发现自己已经有很长一段时间写代码没什么进步了,随便读读FCL的源码,看看之前一直用的方法是如何实现的,也顺便提高下自己。FCL很是庞大,很难下口,于是用最笨的办法,先看常见的命名空间,逐个展开。战五渣的水平,必定有很多理解上的错误,欢迎斧正,不胜感激。
System.Collections 命名空间中的集合包含(如列表、队列、位数组、哈希表和字典)的集合。
本篇目录:
集合的接口
在刚开始写程序的时候的时候经常会写一些接口,哪怕这个接口只被用到了一次,也要抽象一个接口出来,这样显得牛X一些。到后来,接口几乎从日常的代码中消失,能简单就简单。看了FCL的源码,发现,这些接口很有必要,而且抽象的恰到好处,不经拍案叫绝。
很难想象,如果没有这些接口,庞大的FCL将如何构建,如何约束那些类。每个集合的操作方法类似,名称各不相同,对于使用者来说,也绝对是件很苦逼的事情。接口 是一种规范,实现了某一个接口,便具备了改接口的功能。所以了解某一个集合的性质和功能,首先需要了解它实现了哪些接口。
集合中常见的接口有IEnumerable,IEnumerator,ICollection,IComparer,IDictionary,IDictionaryEnumerator,ListDictionaryInternal,IEnumerator,IHashCodeProvider,IList,IStructuralComparable等。彻底晕菜了!新建 Class Diagram ,将几个主要接口拖入后,结构便很清晰了。
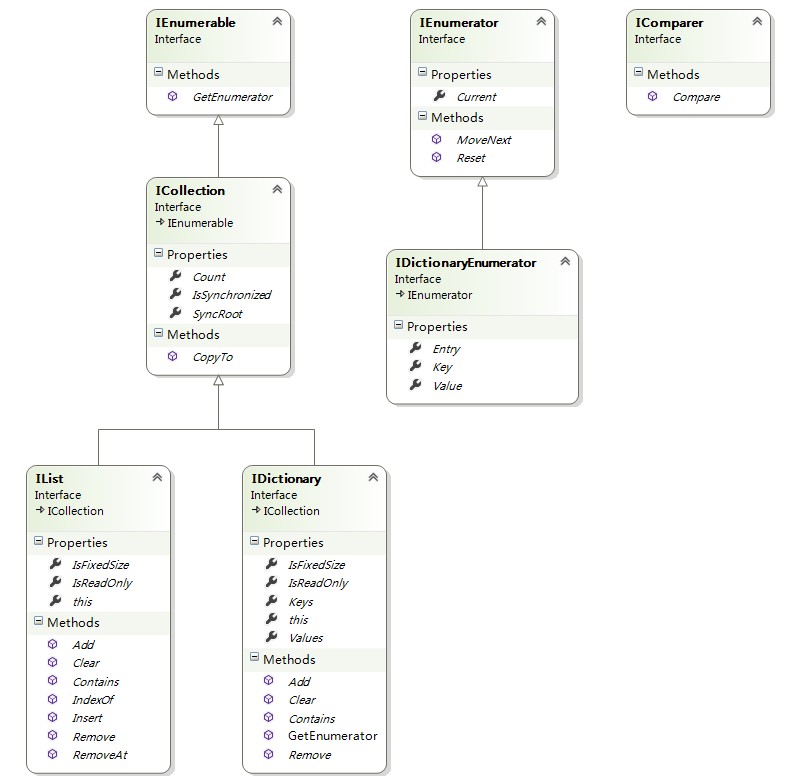
所有的集合都是继承了IEnumerable,逐个分析每个接口的实现。IEnumerable的源码,其中 PureAttribute来表示自己是很纯的,协定的东西。DispId 属性被用来指定一个OLE 的自动化 DISPID,COM交互时会使用。查了下使用的地方在 ComAwareEventInfo.cs 中,请自行查阅。 IEnumerator GetEnumerator(); 使用了组合模式,正是因为这个方法,所有的集合才可以使用Foreach方法。在后面研究集合的时候会详细的看下IEnumerator的实现。
IEnumerable源码
public interface IEnumerable
{
// Interfaces are not serializable
// Returns an IEnumerator for this enumerable Object. The enumerator provides
// a simple way to access all the contents of a collection.
[Pure]
[DispId(-4)]
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
}
IEnumerator源码
public interface IEnumerator
{
bool MoveNext();//索引位置向后移
Object Current {//当前对象
get;
}
void Reset();//重置索引到第一个位置
}
接口ICollection 继承了IEnumerable,定义了集合基本的元素,大小(count)枚举器(继承自IEnumerable 的GetEnumerator),同步方法(使用 IsSynchronized,SyncRoot),这里涉及一个锁的问题,如果对这个集合元素锁定后不可读与写,那么锁定这个集合的本身,如果锁定这个集合,不可写,可以读,那么锁定这个集合的SyncRoot。为什么使用Synchronized 方法返回的类是线程安全的呢,来看下具体的实现方式吧,以ArrayList为例
var al= ArrayList.Synchronized(new ArrayList());
public static ArrayList Synchronized(ArrayList list) {
if (list==null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("list");
Contract.Ensures(Contract.Result<ArrayList>() != null);
Contract.EndContractBlock();
return new SyncArrayList(list);
}
具体的实现在SyncArrayList中下面是部分源码:
private class SyncArrayList : ArrayList
{
private ArrayList _list;
private Object _root;
internal SyncArrayList(ArrayList list)
: base( false )
{
_list = list;
_root = list.SyncRoot;
}
public override int Capacity {
get {
lock(_root) {
return _list.Capacity;
}
}
[SuppressMessage("Microsoft.Contracts", "CC1055")] // Skip extra error checking to avoid *potential* AppCompat problems.
set {
lock(_root) {
_list.Capacity = value;
}
}
}
public override int Count {
get { lock(_root) { return _list.Count; } }
}
public override bool IsReadOnly {
get { return _list.IsReadOnly; }
}
public override bool IsFixedSize {
get { return _list.IsFixedSize; }
}
public override bool IsSynchronized {
get { return true; }
}
public override Object this[int index] {
get {
lock(_root) {
return _list[index];
}
}
set {
lock(_root) {
_list[index] = value;
}
}
}
public override Object SyncRoot {
get { return _root; }
}
public override int Add(Object value) {
lock(_root) {
return _list.Add(value);
}
}
...
}
}
实现的方式也很简单,所有的数据操作全部上锁,所以就线程安全了
学习数据结构的时候,线性表有几种操作,初始化,清空,获取某一个位置元素,判断元素是否存在,插入,删除,获取长度。很多元素是可以标准化的,IList就是干这个的。
IList的具体实现:
public interface IList : ICollection
{
//索引器
Object this[int index] {
get;
set;
}
//插入
int Add(Object value);
//判断是否包含
bool Contains(Object value);
//清空
void Clear();
//判断是否为只读 只读集合在创建之后不允许添加、移除或修改元素。
bool IsReadOnly
{ get; }
//是否是固定大小
bool IsFixedSize
{
get;
}
//取元素索引值
int IndexOf(Object value);
//指定索引位置插入元素
void Insert(int index, Object value);
//删除某个元素
void Remove(Object value);
//删除指定索引的元素
void RemoveAt(int index);
}
字典集合的抽象接口为IDictionary,字典类型的操作有,获取keys,获取values,添加,删除,清空等。实现源码如下:
public interface IDictionary : ICollection
{
// Interfaces are not serializable
// The Item property provides methods to read and edit entries
// in the Dictionary.
Object this[Object key] {
get;
set;
}
// Returns a collections of the keys in this dictionary.
ICollection Keys {
get;
}
// Returns a collections of the values in this dictionary.
ICollection Values {
get;
}
// Returns whether this dictionary contains a particular key.
//
bool Contains(Object key);
// Adds a key-value pair to the dictionary.
void Add(Object key, Object value);
// Removes all pairs from the dictionary.
void Clear();
bool IsReadOnly
{ get; }
bool IsFixedSize
{ get; }
// Returns an IDictionaryEnumerator for this dictionary.
new IDictionaryEnumerator GetEnumerator();
// Removes a particular key from the dictionary.
//
void Remove(Object key);
}
ArrayList
ArrayList动态容量的实现
ArrayList 为动态数组,动态的添加和减少线性表的长度,不用担心长度不够而抛异常。首先我们来探究下,这个动态的长度是如何实现的。查看arraylist.cs文件。
public virtual int Add(Object value) {
Contract.Ensures(Contract.Result<int>() >= 0);
if (_size == _items.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1);
_items[_size] = value;
_version++;
return _size++;
}
ArrayList添加元素方法, Contract.Ensures(Contract.Result<int>() >= 0);这句可以忽略,契约式编程,可以自己搜索。顺腾摸瓜,进入EnsureCapacity函数:
private void EnsureCapacity(int min) {
if (_items.Length < min) {
int newCapacity = _items.Length == 0? _defaultCapacity: _items.Length * 2;//定义一个新的容量,如果当然容量是0,就用默认的,否则就当前容量*2
// Allow the list to grow to maximum possible capacity (~2G elements) before encountering overflow.
// Note that this check works even when _items.Length overflowed thanks to the (uint) cast
if ((uint)newCapacity > Array.MaxArrayLength) newCapacity = Array.MaxArrayLength;//如果新的容量比Array数组的最大值还大,那么就赋最大的值
if (newCapacity < min) newCapacity = min;//如果新的容量比传入的最小值要小,那么赋最小值
Capacity = newCapacity;//容量等于新的容量
}
}
学过数据结构我们都知道,线性表增加容量,肯定要移动元素的。这个地方没看到,那么在找Capacity的Set方法。如下:
public virtual int Capacity {
get {
Contract.Ensures(Contract.Result<int>() >= Count);
return _items.Length;
}
set {
if (value < _size) {
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("value", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_SmallCapacity"));
}
Contract.Ensures(Capacity >= 0);
Contract.EndContractBlock();
// We don't want to update the version number when we change the capacity.
// Some existing applications have dependency on this.
if (value != _items.Length) {
if (value > 0) {
Object[] newItems = new Object[value];
if (_size > 0) {
Array.Copy(_items, 0, newItems, 0, _size);//ArrayList的长度发生改变时,就要来一次迁移
}
_items = newItems;
}
else {
_items = new Object[_defaultCapacity];
}
}
}
}
private const int _defaultCapacity = 4;默认的容量是4.不管容量是变大还是变小,都要移动元素,性能肯定是会有到影响的。
ArrayList 方法底层实现探究
继续跟踪Array.Copy 来看下具体是怎么实现的,最后跟踪的代码:
[System.Security.SecurityCritical] // auto-generated
[ReliabilityContract(Consistency.MayCorruptInstance, Cer.MayFail)]
[ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.None)]
[MethodImplAttribute(MethodImplOptions.InternalCall)]
internal static extern void Copy(Array sourceArray, int sourceIndex, Array destinationArray, int destinationIndex, int length, bool reliable);
[MethodImplAttribute(MethodImplOptions.InternalCall)]由这个属性猜出来,这个是CLR内部实现的,没法看。好奇心有强怎么办,好吧,拿出sscli(.net 2.0 的clr源码),在ecall.cpp里面看到这个
FCFuncElement("Copy", SystemNative::ArrayCopy)//
仔细看,能看出个大概。经过阅读FCL源码会发现,几乎所有的集合Copy,CopyTo 方法,最终都是调用Array.Copy,Array.Copy最终调用的是下面这个CLR中的方法
CLR中的源码如下:
FCIMPL6(void, SystemNative::ArrayCopy, ArrayBase* m_pSrc, INT32 m_iSrcIndex, ArrayBase* m_pDst, INT32 m_iDstIndex, INT32 m_iLength, CLR_BOOL reliable)
{
BYTE *src;
BYTE *dst;
int size;
struct _gc
{
BASEARRAYREF pSrc;
BASEARRAYREF pDst;
} gc;
gc.pSrc = (BASEARRAYREF)m_pSrc;
gc.pDst = (BASEARRAYREF)m_pDst;
//
// creating a HelperMethodFrame is quite expensive,
// so we want to delay this for the most common case which doesn't trigger a GC.
// FCThrow is needed to throw an exception without a HelperMethodFrame
//
WRAPPER_CONTRACT;
STATIC_CONTRACT_SO_TOLERANT;
// cannot pass null for source or destination
if (gc.pSrc == NULL || gc.pDst == NULL) {
FCThrowArgumentNullVoid(gc.pSrc==NULL ? L"source" : L"dest");
}
// source and destination must be arrays
_ASSERTE(gc.pSrc->GetMethodTable()->IsArray());
_ASSERTE(gc.pDst->GetMethodTable()->IsArray());
g_IBCLogger.LogEEClassAndMethodTableAccess(gc.pSrc->GetArrayClass());
// Equal method tables should imply equal rank
_ASSERTE(!(gc.pSrc->GetMethodTable() == gc.pDst->GetMethodTable() && gc.pSrc->GetRank() != gc.pDst->GetRank()));
// Which enables us to avoid touching the EEClass in simple cases
if (gc.pSrc->GetMethodTable() != gc.pDst->GetMethodTable() && gc.pSrc->GetRank() != gc.pDst->GetRank()) {
FCThrowResVoid(kRankException, L"Rank_MustMatch");
}
// Variant is dead.
_ASSERTE(gc.pSrc->GetMethodTable() != COMVariant::s_pVariantClass);
_ASSERTE(gc.pDst->GetMethodTable() != COMVariant::s_pVariantClass);
int srcLB = gc.pSrc->GetLowerBoundsPtr()[0];
int destLB = gc.pDst->GetLowerBoundsPtr()[0];
// array bounds checking
const unsigned int srcLen = gc.pSrc->GetNumComponents();
const unsigned int destLen = gc.pDst->GetNumComponents();
if (m_iLength < 0)
FCThrowArgumentOutOfRangeVoid(L"length", L"ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum");
if (m_iSrcIndex < srcLB || (m_iSrcIndex - srcLB < 0))
FCThrowArgumentOutOfRangeVoid(L"srcIndex", L"ArgumentOutOfRange_ArrayLB");
if (m_iDstIndex < destLB || (m_iDstIndex - destLB < 0))
FCThrowArgumentOutOfRangeVoid(L"dstIndex", L"ArgumentOutOfRange_ArrayLB");
if ((DWORD)(m_iSrcIndex - srcLB + m_iLength) > srcLen)
FCThrowResVoid(kArgumentException, L"Arg_LongerThanSrcArray");
if ((DWORD)(m_iDstIndex - destLB + m_iLength) > destLen)
FCThrowResVoid(kArgumentException, L"Arg_LongerThanDestArray");
int r = 0;
// Small perf optimization - we copy from one portion of an array back to
// itself a lot when resizing collections, etc. The cost of doing the type
// checking is significant for copying small numbers of bytes (~half of the time
// for copying 1 byte within one array from element 0 to element 1).
if (gc.pSrc == gc.pDst)
r = AssignWillWork;
else
r = CanAssignArrayTypeNoGC(gc.pSrc, gc.pDst);
if (r == AssignWrongType) {
FCThrowResVoid(kArrayTypeMismatchException, L"ArrayTypeMismatch_CantAssignType");
}
if (r == AssignWillWork) {
src = (BYTE*)gc.pSrc->GetDataPtr();
dst = (BYTE*)gc.pDst->GetDataPtr();
size = gc.pSrc->GetMethodTable()->GetComponentSize();
g_IBCLogger.LogMethodTableAccess(gc.pSrc->GetMethodTable());
m_memmove(dst + ((m_iDstIndex - destLB) * size), src + ((m_iSrcIndex - srcLB) * size), m_iLength * size);
if (gc.pDst->GetMethodTable()->ContainsPointers())
{
GCHeap::GetGCHeap()->SetCardsAfterBulkCopy( (Object**) (dst + (m_iDstIndex * size)), m_iLength * size);
}
FC_GC_POLL();
return;
}
else if (reliable) {
FCThrowResVoid(kArrayTypeMismatchException, L"ArrayTypeMismatch_ConstrainedCopy");
}
BOOL castEachElement = false;
BOOL boxEachElement = false;
BOOL unboxEachElement = false;
BOOL primitiveWiden = false;
HELPER_METHOD_FRAME_BEGIN_PROTECT(gc);
if (r == AssignDontKnow)
{
r = CanAssignArrayType(gc.pSrc, gc.pDst);
}
CONSISTENCY_CHECK(r != AssignDontKnow);
switch (r)
{
case AssignWrongType:
COMPlusThrow(kArrayTypeMismatchException, L"ArrayTypeMismatch_CantAssignType");
break;
case AssignMustCast:
castEachElement = true;
break;
case AssignWillWork:
break;
case AssignBoxValueClassOrPrimitive:
boxEachElement = true;
break;
case AssignUnboxValueClassAndCast:
castEachElement = true;
unboxEachElement = true;
break;
case AssignPrimitiveWiden:
primitiveWiden = true;
break;
default:
_ASSERTE(!"Fell through switch in Array.Copy!");
}
// If we were called from Array.ConstrainedCopy, ensure that the array copy
// is guaranteed to succeed.
_ASSERTE(!reliable || r == AssignWillWork);
if (m_iLength > 0)
{
// Casting and boxing are mutually exclusive. But casting and unboxing may
// coincide -- they are handled in the UnboxEachElement service.
_ASSERTE(!boxEachElement || !castEachElement);
if (r == AssignWillWork)
{
src = (BYTE*)gc.pSrc->GetDataPtr();
dst = (BYTE*)gc.pDst->GetDataPtr();
size = gc.pSrc->GetMethodTable()->GetComponentSize();
g_IBCLogger.LogMethodTableAccess(gc.pSrc->GetMethodTable());
m_memmove(dst + ((m_iDstIndex - destLB) * size), src + ((m_iSrcIndex - srcLB) * size), m_iLength * size);
if (gc.pDst->GetMethodTable()->ContainsPointers())
{
GCHeap::GetGCHeap()->SetCardsAfterBulkCopy( (Object**) (dst + (m_iDstIndex * size)), m_iLength * size);
}
}
else if (unboxEachElement)
{
UnBoxEachElement(gc.pSrc, m_iSrcIndex - srcLB, gc.pDst, m_iDstIndex - destLB, m_iLength, castEachElement);
}
else if (boxEachElement)
{
BoxEachElement(gc.pSrc, m_iSrcIndex - srcLB, gc.pDst, m_iDstIndex - destLB, m_iLength);
}
else if (castEachElement)
{
_ASSERTE(!unboxEachElement); // handled above
CastCheckEachElement(gc.pSrc, m_iSrcIndex - srcLB, gc.pDst, m_iDstIndex - destLB, m_iLength);
}
else if (primitiveWiden)
{
PrimitiveWiden(gc.pSrc, m_iSrcIndex - srcLB, gc.pDst, m_iDstIndex - destLB, m_iLength);
}
}
HELPER_METHOD_FRAME_END();
}
FCIMPLEND
IndexOf 的具体实现如下,为了更容易阅读,我把里面的前置判断去掉了。可以看到一个简单的函数,但是极为严谨,再回想自己写的代码,弱爆了。加了一点注释。
public static int IndexOf(Array array, Object value, int startIndex, int count) {
int lb = array.GetLowerBound(0);
// Try calling a quick native method to handle primitive types.
int retVal;
bool r = TrySZIndexOf(array, startIndex, count, value, out retVal);
if (r)
return retVal;
Object[] objArray = array as Object[]; //转换为object 数组
int endIndex = startIndex + count;
if (objArray != null) { //转换之后不为null
if (value == null) { //如果传入的值为null,则查找objArray里面为null的,返回改值的位置
for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
if (objArray[i] == null) return i;
}
}
else {//如果传入的值不为null,则逐个查找,找到后返回该值的位置
for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
Object obj = objArray[i]; //这个地方为什么要单独出来呢,直接这样 if (objArray[i]!= null && objArray[i].Equals(value)) ,之前自己的代码全是这么写的。
// 仔细推敲下,在if()里面只要取一次就好,性能应该可以稍微快一点。
if (obj != null && obj.Equals(value)) return i;
}
}
}
else {
for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
Object obj = array.GetValue(i);//这个地方应该和上面类似
if( obj == null) {
if(value == null) return i;
}
else {
if( obj.Equals(value)) return i;
}
}
}
// Return one less than the lower bound of the array. This way,
// for arrays with a lower bound of -1 we will not return -1 when the
// item was not found. And for SZArrays (the vast majority), -1 still
// works for them.
return lb-1;
}
里面的调用,可以在sscli中找到具体的实现
bool r = TrySZIndexOf(array, startIndex, count, value, out retVal);
最终的c++代码,很简单不是么
static int IndexOf(KIND array[], UINT32 index, UINT32 count, KIND value) {
LEAF_CONTRACT;
_ASSERTE(array != NULL && index >= 0 && count >= 0);
for(UINT32 i=index; i<index+count; i++)
if (array[i] == value)
return i;
return -1;
}
LastIndexOf方法和IndexOf方法类似,不详细看了。看下Add和Insert方法的实现:
public virtual int Add(Object value) {
if (_size == _items.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1);//首先确保容量要够,不够会自动成倍添加,上面说过
_items[_size] = value;
_version++;
return _size++;
}
public virtual void Insert(int index, Object value) {
if (index < 0 || index > _size) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("index", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_ArrayListInsert"));
if (_size == _items.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1);
if (index < _size) {//如果插入的index比当前的长度要小,那么index之后的元素要后移
Array.Copy(_items, index, _items, index + 1, _size - index); //调用内部方法,上面已给出
}
_items[index] = value;
_size++;
_version++;
}
有源码可以看出,Add方法是直接添加到线性表的表尾,Insert方法是直接插入到指定位置,制定位置之后的元素要依次后移。显然Add方法的效率要高一些。用于添加的方法还有 AddRange和InsertRange,顾名思义就是插入一个范围数据即插入集合。那这两个方法有什么异同呢?先看AddRange吧
public virtual void AddRange(ICollection c) {
InsertRange(_size, c);
}
AddRange的方法是直接调用的InsertRange,从末尾插入一个集合。InsertRange源码如下:
public virtual void InsertRange(int index, ICollection c) {
int count = c.Count;
if (count > 0) {
EnsureCapacity(_size + count);
// shift existing items
if (index < _size) {//依次向后移位,腾出位置
Array.Copy(_items, index, _items, index + count, _size - index);
}
Object[] itemsToInsert = new Object[count];//新建一个object数组
c.CopyTo(itemsToInsert, 0);//将新加的集合拷贝到新建的object数组中
itemsToInsert.CopyTo(_items, index);//再讲这个新建的数组拷贝到源列表中
_size += count;
_version++;
}
}
下面看下ArrayList的排序方法的实现Sort:
public virtual void Sort()
{
Sort(0, Count, Comparer.Default);
}
//fcl里的最终的实现
public static void Sort(Array keys, Array items, int index, int length, IComparer comparer) {
if (length > 1) {
//如果是默认的,那么调用内部方法,下面会详细给出
if (comparer == Comparer.Default || comparer == null) {
bool r = TrySZSort(keys, items, index, index + length - 1);
if (r)
return;
}
Object[] objKeys = keys as Object[];
Object[] objItems = null;
if (objKeys != null)
objItems = items as Object[];
if (objKeys != null && (items==null || objItems != null)) {
SorterObjectArray sorter = new SorterObjectArray(objKeys, objItems, comparer);
sorter.QuickSort(index, index + length - 1);
}
else {
SorterGenericArray sorter = new SorterGenericArray(keys, items, comparer);
sorter.QuickSort(index, index + length - 1);
}
}
}
可以自己实现一个比较器IComparer,也可以使用默认的比较器。如果使用的是默认的比较器,那么将会调用clr底层的快速排序方法,下面是从sscli中查到的C++源码:
static void QuickSort(KIND keys[], KIND items[], int left, int right) {//KIND 在头部给出了定义 template <class KIND>
WRAPPER_CONTRACT;
// Make sure left != right in your own code.
_ASSERTE(keys != NULL && left < right);
do {
int i = left;
int j = right;
KIND x = keys[i + ((j - i) >> 1)];
do {
while (keys[i] < x) i++;
while (x < keys[j]) j--;
_ASSERTE(i>=left && j<=right);
if (i > j) break;
if (i < j) {
KIND key = keys[i];
keys[i] = keys[j];
keys[j] = key;
if (items != NULL) {
KIND item = items[i];
items[i] = items[j];
items[j] = item;
}
}
i++;
j--;
} while (i <= j);
if (j - left <= right - i) {
if (left < j) QuickSort(keys, items, left, j);
left = i;
}
else {
if (i < right) QuickSort(keys, items, i, right);
right = j;
}
} while (left < right);
}
和Sort方法类似,BinarySearch(二分查找)方法也可以使用自定义的比较器看下BinarySearch的具体实现:
public static int BinarySearch(Array array, int index, int length, Object value, IComparer comparer) {
//去掉一些前置判断
if (comparer == null) comparer = Comparer.Default;
if (comparer == Comparer.Default) {
int retval;
bool r = TrySZBinarySearch(array, index, length, value, out retval);
if (r)
return retval;
}
int lo = index;
int hi = index + length - 1;
Object[] objArray = array as Object[];
if(objArray != null) {
while (lo <= hi) {
// i might overflow if lo and hi are both large positive numbers.
int i = GetMedian(lo, hi);//取中位数
int c;
try {
c = comparer.Compare(objArray[i], value);//比较这个中间值是否是要查找的值,c=0找到 c为负数在右边,c为正数在左边
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new InvalidOperationException(Environment.GetResourceString("InvalidOperation_IComparerFailed"), e);
}
if (c == 0) return i; //找到,返回下标
if (c < 0) {
lo = i + 1;
}
else {
hi = i - 1;
}
}
}
else {
while (lo <= hi) {
int i = GetMedian(lo, hi);
int c;
try {
c = comparer.Compare(array.GetValue(i), value);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new InvalidOperationException(Environment.GetResourceString("InvalidOperation_IComparerFailed"), e);
}
if (c == 0) return i;
if (c < 0) {
lo = i + 1;
}
else {
hi = i - 1;
}
}
}
return ~lo;
}
看下这个TrySZBinarySearch在clr中的具体实现吧,同样很易懂。
static int BinarySearchBitwiseEquals(KIND array[], int index, int length, KIND value) {
WRAPPER_CONTRACT;
_ASSERTE(array != NULL && length >= 0 && index >= 0);
int lo = index;
int hi = index + length - 1;
// Note: if length == 0, hi will be Int32.MinValue, and our comparison
// here between 0 & -1 will prevent us from breaking anything.
while (lo <= hi) {
int i = lo + ((hi - lo) >> 1);
if (array[i] < value) {
lo = i + 1;
}
else if (array[i] > value){
hi = i - 1;
}
else {
return i;
}
}
return ~lo;
}
ArrayList的其他方法,也极为易懂和类似,不在罗列。
Queue
队列是特殊的线性表,先进先出的结构。从源码中可以看出,FCL中的Queue是一种循环队列。先看Queue的属性
private Object[] _array; //存储的数据
private int _head; // 对一个有效元素
private int _tail; // 最后一个有效元素
private int _size; // 元素数量
private int _growFactor; // 增长因素 100 == 1.0, 130 == 1.3, 200 == 2.0,取值范围 1.0到10.0之间
private int _version;
[NonSerialized]
private Object _syncRoot;
private const int _MinimumGrow = 4; //最小增长量
private const int _ShrinkThreshold = 32;//这个地方极为扯淡,定义了没用,下面直接写死32
初始化:
public Queue()
: this(32, (float)2.0) {
}
// Creates a queue with room for capacity objects. The default grow factor
// is used.
//
public Queue(int capacity)
: this(capacity, (float)2.0) {
}
// Creates a queue with room for capacity objects. When full, the new
// capacity is set to the old capacity * growFactor.
//
public Queue(int capacity, float growFactor) {
if (capacity < 0)
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("capacity", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum"));
if (!(growFactor >= 1.0 && growFactor <= 10.0))
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("growFactor", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_QueueGrowFactor", 1, 10));
Contract.EndContractBlock();
_array = new Object[capacity];
_head = 0;
_tail = 0;
_size = 0;
_growFactor = (int)(growFactor * 100);
}
入队操作:
public virtual void Enqueue(Object obj) {
if (_size == _array.Length) {//如果队满,则重新分配容量
int newcapacity = (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_growFactor / 100);
if (newcapacity < _array.Length + _MinimumGrow) {//如果新分配的容量小于当前容量加上最小增长量,那么把当前容量加最小增长量分配给新分配的容量
newcapacity = _array.Length + _MinimumGrow;
}
SetCapacity(newcapacity);//重新设置容量
}
_array[_tail] = obj;
_tail = (_tail + 1) % _array.Length;//如果_taill+1<_array.Length 那么 _tail=_tail+1;否则,_tail=0;表示队列已满。
//循环队列的写法
_size++;
_version++;
}
private void SetCapacity(int capacity) {
Object[] newarray = new Object[capacity];
if (_size > 0) {
if (_head < _tail) {//环形队列头部项索引在尾部索引前面
Array.Copy(_array, _head, newarray, 0, _size);
} else {//环形队列头部项索引在尾部索引后面
Array.Copy(_array, _head, newarray, 0, _array.Length - _head);//copy _head 到 Length部分
Array.Copy(_array, 0, newarray, _array.Length - _head, _tail);//copy 0 到_tail 部分
}
}
_array = newarray;
_head = 0;
_tail = (_size == capacity) ? 0 : _size;
_version++;
}
出队操作Dequeue(),出队,并从队列中删除;Peek()方法,取队列的第一位元素,不从队列中删除。
public virtual Object Dequeue() {
if (Count == 0)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Environment.GetResourceString("InvalidOperation_EmptyQueue"));
Contract.EndContractBlock();
Object removed = _array[_head]; //取元素
_array[_head] = null; //删除元素
_head = (_head + 1) % _array.Length;//循环队列,头部索引移到下一位
_size--;
_version++;
return removed;
}
public virtual Object Peek() {
if (Count == 0)
throw new InvalidOperationException(Environment.GetResourceString("InvalidOperation_EmptyQueue"));
Contract.EndContractBlock();
return _array[_head];
}
可以看出队列的入队和出队的时间复杂度是O(1);但是入列的时候如果需要重置容量,那么时间复杂度会变为O(n)
队列中的其他操作:
//是否包含
public virtual bool Contains(Object obj) {
int index = _head;
int count = _size;
while (count-- > 0) {
if (obj == null) {
if (_array[index] == null)
return true;
} else if (_array[index] != null && _array[index].Equals(obj)) {
return true;
}
index = (index + 1) % _array.Length;//index向后移
}
return false;
}
//取某个元素
internal Object GetElement(int i){
return _array[(_head + i) % _array.Length]
}
和ArrayList类似,Queue也有线程安全的实现,Queue.Synchronized(),返回一个 同步Queue。实现的方式就是在队列的操作上加锁。
Stack
栈,先进后出,像弹夹。属性定义:
private Object[] _array; // Storage for stack elements
private int _size; // Number of items in the stack.
private int _version; // Used to keep enumerator in [....] w/ collection.
private Object _syncRoot;
private const int _defaultCapacity = 10;
可以看出栈的结构属性更为简单,默认的容量是10;初始化操作:
public Stack() {
_array = new Object[_defaultCapacity];
_size = 0;
_version = 0;
}
// Create a stack with a specific initial capacity. The initial capacity
// must be a non-negative number.
public Stack(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("initialCapacity", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum"));
Contract.EndContractBlock();
if (initialCapacity < _defaultCapacity)
initialCapacity = _defaultCapacity; // Simplify doubling logic in Push.
_array = new Object[initialCapacity];
_size = 0;
_version = 0;
}
入栈操作:
public virtual void Push(Object obj) {
//Contract.Ensures(Count == Contract.OldValue(Count) + 1);
if (_size == _array.Length) {//如果容量满了,那么成2倍增加
Object[] newArray = new Object[2*_array.Length];
Array.Copy(_array, 0, newArray, 0, _size);
_array = newArray;
}
_array[_size++] = obj;
_version++;
}
出栈操作:
public virtual Object Pop() {
_version++;
Object obj = _array[--_size];//取元素并将长度减1
_array[_size] = null; // 删除元素
return obj;
}
和Queue类似,Stack也有Peek操作,实现方式类似,同样也有Synchronized方法,实现方式也是类似的。
SortedList
属性:
private Object[] keys;//键数组
private Object[] values;//值数组
private int _size;
private int version;
private IComparer comparer;
private KeyList keyList;//建集合 继承IList 内部使用 SortList 与keys关联
private ValueList valueList;//值集合 继承IList 内部使用 SortList 与 values关联
[NonSerialized]
private Object _syncRoot;
private const int _defaultCapacity = 16;//默认容量 16
private static Object[] emptyArray = EmptyArray<Object>.Value;//空数组 等效 New Object[0];
SortedList的容量也是动态的
private void EnsureCapacity(int min) {
int newCapacity = keys.Length == 0? 16: keys.Length * 2;//2倍增上
// Allow the list to grow to maximum possible capacity (~2G elements) before encountering overflow.
// Note that this check works even when _items.Length overflowed thanks to the (uint) cast
if ((uint)newCapacity > Array.MaxArrayLength) newCapacity = Array.MaxArrayLength;
if (newCapacity < min) newCapacity = min;
Capacity = newCapacity;
}
public virtual int Capacity {
get {
return keys.Length;
}
set {
if (value < Count) {
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("value", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_SmallCapacity"));
}
Contract.EndContractBlock();
if (value != keys.Length) {
if (value > 0) {//如果容量发生改变,新建键数组和值指数组,并将源键值数组复制进去。如果新的容量不大于0则将键数组和值数组置空
Object[] newKeys = new Object[value];
Object[] newValues = new Object[value];
if (_size > 0) {
Array.Copy(keys, 0, newKeys, 0, _size);
Array.Copy(values, 0, newValues, 0, _size);
}
keys = newKeys;
values = newValues;
}
else {
// size can only be zero here.
Contract.Assert( _size == 0, "Size is not zero");
keys = emptyArray;
values = emptyArray;
}
}
}
}
SortedList 的IndexOfKey方法,可以发现内部使用二分法查找,具体C++代码上面ArrayList中已经给出。
public virtual int IndexOfKey(Object key) {
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("key", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentNull_Key"));
Contract.EndContractBlock();
int ret = Array.BinarySearch(keys, 0, _size, key, comparer);
return ret >=0 ? ret : -1;
}
SortedList的IndexOfValue方法内部也是调用的IndexOfKey这个方法,如下:
public virtual int IndexOfValue(Object value) {
return Array.IndexOf(values, value, 0, _size);
}
插入操作如下,很易懂。可以看出,Add一个元素的时候
private void Insert(int index, Object key, Object value) {
if (_size == keys.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1);
if (index < _size) {
Array.Copy(keys, index, keys, index + 1, _size - index);
Array.Copy(values, index, values, index + 1, _size - index);
}
keys[index] = key;
values[index] = value;
_size++;
version++;
}
public virtual void Add(Object key, Object value) {
if (key == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("key", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentNull_Key"));
Contract.EndContractBlock();
int i = Array.BinarySearch(keys, 0, _size, key, comparer);//这个地方是二分法查找。comparer是排序器,可以自己实现。默认的是按照key来排序。每次新添加元素都会重新排序。
if (i >= 0)
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_AddingDuplicate__", GetKey(i), key));
Insert(~i, key, value);//这个地方比较绕,Array.BinarySearch 如果找不到,返回的是index取反,结果为-1,在对这个-1取反,结果为0.在0这个位置插入
}
删除操作,同样也很易懂,代码如下:
public virtual void RemoveAt(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= Count) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("index", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_Index"));
Contract.EndContractBlock();
_size--;
if (index < _size) {
Array.Copy(keys, index + 1, keys, index, _size - index);
Array.Copy(values, index + 1, values, index, _size - index);
}
keys[_size] = null;
values[_size] = null;
version++;
}
public virtual void Remove(Object key) {
int i = IndexOfKey(key);
if (i >= 0)
RemoveAt(i);
}
同样的,SortedList也有线程同步的方法 SortedList.Synchronized() 实现方式和ArrayList,Queue,Stack 并无二致。
至此,告一段落。几个常用的集合,自己有了更为深刻的理解。阅读优秀的代码是一种享受,阅读渣渣的代码,是虐心!