文章图片来自邓俊辉老师课件
先提几个问题去思考学习本文 :
- 红黑树和2-4树(B-Tree)很像,那么它存在的动机又是什么呢
- 插入和删除操作的逻辑又是怎么样的,时间和空间复杂度可以达到怎么样
- 和 AVL 对象有什么区别呢
概述
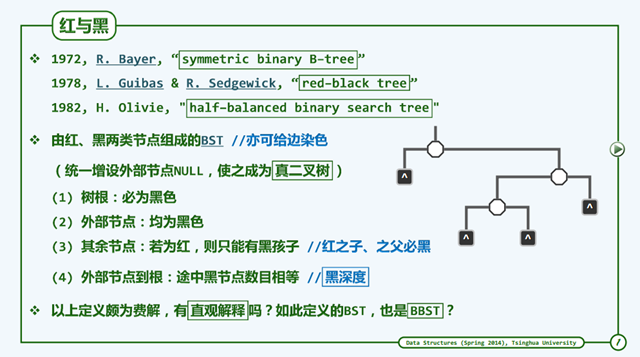
定义
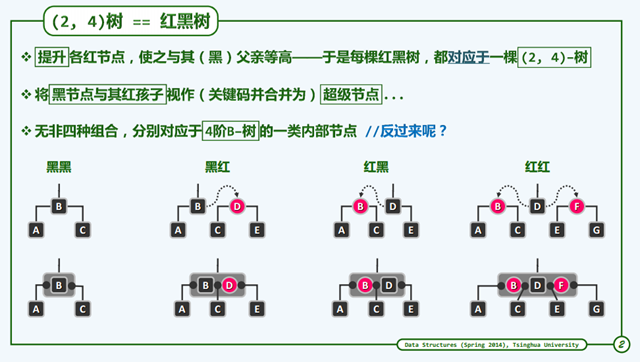
我们可以看到红黑树有4条重要的定义,这4条定义保证了这个平衡树。下面我们看一下它和B-Tree的联系。
从这个结构上说,我们可以知道B-Tree相比于红黑树,红黑树需要维护一个颜色这样的属性,需要空间,而同时红黑树搜索时可以
像二叉树一般查找,而B-Tree每一个超级节点需要维护多个关键码。这方面查看 RST_WIKI 这里的分析。
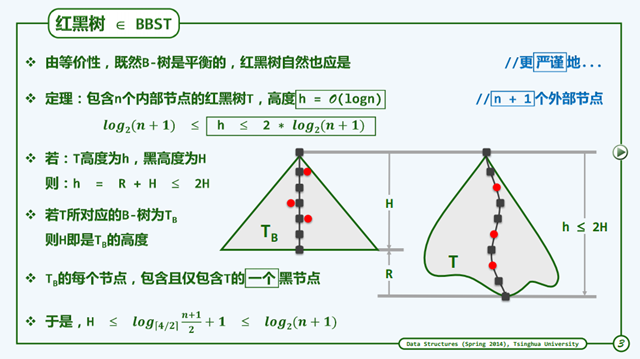
但是这样的树是BBST吗?
上面的数学推算已经向我证明,平均的深度为 h = O(LogN)
动机
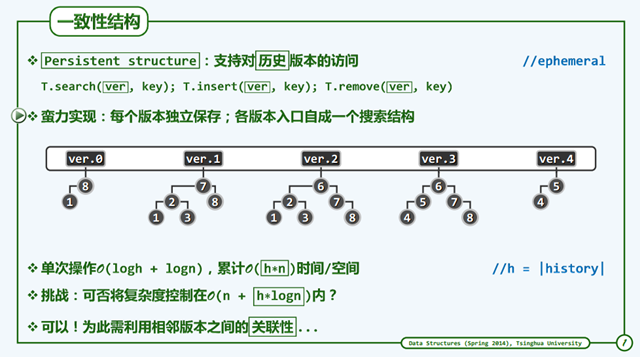
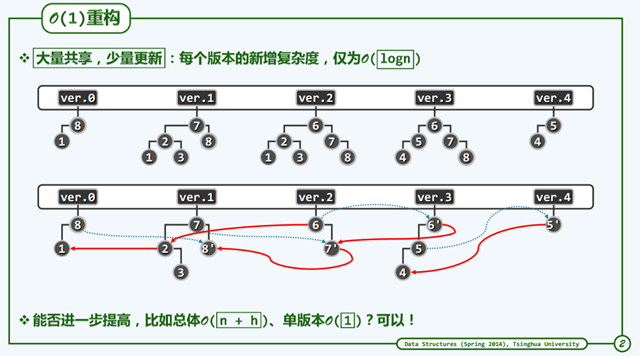
Persistant Structure 一致性
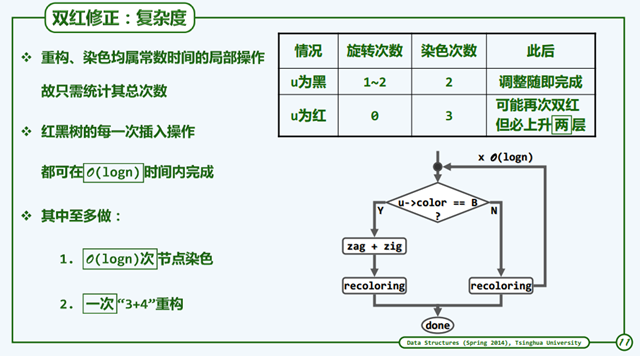
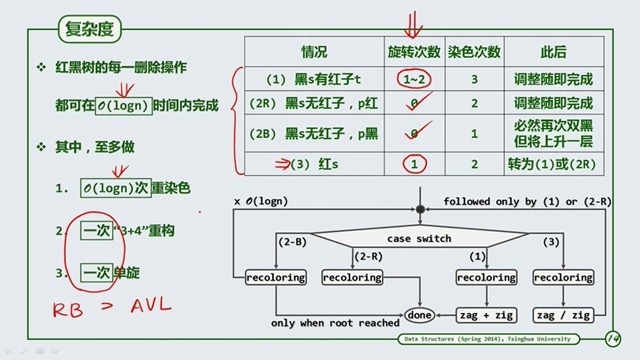
时间和空间复杂度红黑树可以适应条件。同时拓扑结构上,无论是插入还是删除,都可以不超过O(1).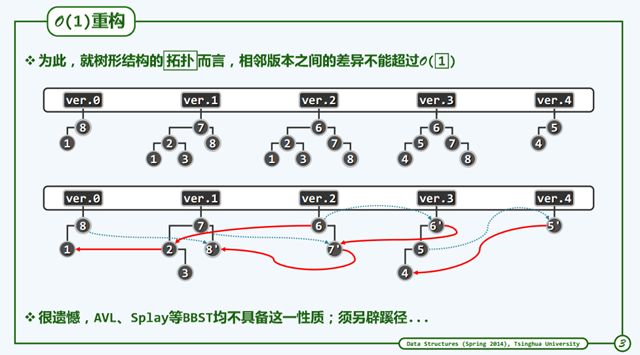
最坏情况下保证插入和删除,查找
这里引用 wiki 上的一段话说明红黑树在这方面的表现。
Red–black trees offer worst-case guarantees for insertion time, deletion time, and search time. Not only does this make them valuable in time-sensitive applications such as real-time applications, but it makes them valuable building blocks in other data structures which provide worst-case guarantees; for example, many data structures used in computational geometry can be based on red–black trees, and the Completely Fair Scheduler used in current Linux kernels and epoll system call implementation[19] uses red–black trees.
时间空间复杂度
出处见参考资料
插入原理解析
我们定义插入的节点为红色,那么就有一种情况,双红,这违反了我们前面红黑树的定义,下面介绍如何解决双红问题。
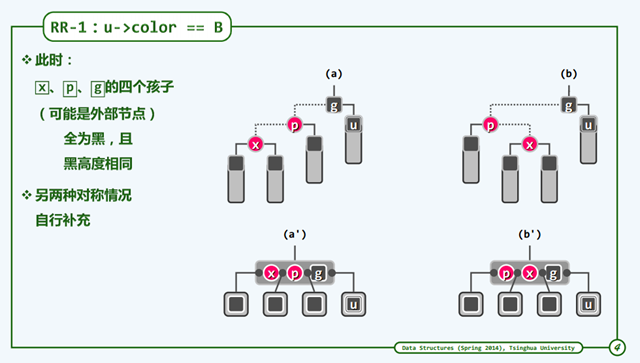
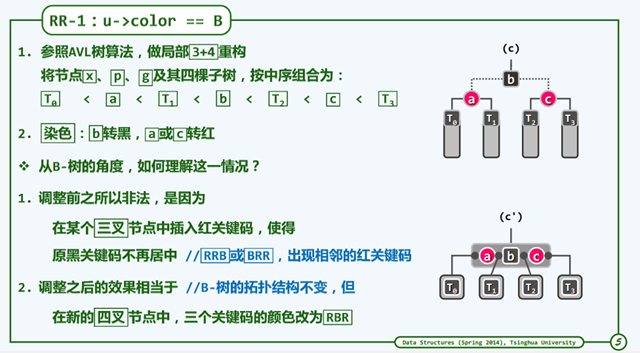
RR-1
第一种情况 u 节点(uncle节点)是黑色的。
我们可以使用3+4实现,让树消除双红现象,3+4实现可以参考这篇文章 : 3+4
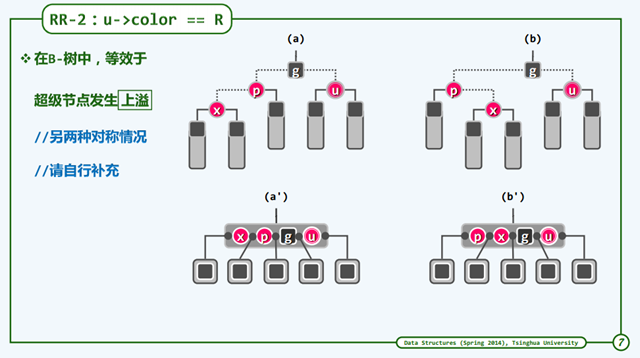
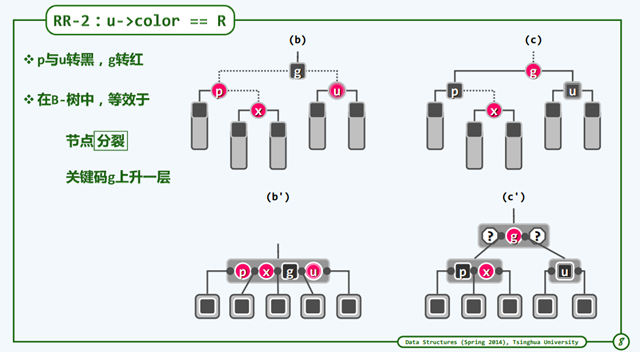
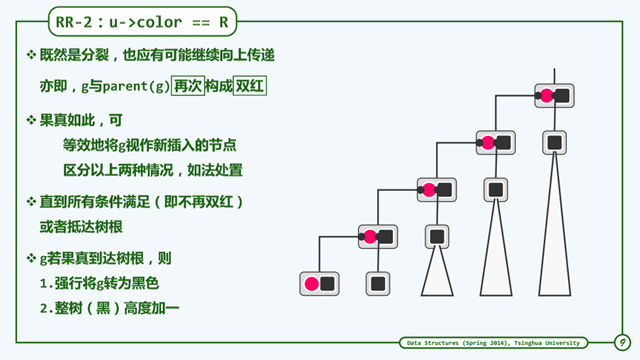
RR-2
u节点是红色的情况下,最终可能导致树高度+1
插入归纳
删除原理解析
我们思考一下,假如先不看颜色,那么二叉树的删除算法中,考察三种情况
- 拥有其中一个子节点
- 无子节点
- 拥有左右子节点
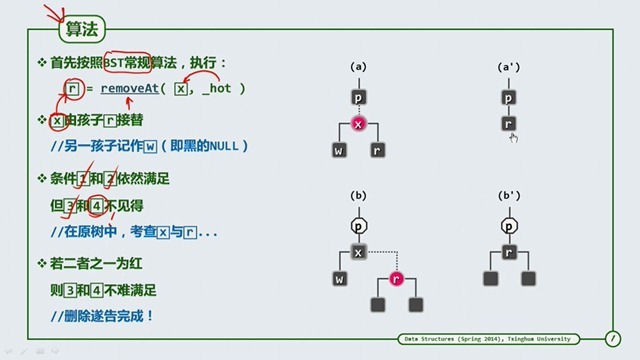
其中第一和第二种情况很好处理,直接删除即可,有其中一个子节点需要重新连接一下父节点。第三种需要找出继承节点,然后替
换掉删除节点。继承节点简单点解释就是右树中最小的一个。
好了,那么此时我们再来思考一下颜色的问题,我们知道红黑树不能红红相联,且每个底部节点到根节点黑节点的数量都相等,要
是删除节点是上面第一种情况和第二种情况且删除节点是红节点,直接删除对树的平衡没有情况影响。
那么要是删除节点和继承节点一黑一白呢,我们只需将删除后,将继承节点染黑就可以了,见下图。
那么删除节点和继承节点都是黑的情况呢?
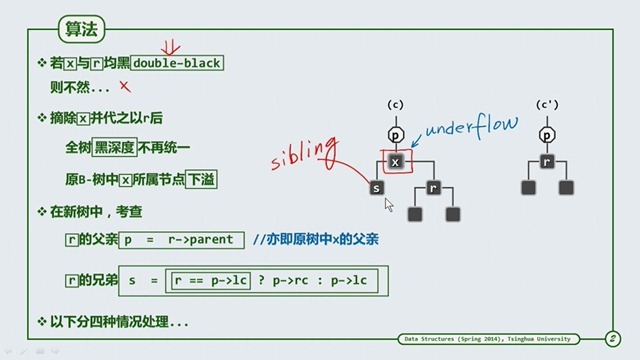
双黑缺陷
可以看到,当删除节点和替代节点都为黑节点,删除会产生下溢(下溢的概念可以参考上篇B-树),需要考察继承节点的父节点p和
兄弟节点 s ,下面分四种情况处理 :
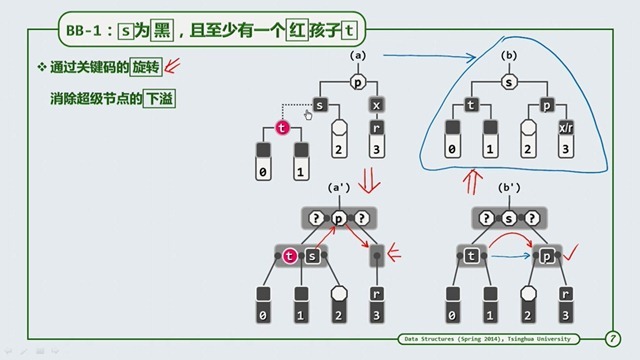
BB-1
a’ 和 b’ 都是B-Tree 的扑拓结构,可以看到当s拥有一个红节点时,产生下溢的节点通过旋转,向兄弟节点借来了一个节点,从而
达到了平衡。而从 a 到 b 的过程,需要借助的是3+4操作。
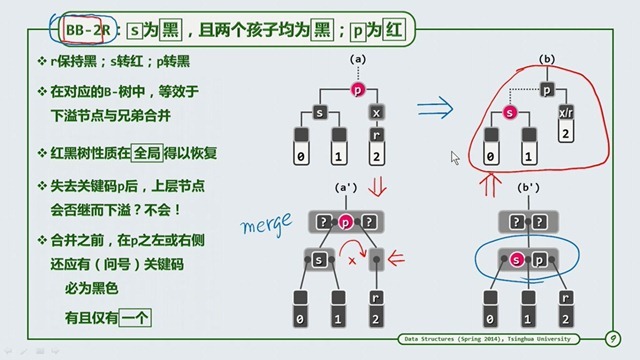
BB-2R
BB-2R的情况,就相当于B-Tree的合并,而我们看到最终的扑拓结构是不变的,只需要进行染色,那么当父节点被拿走了一个,是否会产生下溢呢?不会,因为在父节点中有红节点,那么左或右必有黑节点。
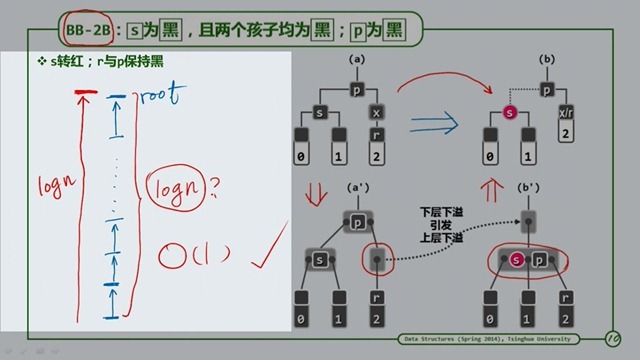
BB-2B
同样也是合并操作,此时不是像BB-2R一样是红色节点了,那么就有可能引发下沉下溢,那么是不是会像AVL一样进行LogN次的旋转操作呢?不会,从a到b,我们可以他们的扑拓结构没有改变,改变的只是颜色,所以不会发生LogN次的旋转。时间复杂度依旧是O(1).
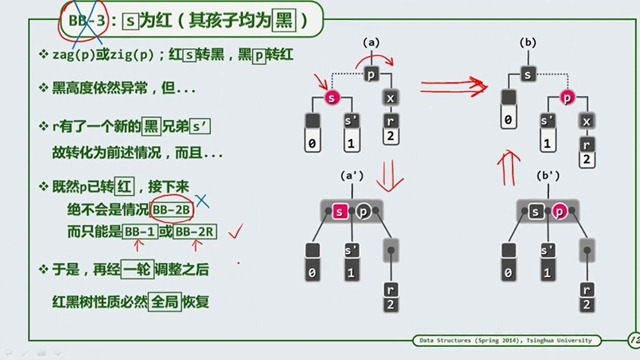
BB-3
可以看到,经过了左旋或是右旋,还有变色,由a到b后,黑高度依旧异常,可以有一个好消息就是,经过旋转变成了我们之前处理
的情况一样,即 BB-1 或是 BB-2R ,不会是 BB-2B的原因是 x 有个新的兄弟节点 s’ ,而且 p 为红节点。
至此,我们双黑的情况全部介绍完毕。
归纳总结和AVL的对比
代码实现
代码实现我们以java中的TreeMap 来解释。本文只会介绍删除操作。
/**
* Removes the mapping for this key from this TreeMap if present.
*
* @param key key for which mapping should be removed
* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}.
* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Returns this map's entry for the given key, or {@code null} if the map
* does not contain an entry for the key.
*
* @return this map's entry for the given key, or {@code null} if the map
* does not contain an entry for the key
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Delete node p, and then rebalance the tree.
*/
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
// If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p
// point to successor.
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
//到了这里,无论p是有几个孩子,p这个变量变成了要删除的节点
//要是 p有两个child,会进入上面那个if,p变为了继承节点
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) { //只存在一个子节点
// Link replacement to parent 重新连接父节点,需要删除的节点置为 null
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement 开始修复,判断是不是黑节点是因为红节点直接删除没有影响 :
// 每个底部节点到根节点的黑色节点数量相等
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node. 该树只有一个节点
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink. 没有子节点
if (p.color == BLACK) //继承节点为黑
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) { //继承节点为红,直接删除
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
// 实际就是解决双黑节点的问题
/** From CLR */
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) { //非根且为黑节点
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); //取右兄弟节点
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateRight(sib);
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
} else { // symmetric //和前面是对称的
Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); // x是左节点
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) { //假如是BB-3,旋转后只能是 BB-1 或者是 BB-2R
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK && //BB-2R 或是 BB-2B
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) { //BB-1 中 红在右边
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateLeft(sib);
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
x = root; //跳出while
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK);
}
参考资料
- 邓俊辉老师数据结构课程
- RST_WIKI