问题
- 堆内外内存的区别是什么
堆内外内存
java 进程的内存占用到底是怎么样的呢?
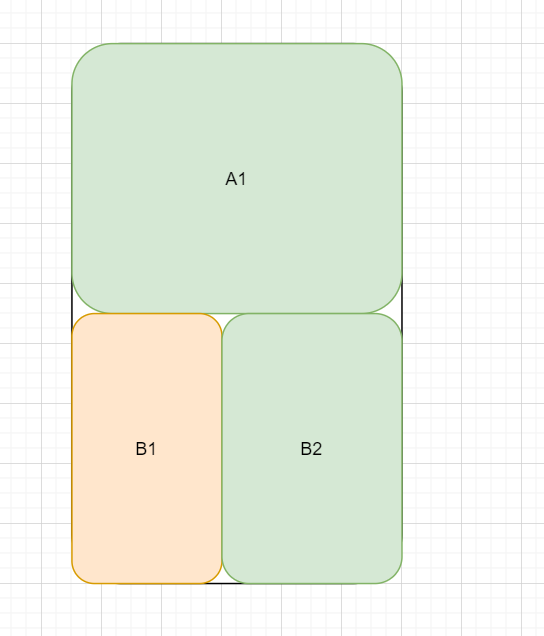
我们都知道 jvm 有垃圾回收机制,并且回收的重点区域就是堆,假如我们以堆内堆外来区分内存区域,上图所示
- 堆内 A1
- 堆外 B1 + B2 B1 有可能是 DirectByteBuffer 分配的堆外内存,而 B2 是 Native Code 分配的内存。
DirectByteBuffer 类
以下描述代码图片来自 : https://blog.csdn.net/mycs2012/java/article/details/93513057 , 非原创
DirectByteBuffer 使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 分配
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(128);
// 写入
buffer.put("写入到直接内存".getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8")));
// 读取
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
System.gc(); // 不是必须
}
内部原理
下面是 DirectByteBuffer 的构造方法
DirectByteBuffer(int cap) {
super(-1, 0, cap, cap);
boolean pa = VM.isDirectMemoryPageAligned(); // 获取是否开启内存页对齐选项
int ps = Bits.pageSize(); // 内存页大小
long size = Math.max(1L, (long)cap + (pa ? ps : 0)); // 计算size,后面按size进行实际内存占用
Bits.reserveMemory(size, cap); // 累加,控制直接内存的访问量
long base = 0;
try {
base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, cap);
throw x;
}
unsafe.setMemory(base, size, (byte) 0);
if (pa && (base % ps != 0)) {
// Round up to page boundary
address = base + ps - (base & (ps - 1)); // 启用内存页对齐时
} else {
address = base; // 未启用内存页对齐时
}
cleaner = Cleaner.create(this, new Deallocator(base, size, cap));
att = null;
}
主要的操作有 : 1、通过unsafe.allocateMemory(size)分配一段大小为size的内存,这是个native方法,表明会通过JNI调用操作系统本地的系统调用接口。该方法最终会调用操作系统的malloc方法,进行内存的分配,分配成功后返回一个基地址,这个基地址最后转换为address,DirectByteBuffer对象就是通过address和size引用这段内存。
2、创建Cleaner对象,后续用于清理直接内存。
而这个 Cleaner 类是如何达到回收内存的效果的呢 , Cleaner 对象会持有Deallocator,在执行收集的时候调用其 run 方法
public class Cleaner extends PhantomReference<Object> {
....
}
Cleaner 是虚引用的之类,虚引用的容易被回收,当被回收就回调用 Cleaner 的 clean 方法
private static class Deallocator
implements Runnable
{
private static Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private long address;
private long size;
private int capacity;
private Deallocator(long address, long size, int capacity) {
assert (address != 0);
this.address = address;
this.size = size;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public void run() {
if (address == 0) {
// Paranoia
return;
}
// 使用unsafe方法释放内存
unsafe.freeMemory(address);
address = 0;
// 更新统计变量
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, capacity);
}
}
参考
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/K-6CPo1haIe65KZPdTHSrA(堆外内存泄漏分析)
- https://blog.csdn.net/mycs2012/article/details/93513057 (DirectByteBuffer 原理文章)