2; v.b = b; return Intersection(u, v); }
4.5 求三角形费马点
struct Point { double x, y; }; struct Line{ Point a, b; }; inline double Dist(Point p1, Point p2){ return sqrt((p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y)*(p1.y - p2.y)); } //三角形费马点 //到三角形三顶点距离之和最小的点 Point Ferment(Point a, Point b, Point c){ Point u, v; double step = fabs(a.x) + fabs(a.y) + fabs(b.x) + fabs(b.y) + fabs(c.x) + fabs(c.y); u.x = (a.x + b.x + c.x)/3; u.y = (a.y + b.y + c.y)/3; while(step >1e-10){ for(int k = 0; k < 10; step /= 2, k++){ for(int i = -1; i <= 1; ++i){ for(int j = -1; j <= 1; ++j){ v.x = u.x + step*i; v.y = u.y + step*j; double t1 = Dist(u, a) + Dist(u, b) + Dist(u, c); double t2 = Dist(v, a) + Dist(v, b) + Dist(v, c); if (t1 > t2) u = v; } } } } return u; }
5 多边形
5.1 求多边形有向面积
//多边形有向面积 double PolygonArea(Point* p, int n){//p为端点集合,n为端点个数 double s = 0; for(int i = 1; i < n-1; ++i) s += Cross(p[i]-p[0], p[i+1]-p[0]); return s; }
5.2 判断点是否在多边形内
//判断点是否在多边形内,若点在多边形内返回1,在多边形外部返回0,在多边形上返回-1 int isPointInPolygon(Point p, vector<Point> poly){ int wn = 0; int n = poly.size(); for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){ if(OnSegment(p, poly[i], poly[(i+1)%n])) return -1; int k = sgn(Cross(poly[(i+1)%n] - poly[i], p - poly[i])); int d1 = sgn(poly[i].y - p.y); int d2 = sgn(poly[(i+1)%n].y - p.y); if(k > 0 && d1 <= 0 && d2 > 0) wn++; if(k < 0 && d2 <= 0 && d1 > 0) wn--; } if(wn != 0) return 1; return 0; }
6 圆
6.1 求圆与直线交点
int getLineCircleIntersection(Line L, Circle C, double& t1, double& t2, vector<Point>& sol){ double a = L.v.x, b = L.p.x - C.c.x, c = L.v.y, d = L.p.y - C.c.y; double e = a*a + c*c, f = 2*(a*b + c*d), g = b*b + d*d - C.r*C.r; double delta = f*f - 4*e*g;//判别式 if(sgn(delta) < 0)//相离 return 0; if(sgn(delta) == 0){//相切 t1 = -f /(2*e); t2 = -f /(2*e); sol.push_back(L.point(t1));//sol存放交点本身 return 1; } //相交 t1 = (-f - sqrt(delta))/(2*e); sol.push_back(L.point(t1)); t2 = (-f + sqrt(delta))/(2*e); sol.push_back(L.point(t2)); return 2; }
6.2 求两圆交点
6.3 求点到圆的切线
6.4 求两圆公切线
6.5 求两圆相交面积
double AreaOfOverlap(Point c1, double r1, Point c2, double r2){ double d = Length(c1 - c2); if(r1 + r2 < d + eps) return 0.0; if(d < fabs(r1 - r2) + eps){ double r = min(r1, r2); return pi*r*r; } double x = (d*d + r1*r1 - r2*r2)/(2.0*d); double p = (r1 + r2 + d)/2.0; double t1 = acos(x/r1); double t2 = acos((d - x)/r2); double s1 = r1*r1*t1; double s2 = r2*r2*t2; double s3 = 2*sqrt(p*(p - r1)*(p - r2)*(p - d)); return s1 + s2 - s3; }
6.6 用给定半径的圆覆盖最多的点
const int maxn = 3e2 + 5; const double PI = acos(-1.0); struct Point{ double x, y; }p[maxn]; struct Angle{ double pos; bool in; bool operator < (const Angle& a) const { return pos < a.pos; } }a[maxn<<1]; inline double Dist(Point& p1, Point& p2){ return sqrt((p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y)*(p1.y - p2.y)); } //点集的大小n,给定圆的半径r,返回最多覆盖的点的个数 int solve(int n, double r){ int ret = 1; for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){ int m = 0; for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j){ if(i == j) continue; double d = Dist(p[i], p[j]); if(d > 2*r) continue; double alpha = atan2(p[j].y - p[i].y, p[j].x - p[i].x); double beta = acos(d/(2*r)); a[m].pos = alpha - beta; a[m++].in = true; a[m].pos = alpha + beta; a[m++].in = false; } sort(a, a + m); int t = 1; for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j){ if(a[j].in) ++t; else --t; if(ret < t) ret = t; } } return ret; }
7 凸包
7.1 GrahamScan O(nlogn)
const int maxn = 1e3 + 5; const double eps = 1e-9; struct Point { double x, y; Point(double x = 0, double y = 0):x(x),y(y){} }; typedef Point Vector; Point lst[maxn]; int stk[maxn], top; Vector operator - (Point A, Point B){ return Vector(A.x-B.x, A.y-B.y); } int sgn(double x){ if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0; if(x < 0) return -1; return 1; } double Cross(Vector v0, Vector v1) { return v0.x*v1.y - v1.x*v0.y; } double Dis(Point p1, Point p2) { //计算 p1p2的 距离 return sqrt((p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); } bool cmp(Point p1, Point p2) { //极角排序函数 ,角度相同则距离小的在前面 int tmp = sgn(Cross(p1 - lst[0], p2 - lst[0])); if(tmp > 0) return true; if(tmp == 0 && Dis(lst[0], p1) < Dis(lst[0], p2)) return true; return false; } //点的编号0 ~ n - 1 //返回凸包结果stk[0 ~ top - 1]为凸包的编号 void Graham(int n) { int k = 0; Point p0; p0.x = lst[0].x; p0.y = lst[0].y; for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { if( (p0.y > lst[i].y) || ((p0.y == lst[i].y) && (p0.x > lst[i].x)) ) { p0.x = lst[i].x; p0.y = lst[i].y; k = i; } } lst[k] = lst[0]; lst[0] = p0; sort(lst + 1, lst + n, cmp); if(n == 1) { top = 1; stk[0] = 0; return ; } if(n == 2) { top = 2; stk[0] = 0; stk[1] = 1; return ; } stk[0] = 0; stk[1] = 1; top = 2; for(int i = 2; i < n; ++i) { while(top > 1 && Cross(lst[stk[top - 1]] - lst[stk[top - 2]], lst[i] - lst[stk[top - 2]]) <= 0) --top; stk[top] = i; ++top; } return ; }
7.2 Andrew O(nlogn)
struct Point { double x, y; Point(double x = 0, double y = 0):x(x),y(y){} }; typedef Point Vector; Vector operator - (Point A, Point B){ return Vector(A.x-B.x, A.y-B.y); } bool operator < (const Point& a, const Point& b){ if(a.x == b.x) return a.y < b.y; return a.x < b.x; } double Cross(Vector v0, Vector v1) { return v0.x*v1.y - v1.x*v0.y; } //计算凸包,输入点数组为 p,个数为 n, 输出点数组为 ch。函数返回凸包顶点数 //如果不希望凸包的边上有输入点,则把两个 <= 改为 < //在精度要求高时建议用dcmp比较 //输入不能有重复点,函数执行完后输入点的顺序被破坏 int ConvexHull(Point* p, int n, Point* ch) { sort(p, p+n); int m = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { while(m > 1 && Cross(ch[m-1] - ch[m-2], p[i] - ch[m-2]) <= 0) m--; ch[m++] = p[i]; } int k = m; for(int i = n-2; i>= 0; --i) { while(m > k && Cross(ch[m-1] - ch[m-2], p[i] - ch[m-2]) <= 0) m--; ch[m++] = p[i]; } if(n > 1) --m; return m; }
8 半平面交 O(nlogn)
const double eps = 1e-6; struct Point{ double x, y; Point(double x = 0, double y = 0):x(x),y(y){} }; typedef Point Vector; Vector operator + (Vector A, Vector B){ return Vector(A.x+B.x, A.y+B.y); } Vector operator - (Point A, Point B){ return Vector(A.x-B.x, A.y-B.y); } Vector operator * (Vector A, double p){ return Vector(A.x*p, A.y*p); } int sgn(double x){ if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0; if(x < 0) return -1; return 1; } double Dot(Vector A, Vector B){ return A.x*B.x + A.y*B.y; } double Cross(Vector A, Vector B){ return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x; } double Length(Vector A){ return sqrt(Dot(A, A)); } Vector Normal(Vector A){//向量A左转90°的单位法向量 double L = Length(A); return Vector(-A.y/L, A.x/L); } struct Line{ Point p;//直线上任意一点 Vector v;//方向向量,它的左边就是对应的半平面 double ang;//极角,即从x轴正半轴旋转到向量v所需要的角(弧度) Line(){} Line(Point p, Vector v) : p(p), v(v){ ang = atan2(v.y, v.x); } bool operator < (const Line& L) const {//排序用的比较运算符 return ang < L.ang; } }; //点p在有向直线L的左侧 bool OnLeft(Line L, Point p){ return Cross(L.v, p - L.p) > 0; } //两直线交点。假定交点唯一存在 Point GetIntersection(Line a, Line b){ Vector u = a.p - b.p; double t = Cross(b.v, u)/Cross(a.v, b.v); return a.p + a.v*t; } //半平面交的主过程 int HalfplaneIntersection(Line* L, int n, Point* poly){ sort(L, L + n);//按照极角排序 int fst = 0, lst = 0;//双端队列的第一个元素和最后一个元素 Point *P = new Point[n];//p[i] 为 q[i]与q[i + 1]的交点 Line *q = new Line[n];//双端队列 q[fst = lst = 0] = L[0];//初始化为只有一个半平面L[0] for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){ while(fst < lst && !OnLeft(L[i], P[lst - 1])) --lst; while(fst < lst && !OnLeft(L[i], P[fst])) ++fst; q[++lst] = L[i]; if(sgn(Cross(q[lst].v, q[lst - 1].v)) == 0){ //两向量平行且同向,取内侧一个 --lst; if(OnLeft(q[lst], L[i].p)) q[lst] = L[i]; } if(fst < lst) P[lst - 1] = GetIntersection(q[lst - 1], q[lst]); } while(fst < lst && !OnLeft(q[fst], P[lst - 1])) --lst; //删除无用平面 if(lst - fst <= 1) return 0;//空集 P[lst] = GetIntersection(q[lst], q[fst]);//计算首尾两个半平面的交点 //从deque复制到输出中 int m = 0; for(int i = fst; i <= lst; ++i) poly[m++] = P[i]; return m; }
9 平面最近点对 O(nlogn)
struct Point { double x,y; bool operator <(const Point &a)const { return x < a.x; } }; inline double dist(const Point &p1, const Point &p2) { return sqrt((p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y)); } Point p[maxn], q[maxn]; double ClosestPair(int l, int r) { if(l == r) return inf; int mid = (l+r)>>1; double tx = p[mid].x; int tot = 0; double ret = min(ClosestPair(l, mid), ClosestPair(mid + 1, r)); for(int i = l, j = mid + 1; (i <= mid || j <= r); ++i) { while(j <= r && (p[i].y > p[j].y || i > mid)) { q[tot++] = p[j]; j++; //归并按y排序 } if(abs(p[i].x - tx) < ret && i <= mid) { //选择中间符合要求的点 for(int k = j - 1; k > mid && j - k < 3; --k) ret = min(ret, dist(p[i], p[k])); for(int k = j; k <= r && k-j < 2; ++k) ret = min(ret, dist(p[i], p[k])); } if(i <= mid) q[tot++] = p[i]; } for(int i = l, j = 0; i <= r; ++i, ++j) p[i] = q[j]; return ret; }
10 旋转卡壳
10.1 求凸包直径
double Dist2(Point p1, Point p2) { //计算距离的平方 double ret = Dot(p1 - p2, p1 - p2); return ret; } double RotatingCalipers(Point* ch, int m) {//返回平面最大距离的平方 if(m == 1) return 0.0; if(m == 2) return Dist2(ch[0], ch[1]); double ret = 0.0; ch[m] = ch[0]; int j = 2; for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { while(Cross(ch[i + 1] - ch[i], ch[j] - ch[i]) < Cross(ch[i + 1] - ch[i], ch[j + 1] - ch[i])) j = (j + 1)%m; ret = max(ret, max(Dist2(ch[j], ch[i]), Dist2(ch[j], ch[i + 1]))); } return ret; }
10.2 求凸包的宽(凸包对踵点的最小值)
double dist(Point a, Point b){ double ret = sqrt((a.x - b.x)*(a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y)*(a.y - b.y)); return ret; } double mxid[maxn]; double RotateCalipersWide(Point* p, int n){ int j = 1; p[n] = p[0]; for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){ while(fabs(Cross(p[i + 1] - p[i], p[j + 1] - p[i])) > fabs(Cross(p[i + 1] - p[i], p[j] - p[i]))) j = (j + 1)%n; mxid[i] = fabs(Cross(p[j] - p[i], p[i + 1] - p[i]))/dist(p[i], p[i + 1]); } double ret = 1e18; for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ret = min(ret, mxid[i]); return ret; }
11 网格图
11.1 Pick定理

11.2 多边形与网格点
struct Point{ int x, y; }; //多边形上的网格点个数 int Onedge(int n, Point* p){ int ret = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ret += __gcd(abs(p[i].x - p[(i + 1)%n].x), abs(p[i].y - p[(i + 1)%n].y)); return ret; } //多边形内的网格点个数 int Inside(int n, Point* p){ int ret = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ret += p[(i + 1)%n].y*(p[i].x - p[(i + 2)%n].x); ret = (abs(ret) - Onedge(n, p))/2 + 1; return ret; }
相关博客: