算法 1
设半径为$R$。
$x = r ast cos( heta)$
$y = r ast sin( heta)$
其中 $0leqslant r leqslant R$,$t$为0-1均匀分布产生的随机数,$r = sqrt(t) ast R$,$ heta = 2pi ast t, t sim U(0, 1)$ 证明:url
1 import numpy as np 2 import random 3 import math 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 import matplotlib as mpl 6 mpl.rcParams['agg.path.chunksize'] = 10000 # the default is 0 7 N = int(10000) 8 x1 = 1.5 9 x2 = 0.5 10 radius = 2 11 a = 2 * math.pi * np.array([random.random() for _ in range(N)]) 12 r = np.array([random.random() for _ in range(N)]) 13 x = radius*np.sqrt(r)*np.cos(a) + x1; 14 y = radius*np.sqrt(r)*np.sin(a) + x2; 15 plt.scatter(x, y, s=1) 16 plt.show()
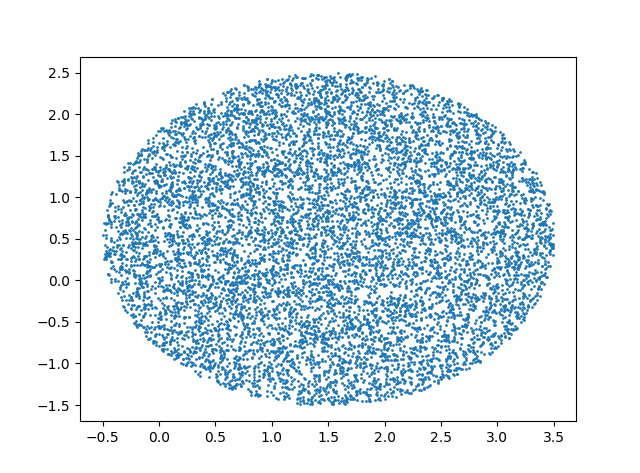
下面的算法是错误的
原因在于对$R$求开方,导致$r = sqrt(R)*t$平方后不在满足均匀分布。
1 import numpy as np 2 import random 3 import math 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 import matplotlib as mpl 6 mpl.rcParams['agg.path.chunksize'] = 10000 # the default is 0 7 N = int(10000) 8 x1 = 1.5 9 x2 = 0.5 10 radius = 2 11 a = 2 * math.pi * np.array([random.random() for _ in range(N)]) 12 r = np.array([random.random() for _ in range(N)]) 13 #x = radius*np.sqrt(r)*np.cos(a) + x1; 14 #y = radius*np.sqrt(r)*np.sin(a) + x2; 15 x = np.sqrt(radius)*r*np.cos(a) + x1; 16 y = np.sqrt(radius)*r*np.sin(a) + x2; 17 plt.scatter(x, y, s=1) 18 plt.show()
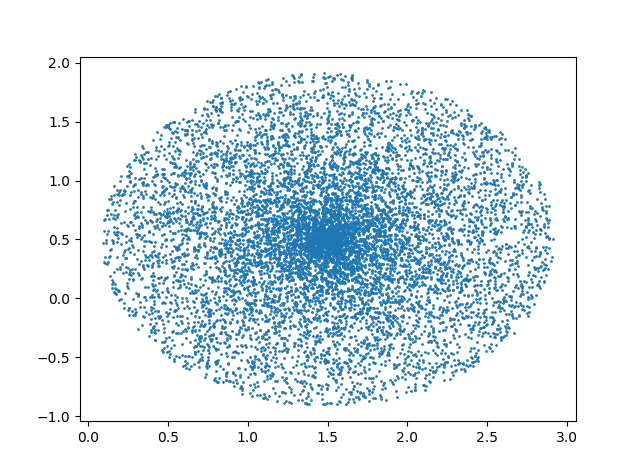
参考链接:JustDoIT