| 导读 |
在平时编程中有时需要获取当前的时间或者日期,然而不同的平台不同的场景下,有时使用的API也不尽相同。一般来说,C/C++中关于时间的标准库函数在不同的平台的都可以使用,可一些与平台相关的函数就只能在特定的平台上使用了。 本文将记录C++ 中与时间相关的日期相关的函数 和 相关的数据类型。同时对不同系统平台的API进行对比,区别以加深相关知识的记忆。 |
| 目录 |
参考:C++ API 在线
C++ 支持两种类型的时间操作:
- chrono 库,一个多样的函数集合,可以多样的、不同的精度来表示时间。 (e.g. std::chrono::time_point).(C11后的标准,有兴趣可以进一步了解)
- C类型 的时间和日期库。(e.g. std::time)
在这里主要记录常用的C类型的 时间和日期库。
函数:
时间操作 |
|
|
头文件:
<time.h> |
|
| (函数)计算2个时间的差值 (参数为2个time_t数据,arg1-arg2,返回值为double) | |
| (函数)返回自格林威治1970.01.01 到现在的系统日历时间 (struct tm) |
|
| (函数)返回自程序启动以来的 原生处理器时钟时间 ( raw processor clock time) |
|
|
(since C11)
|
(函数)返回基于一个给定 time base (如 TIME_UTC) 的日历时间 (struct timespec) |
格式转换 |
|
|
头文件:
<time.h> |
|
(函数)将 tm 对象转为文本表示(通过Www Mmm dd hh:mm:ss yyyy定制) |
|
(函数)将 time_t 对象转为文本表示 |
|
(函数)将 tm 对象转为 自定义 的文本表示 |
|
|
头文件:
<wchar.h> |
|
|
(C95)
|
(函数)将 tm 对象转换为 自定义的 宽字节 字符串文本 |
|
头文件:
<time.h> |
|
| (函数)time_t 转为 tm (UTC 时间) |
|
| (函数) time_t 转为 tm (本地时间) |
|
| (函数) tm 转为time_t (自格林威治19700101) |
|
常量:
|
头文件:
<time.h> |
|
| 每秒的处理器时钟数 (macro constant) |
|
类型:
|
头文件
<time.h> |
|
| (struct)日历时间类型 | |
| (typedef)日历时间 since epoch type | |
| (typedef)处理器时间 since era type | |
|
(since C11)
|
(struct)包括秒和纳秒的 时间 [可通过 函数int clock_gettime(clockid_t clock_id, struct timespec *tp);获得,如 clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &t)] |
函数和类型参考 这里
函数关系图:
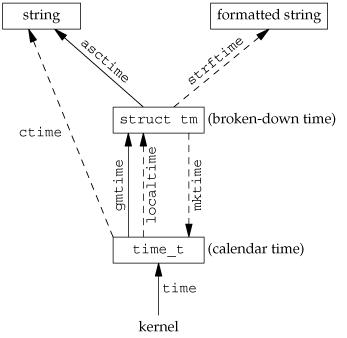
微软官方文档:时间函数
函数常用的有:(头文件:windows.h)
GetSystemTime 获得UTC(等于GMT)时间
GetLocalTime 获得系统本地时间
类型:

typedef struct _SYSTEMTIME { WORD wYear; WORD wMonth; WORD wDayOfWeek; WORD wDay; WORD wHour; WORD wMinute; WORD wSecond; WORD wMilliseconds; } SYSTEMTIME, *PSYSTEMTIME;
例子:
#include <windows.h> #include <stdio.h> void main() { SYSTEMTIME st, lt; GetSystemTime(&st); GetLocalTime(<); printf("The system time is: %02d:%02d ", st.wHour, st.wMinute); printf("The local time is: %02d:%02d ", lt.wHour, lt.wMinute); }
运行结果:
The system time is: 19:34 The local time is: 12:34
函数:
gettimeofday 头文件 <sys/time.h> 得到 timeval(精确到微秒)
接口:int gettimeofday(struct timeval *restrict tp, void *restrict tzp);(第二个形参是基于平台实现的,使用的时候最好用NULL)
类型:
timeval
struct timeval{ time_t tv_sec; /*** second ***/ susecond_t tv_usec; /*** microsecond 微妙***/ }
实例:

#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/time.h> int main() { struct timeval start, end; gettimeofday( &start, NULL ); sleep(3); gettimeofday( &end, NULL ); //求出两次时间的差值,单位为us int timeuse = 1000000 * ( end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec ) + end.tv_usec - start.tv_usec; printf("time: %d us ", timeuse); return 0; }
附:内核时间
内核有两个重要的全局变量:
unsigned long jiffies;
timeval xtime ;
jiffies 是记录着从电脑开机到现在总共的"时钟中断"的次数。
文件linux-2.6.24/kernel/timer.c
void do_timer(unsigned long ticks)
{
jiffies_64 += ticks;
update_times(ticks);
}
xtime 是从cmos电路或rtc芯片中取得的时间,一般是从某一历史时刻开始到现在的时间。
这个就是所谓的"墙上时钟walltimer",通过它可计算得出操作系统需要的日期时间,它的精确度是微秒。
xtime第一次赋值是在系统启动时调用timekeeping_init或time_init进行的
再调用read_persistent_clock进一步调用get_rtc_time得到的
PS:在/proc/uptime里面的两个数字分别表示:
the uptime of the system(seconds),
and the amount of time spent in idle process(seconds).
time_t 与 SYSTEMTIME 的转换:(Click Here)
