图的遍历BFS广度优先搜索
1. 简介
BFS(Breadth First Search,广度优先搜索,又名宽度优先搜索),与深度优先算法在一个结点“死磕到底“的思维不同,广度优先算法关注的重点在于每一层的结点进行的下一层的访问。
2. BFS算法介绍
BFS算法和核心思路就是:从某个点一直把其邻接点走完,然后任选一个邻接点把与之邻接的未被遍历的点走完,如此反复走完所有结点。类似于树的层序遍历。
BFS的核心就是要把当前在哪作为一个状态存储,并将这个状态交给队列进行入队操作,故而,
算法步骤(用队列实现)
a) 访问指定起始点。
b) 访问当前顶点的邻接顶点有未被访问的顶点,并将之放入队列中。
c) 删除队列的队首节点。访问当前队列的队首,前面的步骤。直到队列为空。
d) 若若途中还有顶点未被访问,则再选一个点作为起始顶点。重复前面的步骤。(针对非连通图)。
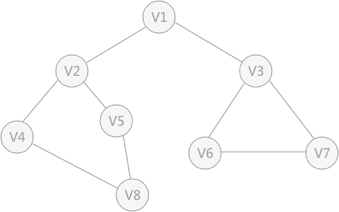
3. 案例图示
4. 相关代码
BFS的模板代码如下:
/**
* 返回合适的检索数据
*/
int BFS(Node root, Node target)
{
Queue<Node> queue; //创建队列
int step = 0; // 当前队列的步骤点
// initialize
add root to queue;
// BFS
while (queue is not empty)
{
step = step + 1;
//步数逐渐增加
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
Node cur = the first node in queue;
if cur is target
return step - 1;
for (Node next : the neighbors of cur)
{//这里常用一个二维方向数组实现
add next to queue;
}
remove the first node from queue;
}
}
return -1; //出错返回值
}
完整代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define matrix_size 20
typedef struct {
int weight;
}AdjMatrix[matrix_size][matrix_size];
struct Queue{
int data;
Queue* next;
};
struct MGraph{
int vex[matrix_size];
AdjMatrix arcs;
int vexnum,arcnum;
};
bool visited[matrix_size];
int LocateVex(MGraph *G ,int v){
int i;
for ( i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++)
{
if (G->vex[i]==v)
{
break;
}
}
if (i>G->vexnum)
{
cout<<"not such vertex"<<endl;
return -1;
}
return i;
}
//构造无向图
void CreateDN(MGraph *G){
cin>>G->vexnum>>G->arcnum;
for (int i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++)
{
cin>>G->vex[i];
}
for (int i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<G->vexnum; j++) {
G->arcs[i][j].weight=0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < G->arcnum; i++)
{
int v1,v2;
cin>>v1>>v2;
int n=LocateVex(G,v1);
int m=LocateVex(G,v2);
if (m==-1||n==-1)
{
cout<<"not this vertex"<<endl;
return ;
}
G->arcs[n][m].weight=1;
G->arcs[m][n].weight=1;
}
return ;
}
//输出函数
void PrintGrapth(MGraph G)
{
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++)
{
cout<<G.arcs[i][j].weight<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
void visitVex(MGraph G,int v){
cout<<G.vex[v]<<" ";
}
int FirstAdjVex(MGraph G,int v){
for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
//查找与数组下标为v的顶点之间有边的顶点,返回它在数组中的下标
if (G.arcs[v][i].weight)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int NextAdjVex(MGraph G,int v,int w)
{
//从前一个访问位置w的下一个位置开始,查找之间有边的顶点
for(int i = w+1; i<G.vexnum; i++){
if(G.arcs[v][i].weight){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
Queue* InitQueue(){
Queue* Q=new Queue;
Q->next=NULL;
return Q;
}
//顶点元素v进队列
void EnQueue(Queue * Q,int v){
Queue *element = new Queue;
element->data=v;
element->next=NULL;
Queue* temp=Q;
while (temp->next!=NULL)
{
temp=temp->next;
}
temp->next=element;
// cout<<"in enqueue "<<element->data<<" ";
}
//队头元素出队列
Queue * DeQueue(Queue *Q,int *u){
(*u)=Q->next->data;
Q=Q->next;
return Q;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue *Q){
if (Q->next==NULL)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
//广度优先搜索
void BFSTraverse(MGraph G){
int v;
for ( v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)
{
visited[v]=false;
}
Queue * Q;
Q=InitQueue();
for (v=0 ; v <G.vexnum ; v++)
{
if (!visited[v])
{
visited[v]=true;
visitVex(G,v);
EnQueue(Q,G.vex[v]);
while (!QueueEmpty(Q))
{
int u;
Q=DeQueue(Q,&u);
u = LocateVex(&G,u);
for (int w=FirstAdjVex(G, u); w>=0; w=NextAdjVex(G, u, w)) {
if (!visited[w]) {
visited[w]=true;
visitVex(G, w);
EnQueue(Q, G.vex[w]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
MGraph G;//建立一个图的变量
CreateDN(&G);//初始化图
BFSTraverse(G);//广度优先搜索图
return 0;
}
结果:
8 9
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 2
2 4
2 5
4 8
5 8
1 3
3 6
6 7
7 3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8