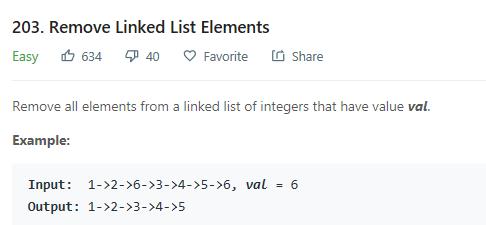


该逻辑对于删除第一个元素不适用。
这样的代码不优美
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { while(head!=NULL && head->val == val){ ListNode* delNode = head; head = delNode ->next; delete delNode; } if(head == NULL) return NULL; ListNode* cur = head; while(cur->next != NULL){ if(cur->next->val == val){ //删除 ListNode* delNode = cur->next; cur->next = delNode->next; delete delNode; } else cur = cur->next; } return head; } };
可以设置一个虚拟的头结点:

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead->next = head; ListNode* cur = dummyHead; while(cur->next != NULL){ if(cur->next->val == val){ //删除 ListNode* delNode = cur->next; cur->next = delNode->next; delete delNode; } else cur = cur->next; } ListNode* retNode = dummyHead->next; delete dummyHead; return retNode; } };


这道题想了好久,原因是要把重复的所有元素都删除,这里设立一个duplicate标志位来记录当前cur是否与下一个结点重复。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) { ListNode* h = new ListNode(-1); h->next = head; ListNode* pre = h; ListNode* cur = head; while(cur!=NULL){ bool duplicate = false; while(cur->next!=NULL && cur->val==cur->next->val){ ListNode* delNode = cur; cur = cur->next; delete delNode; duplicate = true; } if(duplicate == false){ pre = cur; cur = cur->next; } else{ pre->next = cur->next; ListNode* delNode = cur; cur = cur->next; delete delNode; } } return h->next; } };
又重新做了一遍这道题,思路和前面设置标志位记录重复的不太一样。重点在于在两个结点不相同时,需要判断在它们前面是否存在重复的元素,若存在,pre需要跳过这些结点;若不存在,pre直接指向pre->next即cur即可。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL) return NULL; ListNode dummy(0); dummy.next = head; ListNode* pre = &dummy, *cur = head; while(cur){ ListNode* next = cur->next; while(next && next->val == cur->val){ cur = cur->next; next = next->next; } if(cur != pre->next){ cur = next; //将最后一个重复的跳过 pre->next = cur; } else{ //pre和cur之间没有重复的 pre = cur; cur = next; } } return dummy.next; } };
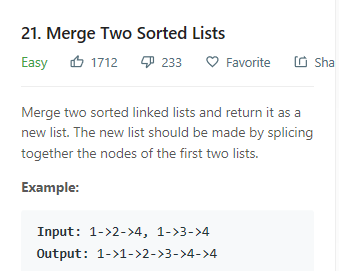
归并两个有序的链表。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { ListNode* h = new ListNode(-1); ListNode* cur = h; ListNode* cur1 = l1; ListNode* cur2 = l2; while(cur1 != NULL && cur2 != NULL){ if(cur1->val <= cur2->val){ cur->next = cur1; cur1 = cur1->next; } else{ cur->next = cur2; cur2 = cur2->next; } cur = cur->next; } if(cur1 != NULL){ cur->next = cur1; } if(cur2 != NULL){ cur->next = cur2; } ListNode* ret = h->next; delete h; return ret; } };
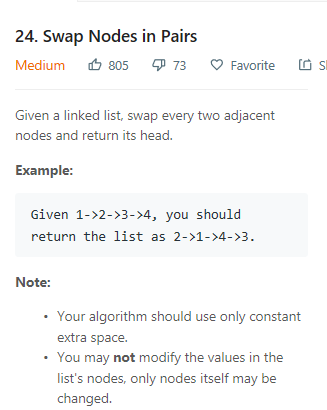

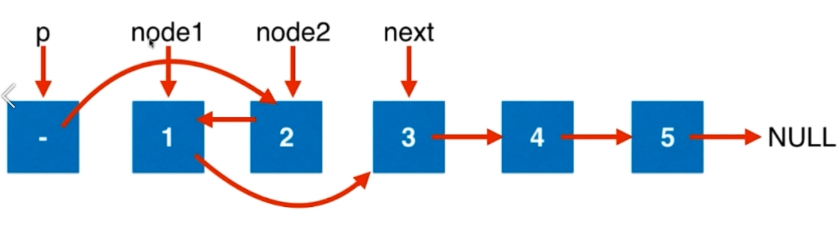

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) { ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead->next = head; ListNode* p = dummyHead; while(p->next && p->next->next){ ListNode* node1 = p->next; ListNode* node2 = node1->next; ListNode* next = node2->next; node2->next = node1; node1->next = next; p->next = node2; p = node1; } ListNode* ret = dummyHead->next; delete dummyHead; return ret; } };


/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) { if(!head || k==1) return head; ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); ListNode* pre = dummy, *cur = head; dummy->next = head; int i = 0; while(cur){ i++; if(i%k == 0){ pre = reverseOneGroup(pre, cur->next); cur = pre->next; } else{ cur = cur->next; } } return dummy->next; } ListNode* reverseOneGroup(ListNode* pre, ListNode* next){ ListNode* last = pre->next; ListNode* cur = last->next; while(cur!=next) { last->next = cur->next; cur->next = pre->next; //注意这里是指向pre->next pre->next = cur; cur = last->next; } return last; //返回需要翻转的最后一个元素 } };

用链表来实现插入排序。
思路:创建一个辅助的新链表,并且使用一个指针遍历原链表,每次将原链表中的一个节点插入到新链表的合适位置(即该节点的值大于新链表上的节点的值,又小于后一节点的值)。最后将新链表的头部返回即可。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head; ListNode* pre = new ListNode(-1), *ans = pre; //创建一个新链表的头结点,并用一个临时变量来保存 ListNode* cur = head; //cur是原链表的指针 while(cur != NULL){ //每次循环前重置pre为头结点,保证每次都从头到尾遍历 pre = ans; while(pre->next != NULL && pre->next->val < cur->val){ pre = pre->next; } //此时,pre->next->val大于cur->val,应把cur插入到pre后 //保存原链表当前节点的下一个节点 ListNode* tmp = cur->next; //插入cur到pre后 cur->next = pre->next; pre->next = cur; cur = tmp; //cur在原链表中后移一位 } return ans->next; } };
一样的思路,又写了一遍,创建一个新链表,dummy指向新链表的头结点。扫描原链表,对于每个结点v,从前往后扫描已排序好的结果链表,找到第一个比v大的u结点,将v插入到u之前。
时间复杂度:共遍历n个结点,为每个结点找到合适的位置,最多再遍历n次,所以总的时间复杂度是O(n^2)
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) { ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(-1); //dummy指向已排序链表的头结点 while(head){ ListNode* next = head->next; ListNode *p = dummy; while(p->next && p->next->val <= head->val) p = p -> next; //p->next指向比head大的第一个结点,则p指向比head小的最后一个结点 //将head插入到p和p->next之间 head->next = p->next; p->next = head; head = next; } return dummy->next; } };
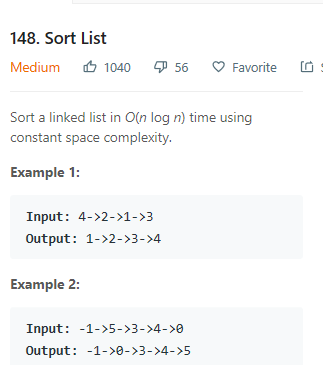
本题适用于归并排序,难点是:怎么样找到分治时的middle指针,采用快慢指针的思想。快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,当快指针走到头时,慢指针刚好走到中间位置,此位置即为middle的位置。
快慢指针思想:
快慢指针是指指针移动的步长,快指针移动的快,慢指针移动的慢,例如可以让快指针一次移动两个步长,让慢指针一次移动一个步长。
快慢指针有两个比较重要的应用:
1、判断链表是否为单链表
2、在有序链表中寻找中位数
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) { //将一个链表平分为两个链表 if(!head || !head->next) return head; ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head, *pre = head; while(fast && fast->next){ pre = slow; slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } pre->next = NULL; return merge(sortList(head), sortList(slow)); } ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2){ ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); ListNode* cur = dummy; while(l1 && l2){ if(l1->val < l2->val){ cur->next = l1; l1 = l1->next; } else{ cur->next = l2; l2 = l2->next; } cur = cur->next; } if(l1) cur->next = l1; if(l2) cur->next = l2; return dummy->next; } };


改变节点的值来解决问题。

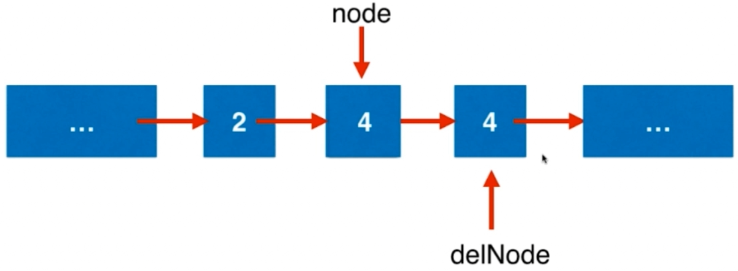
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void deleteNode(ListNode* node) { if(node == NULL) return; if(node->next == NULL){ delete node; node = NULL; return; } node->val = node->next->val; ListNode* delNode = node->next; node->next = delNode->next; delete delNode; return; } };