首先解释下这块, root代表当前登录用户,localhost代表主机名, ~代表当前主机目录,#代表用户权限 #表示超级用户,$表示普通用户;
进入根目录
cd ../
查询目录中内容命令 ls (list缩写)
格式 ls [选项] [文件或目录]
选项:
-a 显示所有文件,包括隐藏文件
-l 显示详细信息
-d 查看目录属性
-h 人性化显示文件大小
-i 显示inode
超级用户root默认的当前目录是 root目录
我们可以用pwd命名(Print Working Directory 打印当前工作目录)看到
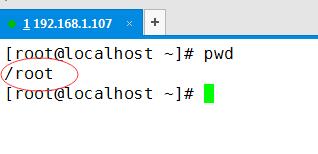
我们打印下当前目录下文件信息:
[root@localhost ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg
只有一个文件
假如我们要列出所有文件 用 ls -a 把隐藏文件也显示出来
[root@localhost ~]# ls -a
. anaconda-ks.cfg .bash_logout .bashrc .tcshrc
.. .bash_history .bash_profile .cshrc
多了一些文件
我们也可以看其他目录的文件:
[root@localhost ~]# ls /etc/
adjtime modprobe.d
aliases modules-load.d
aliases.db motd
alternatives mtab
anacrontab my.cnf
asound.conf my.cnf.d
audisp NetworkManager
audit networks
同样也可以看具体某个文件
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /etc/vconsole.conf
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 37 6月 10 05:23 /etc/vconsole.conf
我们用 -l 或者 -la 组合 列出详细信息;
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l
总用量 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1237 6月 10 05:24 anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@localhost ~]# ls -la
总用量 24
dr-xr-x---. 2 root root 135 6月 11 21:13 .
dr-xr-xr-x. 17 root root 224 6月 10 05:23 ..
-rw-------. 1 root root 1237 6月 10 05:24 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-------. 1 root root 0 6月 11 21:13 .bash_history
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 18 12月 29 2013 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 176 12月 29 2013 .bash_profile
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 176 12月 29 2013 .bashrc
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 100 12月 29 2013 .cshrc
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 129 12月 29 2013 .tcshrc
[root@localhost ~]#
这里第一列 比如 dr-xr-xr-x. 代表文件类型以及所有者,所属组以及其他者权限
第一位d代表文件类型 常见的有 - 文件 d目录 | 软件链接文件
后面9位 每3位一个组 分别是 所有者u 所属组g 以及 其他者o的权限
权限分三种 r读 w写 x执行
比如 dr-xr-xr-x 这个目录 所有者 所属组 以及其他者 都有 读和执行权限;
比如 -rw------- 这个文件 所有者有读写权限 所属组以及其他者没有权限;
第二列 那个数字 是 硬链接次数 后面再说;
第三列 root 是 所有者;
第四列 root 是 所属组;
第五列 是文件大小;假如看不惯 可用 ls -lh
[root@localhost ~]# ls -lh
总用量 4.0K
-rw-------. 1 root root 1.3K 6月 10 05:24 anaconda-ks.cfg
第六列的日期是该文件最后一次修改时间;
最后一列 是文件名称;
查看目录属性 要加 -d
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ld /etc/
drwxr-xr-x. 78 root root 8192 6月 13 15:50 /etc/
[root@localhost ~]#
查看文件的inode属性 类似 主键 唯一识别文件的Id 用 -i
[root@localhost ~]# ls -li
总用量 4
33574979 -rw-------. 1 root root 1237 6月 10 05:24 anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@localhost ~]#
33574979 就是inode属性