● 关键字typeof
|
作用: 为一个已有的数据类型起一个或多个别名(alias), 从而增加了代码的可读性. typedef known_type_name new_type_name1, new_type_name2... 例如: typedef double Area, Volume; //double类型有Area和Volume两个别名 typedef int integer; integer a, b; //就相当于int a, b; |
|
#include <iostream.h> typedef char * String; //一般将typeof语句置于声明区, 头文件声明和宏定义之后; 为字符型指针起一个别名, 即String
void main() { String str; char temp[]="Hello World"; str=temp; cout << str << endl; } |
|
|
● typedef后接两个别名
|
typedef char *PCHAR,*PSTR; //给char*取了两个新名字:一个叫PCHAR,另一个叫PSTR。 typedef char *PCHAR,PSTR; //给char*取个新名字叫PCHAR,给char取新名字叫PSTR。 |
● 预编译=预处理
|
预编译=预处理Precompiling=Preprocessing 预处理包括: ① 宏定义(上文已讲述); ② 文件包含; ③ 条件编译 |
● 文件包含
|
header file: 头文件, 可能翻译成"标题文件"更好 如果include包含的头文件在C/C++库函数中,那么就用#include < >, 如果包含的文件在当前目录下,那么用#inlclude " "。 |
|
//file1.h #define AAA 2 const int a = 3;
//file2.c #include <stdio.h> #include "file1.h"
void print_OK(int a) { printf("OK, %d ", a); }
int main(void) { #if AAA //如果AAA宏定义的值为真(即非0) print_OK(a); #endif return 0; //结束一个#if……#else条件编译块 }
//文件包含命令执行后, file1.c #include <stdio.h> #define AAA 2 const int a = 3;
void print_OK(int a) { printf("OK, %d ", a); }
int main(void) { #if AAA //如果AAA宏定义的值为真(即非0) print_OK(a); #endif return 0; //结束一个#if……#else条件编译块 } |
|
● 一般将如下内容放到.h文件中: ① 宏定义; ② 结构体, 联合体和枚举声明 ③ typedef声明
※ 在需要调用函数的文件中,用extern对函数声明,表示该函数是在其他文件中定义的外部函数
|
● 条件编译(conditional compilation)
|
作用: 只对满足一定条件的代码进行编译, 使用条件编译可方便地处理程序的调试版本(Debug Version)和正式(发行)版本(Release Version), 同时增强程序的可移植性. |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
● ① #if 指令 #if directive, ② #else指令, ③ #elif指令
|
① #if 指令 #if directive, ② #else指令, ③ #elif指令 ※ define 标识符 字符串 |
|
① 简单形式: #if constant_expression block_statement; #endif 例如: #if CPU == Pentium4 //如果是一个整型常数, 非0为真, 执行下面的语句, 0为假, 不执行下面的语句 printf(" Performance should be good." ); #endif
② 复杂形式: #if condition_1 statement_block_1; #elif condition_2 statement_block_2; ... #elif condition_n statement_block_n; #else default_statement_block; #endif |
|
//案例1: #include<stdio.h> #define NUM 50
main() { int i=0; #if NUM>50 /*判断NUM是否大于50*/ i++; #endif #if NUM==50 i=i+50; #endif #if NUM<50 i--; #endif printf("Now i is:%d ",i); }
|
|
//案例2: #include<stdio.h> #define NUM 50
main() { int i=0; #if NUM>50 i++; #else #if NUM<50 i--; #else i=i+50; #endif #endif //第一个#if和最后一个#endif搭配, 第二个#if和倒数第二个if搭配 printf("i is:%d ",i); }
|
|
//案例3: #include<stdio.h> #define NUM 50 main() { int i=0; #if NUM>50 i++; #elif NUM<50 i--; #else i=i+50; #endif printf("i is:%d ",i); }
|
● #ifdef指令, #ifndef指令
|
//#ifdef的使用: #ifdef macro_name block_statement_1; #endif //或者: #ifdef macro block_statement_1; #else block_statement_2; #endif
//#ifndef的使用: #ifndef macro_name block_statement_1; #endif //或者: #ifndef macro block_statement_1; #else block_statement_2; #endif |
|
//案例: #include<stdio.h> #define STR "diligence is the parent of success "
main() { #ifdef STR printf(STR); #else printf("idleness is the root of all evil "); #endif printf(" "); #ifndef ABC printf("idleness is the root of all evil "); #else printf(STR); #endif }
|
● #undef指令
|
作用: 将宏定义局限在仅需要它的代码中 |
|
#undef macro_name |
|
#define MAX_SIZE 100 char array[MAX_SIZE]; #undef MAX_SIZE |
● 预定义宏(predefined macros) / 预定义标识符(predefined identifiers)
|
__DATE__: 进行预处理的日期("Mmm dd yyyy"形式的字符串文字) __FILE__: 代表当前源代码文件名的字符串文字 __LINE__: 代表当前源代码中的行号的整数常量 __TIME__: 源文件编译时间,格式微"hh:mm:ss" __func__: 当前所在函数名(在有的编译器中是: __FUNC__或__FUNCTION__) |
|
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> void why_me();
int main() { printf( "The file is %s. ", __FILE__ ); printf( "The date is %s. ", __DATE__ ); printf( "The time is %s. ", __TIME__ ); printf( "This is line %d. ", __LINE__ ); //printf( "This function is %s./n", __func__ ); VC++ 6.0不能识别__func__ why_me(); return 0; }
void why_me() { //printf( "This function is %s/n", __func__ ); printf( "The file is %s. ", __FILE__ ); printf( "This is line %d. ", __LINE__ ); } |
|
|
●
#line指令
|
#include "iostream" #line 100 "test.cpp" //如果不指定文件, 就处理当前文件 using namespace std; //从这一行开始记作第100行
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { cout<<"__LINE__: "<<__LINE__<<endl; return 0; } |
|
|
● #error指令
|
#error [用户自定义的错误消息] //方括号"[]"代表用户自定义的错误消息, 可以省略不写 |
|
/* 检查编译此源文件的编译器是不是C++编译器 如果使用的是C语言编译器则执行#error命令 如果使用的是 C++ 编译器则跳过#error命令 */ #ifndef __cplusplus #error 亲,您当前使用的不是C++编译器噢! #endif #include <stdio.h> int main() { printf("Hello,World!"); return 0; } |
|
|
● #pragma指令
|
#pragma指令(预处理指令中最复杂的指令) 作用是设定编译器的状态, 或者提示编译器完成一些特定的动作 |
|
例如: ① 在开发C99时,用C9X代表C99。编译器可以使用下面的编译指示(pragma)来启用对C9X的支持: #pragma c9x on
② #pragma warning(disable: n) //作用是将某个警报置为失效 例如, Visual C++ 2012 使用了更加安全的 run-time library routines, 所以在VS 2012 中编译 C 语言项目,如果使用了 scanf 函数,编译时便会提示如下错误:error C4996: 'scanf': This function or variable may be unsafe. Consider using scanf_s instead. To disable deprecation, use _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS. See online help for details.
在声明区写上#pragma warning (disable : 4996)即可忽略编译的错误提示 |
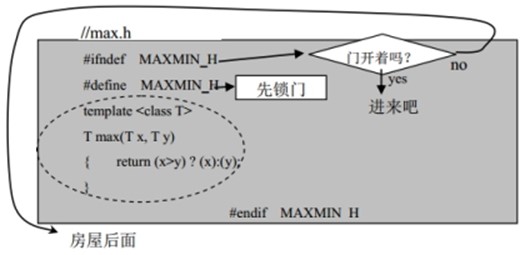
● 如何避免头文件被重复包含?
|
一般情况下,我们都是把函数声明、类定义、 模板定义等写到一个头文件里, 需要时将相应的头文件用#include 包含到源文件( *.cpp 文件)里来。 但头文件中又允许包含其它的头文件,这样就难免发生某个头文件被重复地包含。 我们可以使用编译预处理命令避免这种情况的发生。 例如, 你想确保头文件 max.h 不会被重复包含,则你可以采取如下的形式:
第一条预处理命令是说,如果 MAXMIN_H 不为真,说明此文件没被包含过,此命令后面的源代码有效(相当于:'如果大门没关, 请您进来'); 第二条预处理命令把 MAXMIN_H 置为真(相当于请您把门锁插上,不让第二个人进来)。 最后一条预处理命令是为了标出接受上述处理的源程序的范围(相当于您已经走到了后门)。 |