搬讲义



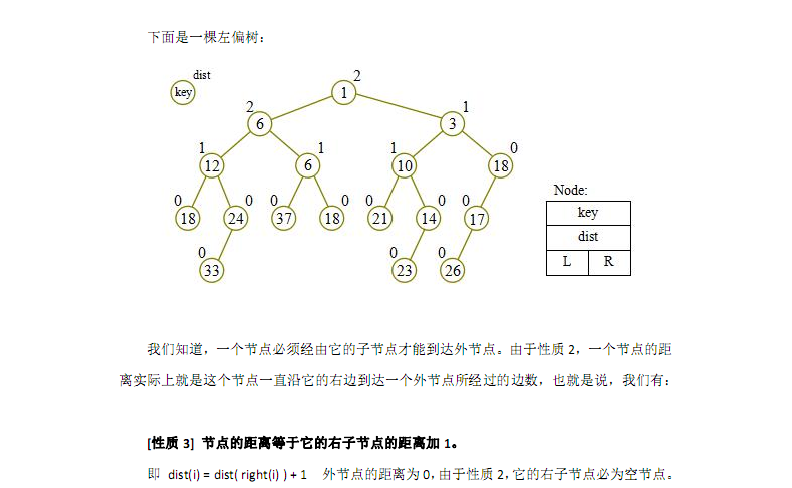


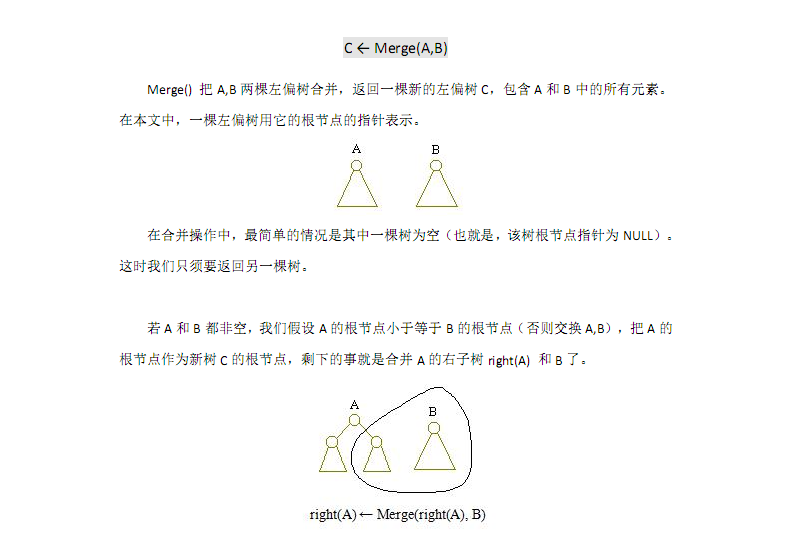
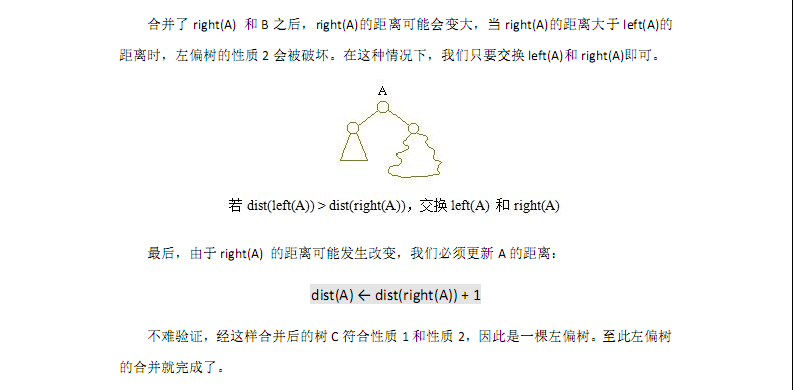
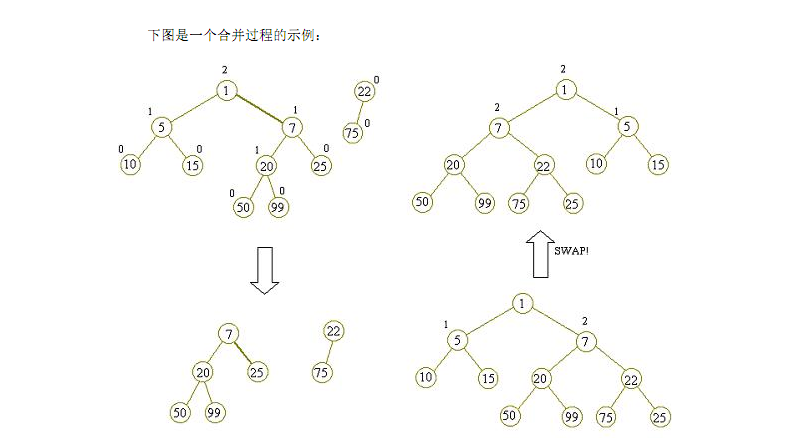
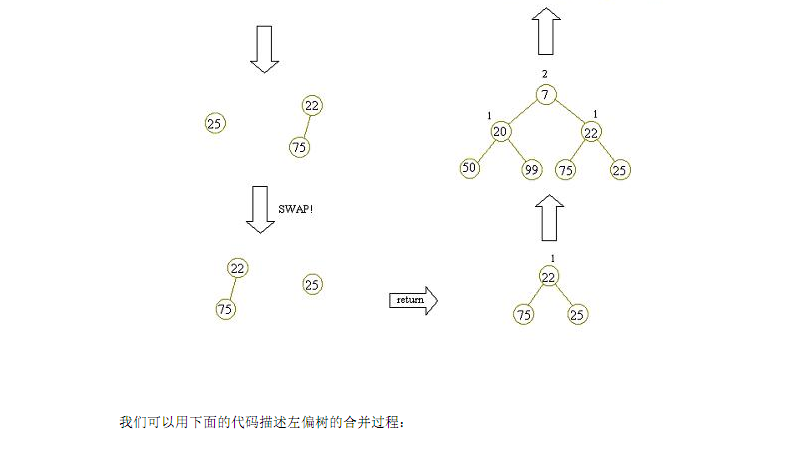



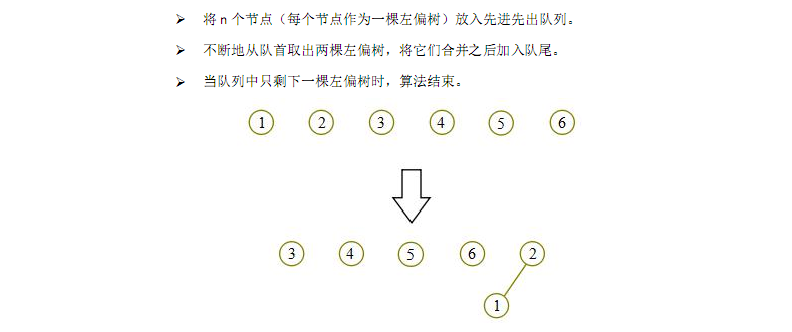
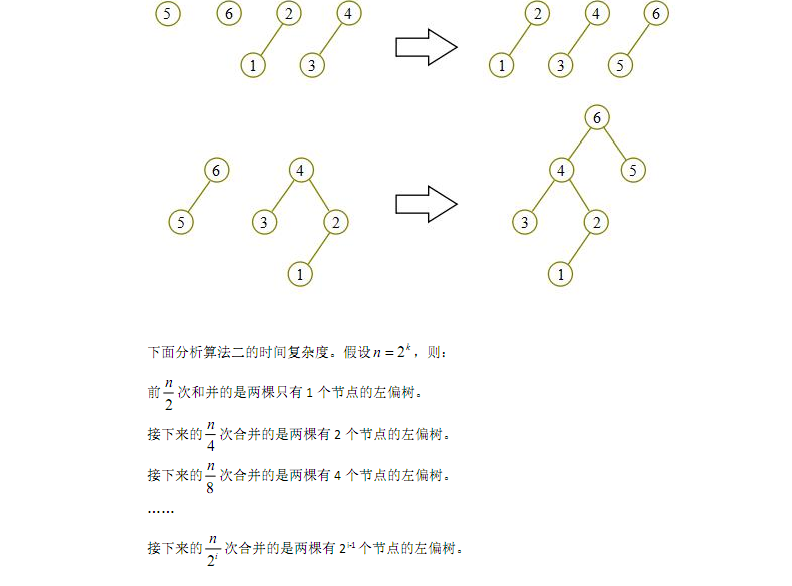

最后删除已知节点的操作我就不搬了···因为如果要执行这种操作了还不如用splay之类的平衡树······
例题1(罗马游戏 bzoj1455):
Description
罗马皇帝很喜欢玩杀人游戏。 他的军队里面有n个人,每个人都是一个独立的团。最近举行了一次平面几何测试,每个人都得到了一个分数。 皇帝很喜欢平面几何,他对那些得分很低的人嗤之以鼻。他决定玩这样一个游戏。 它可以发两种命令: 1. Merger(i, j)。把i所在的团和j所在的团合并成一个团。如果i, j有一个人是死人,那么就忽略该命令。 2. Kill(i)。把i所在的团里面得分最低的人杀死。如果i这个人已经死了,这条命令就忽略。 皇帝希望他每发布一条kill命令,下面的将军就把被杀的人的分数报上来。(如果这条命令被忽略,那么就报0分)
Input
第一行一个整数n(1<=n<=1000000)。n表示士兵数,m表示总命令数。 第二行n个整数,其中第i个数表示编号为i的士兵的分数。(分数都是[0..10000]之间的整数) 第三行一个整数m(1<=m<=100000) 第3+i行描述第i条命令。命令为如下两种形式: 1. M i j 2. K i
Output
如果命令是Kill,对应的请输出被杀人的分数。(如果这个人不存在,就输出0)
Sample Input
100 90 66 99 10
7
M 1 5
K 1
K 1
M 2 3
M 3 4
K 5
K 4
Sample Output
100
0
66
模板题····删除最小节点与合并操作···
注意每个堆的根节点用并查集维护····
代码:
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cctype> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=1000005; struct node { int l,r,dis,val,fa; bool ifdead; }p[N]; int n,m; inline int R() { char c;int f=0; for(c=getchar();c<'0'||c>'9';c=getchar()); for(;c<='9'&&c>='0';c=getchar()) f=(f<<3)+(f<<1)+c-'0'; return f; } inline int getfa(int a) { if(p[a].fa==a) return a; else return p[a].fa=getfa(p[a].fa); } inline int merge(int a,int b) { if(!a) return b; if(!b) return a; if(p[a].val>p[b].val) swap(a,b); p[a].r=merge(p[a].r,b); if(p[p[a].r].dis>p[p[a].l].dis) swap(p[a].l,p[a].r); p[a].dis=p[p[a].r].dis+1; return a; } int main() { //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); n=R();char s[5];int a,b; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i].val=R(),p[i].fa=i; m=R(); while(m--) { scanf("%s",s);a=R(); if(s[0]=='M') { b=R(); if(p[a].ifdead||p[b].ifdead) continue; int faa=getfa(a),fab=getfa(b); if(faa==fab) continue; int t=merge(faa,fab); p[faa].fa=p[fab].fa=t; } if(s[0]=='K') { if(p[a].ifdead) { printf("0 ");continue; } int t=getfa(a); printf("%d ",p[t].val); p[t].ifdead=true; p[t].fa=merge(p[t].l,p[t].r); p[p[t].fa].fa=p[t].fa; } } return 0; }
例题2:dispatching(bzoj2809)
Description
Input
Output
Sample Input
0 3 3
1 3 5
2 2 2
1 2 4
2 3 1
Sample Output
先说下大概思路,维护每一个节点所在子树的大根堆···如果堆的总和超过m就弹出堆顶元素···然后更新答案,我们肯定不能每次枚举一个节点暴力构堆,因此我们dfs,每df完一个节点的儿子将儿子的大根堆加入到该节点的大根堆中·····
值得注意的是,一个节点的大根堆里可能并不包含该节点,因为有可能该节点并没有取,但为了方便维护,我们用fa[i]表示一个节点的所在子树部分元素组成的大根堆的堆顶元素···而不是表示i节点所在大根堆的堆顶元素······下面代码中的sum[i],size[i]同理
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cctype> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<string> using namespace std; const int N=1e5+5; struct node { int ls,rs,dis,c; }p[N]; int n,m,first[N],go[N*2],next[N*2],tot,root,fa[N],size[N],sum[N],l[N],val[N]; long long ans; inline int R() { char c;int f=0; for(c=getchar();c<'0'||c>'9';c=getchar()); for(;c<='9'&&c>='0';c=getchar()) f=(f<<3)+(f<<1)+c-'0'; return f; } inline int getfa(int a) { if(fa[a]==a) return a; else return fa[a]=getfa(fa[a]); } inline void comb(int a,int b) { next[++tot]=first[a],first[a]=tot,go[tot]=b; next[++tot]=first[b],first[b]=tot,go[tot]=a; } inline int merge(int a,int b) { if(!a) return b; if(!b) return a; if(p[a].c<p[b].c) swap(a,b); p[a].rs=merge(p[a].rs,b); if(p[p[a].rs].dis>p[p[a].ls].dis) swap(p[a].ls,p[a].rs); p[a].dis=p[p[a].rs].dis+1; return a; } inline void pop(int u) { int t=fa[u]; fa[u]=merge(p[t].ls,p[t].rs); size[u]--;sum[u]-=p[t].c; p[t].c=p[t].ls=p[t].rs=0; } inline void dfs(int u,int pre) { for(int e=first[u];e;e=next[e]) { int v=go[e]; if(v==pre) continue; dfs(v,u); size[u]+=size[v],sum[u]+=sum[v]; fa[u]=fa[v]=merge(fa[u],fa[v]); while(sum[u]>m) pop(u); } size[u]+=1;sum[u]+=val[u]; p[u].c=val[u];fa[u]=merge(fa[u],u); while(sum[u]>m) pop(u); ans=max(ans,(long long)size[u]*l[u]); } int main() { //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); n=R(),m=R();int a; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { a=R(),val[i]=R(),l[i]=R(); if(!a) root=i; else comb(a,i); } dfs(root,0); cout<<ans<<endl; return 0; }
例题3:monkey king(hdu1512)
Problem Description
Assume that every money has a strongness value, which will be reduced to only half of the original after a duel(that is, 10 will be reduced to 5 and 5 will be reduced to 2).
And we also assume that every monkey knows himself. That is, when he is the strongest one in all of his friends, he himself will go to duel.
Input
First part: The first line contains an integer N(N<=100,000), which indicates the number of monkeys. And then N lines follows. There is one number on each line, indicating the strongness value of ith monkey(<=32768).
Second part: The first line contains an integer M(M<=100,000), which indicates there are M conflicts happened. And then M lines follows, each line of which contains two integers x and y, indicating that there is a conflict between the Xth monkey and Yth
Output
Sample Input
Sample Output
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cctype> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=1e5+5; struct node { int l,r,dis,val,fa; }p[N]; int n,m; inline int R() { char c;int f=0; for(c=getchar();c<'0'||c>'9';c=getchar()); for(;c<='9'&&c>='0';c=getchar()) f=(f<<3)+(f<<1)+c-'0'; return f; } inline int getfa(int u) { if(p[u].fa==u) return u; else return p[u].fa=getfa(p[u].fa); } inline int merge(int a,int b) { if(!(a*b)) return a+b; if(p[a].val<p[b].val) swap(a,b); p[a].r=merge(p[a].r,b);p[p[a].r].fa=a;//细节1 if(p[p[a].r].dis>p[p[a].l].dis) swap(p[a].r,p[a].l); p[a].dis=p[p[a].r].dis+1; return a; } inline int change(int a,int b) { p[p[a].l].fa=p[a].l;p[p[a].r].fa=p[a].r; //细节2 int tmp1=merge(p[a].l,p[a].r); p[a].val/=2;p[a].l=p[a].r=0;p[a].dis=0; int t1=merge(a,tmp1); p[p[b].l].fa=p[b].l;p[p[b].r].fa=p[b].r; //细节3 int tmp2=merge(p[b].l,p[b].r); p[b].val/=2;p[b].l=p[b].r=0;p[b].dis=0; int t2=merge(b,tmp2); return merge(t1,t2); } int main() { //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { int a,b; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i].val=R(),p[i].fa=i,p[i].dis=p[i].l=p[i].r=0; m=R(); while(m--) { a=R(),b=R(); int faa=getfa(a),fab=getfa(b); if(faa==fab) { printf("-1 ");continue; } int t=change(faa,fab); printf("%d ",p[t].val); } } return 0; }