Lattice animal is a set of connected sites on a lattice. Lattice animals on a square lattice are especially popular subject of study and are also known as polyominoes. Polyomino is usually represented as a set of sidewise connected squares. Polyomino with n squares is called n-polyomino. In this problem you are to find a number of distinct free n-polyominoes that fit into rectangle w×h. Free polyominoes can be rotated and flipped over, so that their rotations and mirror images are considered to be the same. For example, there are 5 different pentominoes (5-polyominoes) that fit into 2×4 rectangle and 3 different octominoes (8-polyominoes) that fit into 3×3 rectangle.
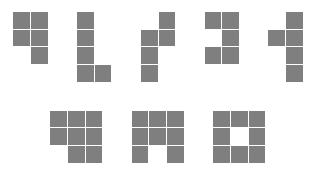
Input
The input file contains several test cases, one per line. This line consists of 3 integer numbers n, w, and h ( 1![]() n
n![]() 10, 1
10, 1![]() w, h
w, h![]() n).
n).
Output
For each one of the test cases, write to the output file a single line with a integer number -- the number of distinct free n-polyominoes that fit into rectangle w×h.
Sample Input
5 1 4 5 2 4 5 3 4 5 5 5 8 3 3
Sample Output
0 5 11 12 3
输入n,w,h (1<=n<=10,1<=w,h<=n),求能放在w*h网格里的不同的n连块的个数(注意,平移,旋转,翻转后相同的算作同一种)。例如,2*4里的5连块有5种(第一行),而3*3里的8连块有以下3种(第二行)。
难点:
1.以每个格子来扩展。先枚举1连块,在对1连块的每个格子的4个方向进行扩展,枚举2连块,依次类推。
2.将n连块表示成n个格子的集合,将所有的n连块又表示成集合,判重任务交给set.
3.判重时要将n连块进行8个方向的旋转,并且每个n连块需要规范化(左下角的格子在(0,0)).
4.得到n连块后判断是否能放进w*h的网格中,由于n连块已经规范化,得到n连块的格子最大x,y坐标,即能盛下该n连块的长和宽。
#include <cstdio>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 10
// 代表一个网格节点
typedef struct cell
{
int x, y; //网格节点的坐标
// 构造函数
cell(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
bool operator < (const struct cell& a) const
{
return x < a.x || (x == a.x && y < a.y);
}
}cell;
// 一个Polyomino就是一堆cell的集合
typedef set<cell> poly;
// poly_set[i]代表有i个cell的poly集合
set<poly> poly_set[maxn+1];
// answer[n][w][h]的答案
int answer[maxn+1][maxn+1][maxn+1];
void gen_poly();
void check_poly(const poly& this_p, cell& this_c);
poly normalize(poly& p);
poly rotate(poly& p);
poly flip(poly& p);
int main()
{
// 生成所有poly
gen_poly();
// printf("here
");
int n, w, h;
while(scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &w, &h) == 3)
{
printf("%d
", answer[n][w][h]);
}
return 0;
}
int dic_x[4] = {-1,0,1,0};
int dic_y[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
// 生成所有poly
void gen_poly()
{
for(int i = 1; i <= maxn; i++)
poly_set[i] = set<poly>();
// 先生成有1个cell的poly
poly p1;
p1.insert(cell(0,0));
poly_set[1].insert(p1);
// 分别根据有i-1个cell的poly集合来生成有i个cell的poly集合
for(int i = 2; i <= maxn; i++)
{
// 对每个poly中的每个cell尝试在不同的四个方向增加一个cell
for(set<poly>::iterator p = poly_set[i-1].begin(); p != poly_set[i-1].end(); p++)
{
for(poly::const_iterator q = p->begin(); q != p->end(); q++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
cell new_c(q->x+dic_x[j], q->y+dic_y[j]);
// cell new_c;
if(p->find(new_c) == p->end())
{
// 检查形成的这个poly是否存在,如果不存在就加入
check_poly(*p, new_c);
}
}
}
}
}
// 对所有n,w,h生成答案
for(int i = 1; i <= maxn; i++)
{
for(int w = 1; w <= i; w++)
{
for(int h = 1; h <= i; h++)
{
int count = 0;
for(set<poly>::iterator p = poly_set[i].begin(); p != poly_set[i].end(); p++)
{
int max_x = p->begin()->x, max_y = p->begin()->y;
for(poly::iterator q = p->begin(); q != p->end(); q++)
{
if(max_x < q->x)
max_x = q->x;
if(max_y < q->y)
max_y = q->y;
}
if(min(max_x, max_y) < min(w, h) && max(max_x, max_y) < max(w, h))
{
count++;
}
}
/* if(count != 0)
printf("answer[%d][%d][%d] = %d
", i, w, h, count);
*/ answer[i][w][h] = count;
}
}
}
}
// 检查形成的这个poly加上这个cell是否存在,如果不存在就加入
void check_poly(const poly& this_p, cell& this_c)
{
poly p = this_p;
p.insert(this_c);
// 规范化到最小点为(0,0)
p = normalize(p);
int n = p.size();
// 检查旋转的8个方向是否存在,如果不存在就加入到poly集合
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if(poly_set[n].find(p) != poly_set[n].end())
return;
// 对该poly向右旋转90度
p = rotate(p);
}
// 将该poly向下反转180度
p = flip(p);
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if(poly_set[n].find(p) != poly_set[n].end())
return;
// 对该poly向右旋转90度
p = rotate(p);
}
poly_set[n].insert(p);
}
// 规范化到最小点为(0,0)
poly normalize(poly& p)
{
poly this_p;
int min_x = p.begin()->x, min_y = p.begin()->y;
for(poly::iterator q = p.begin(); q != p.end(); q++)
{
if(q->x < min_x)
min_x = q->x;
if(q->y < min_y)
min_y = q->y;
}
for(poly::iterator q = p.begin(); q != p.end(); q++)
{
this_p.insert(cell(q->x-min_x,q->y-min_y));
}
return this_p;
}
// 对该poly向右旋转90度
poly rotate(poly& p)
{
poly this_p;
for(poly::iterator q = p.begin(); q != p.end(); q++)
{
this_p.insert(cell(q->y,-q->x));
}
return normalize(this_p);
}
// 将该poly向下反转180度
poly flip(poly& p)
{
poly this_p;
for(poly::iterator q = p.begin(); q != p.end(); q++)
{
this_p.insert(cell(q->x,-q->y));
}
return normalize(this_p);
}