EC2 with Elastic IP
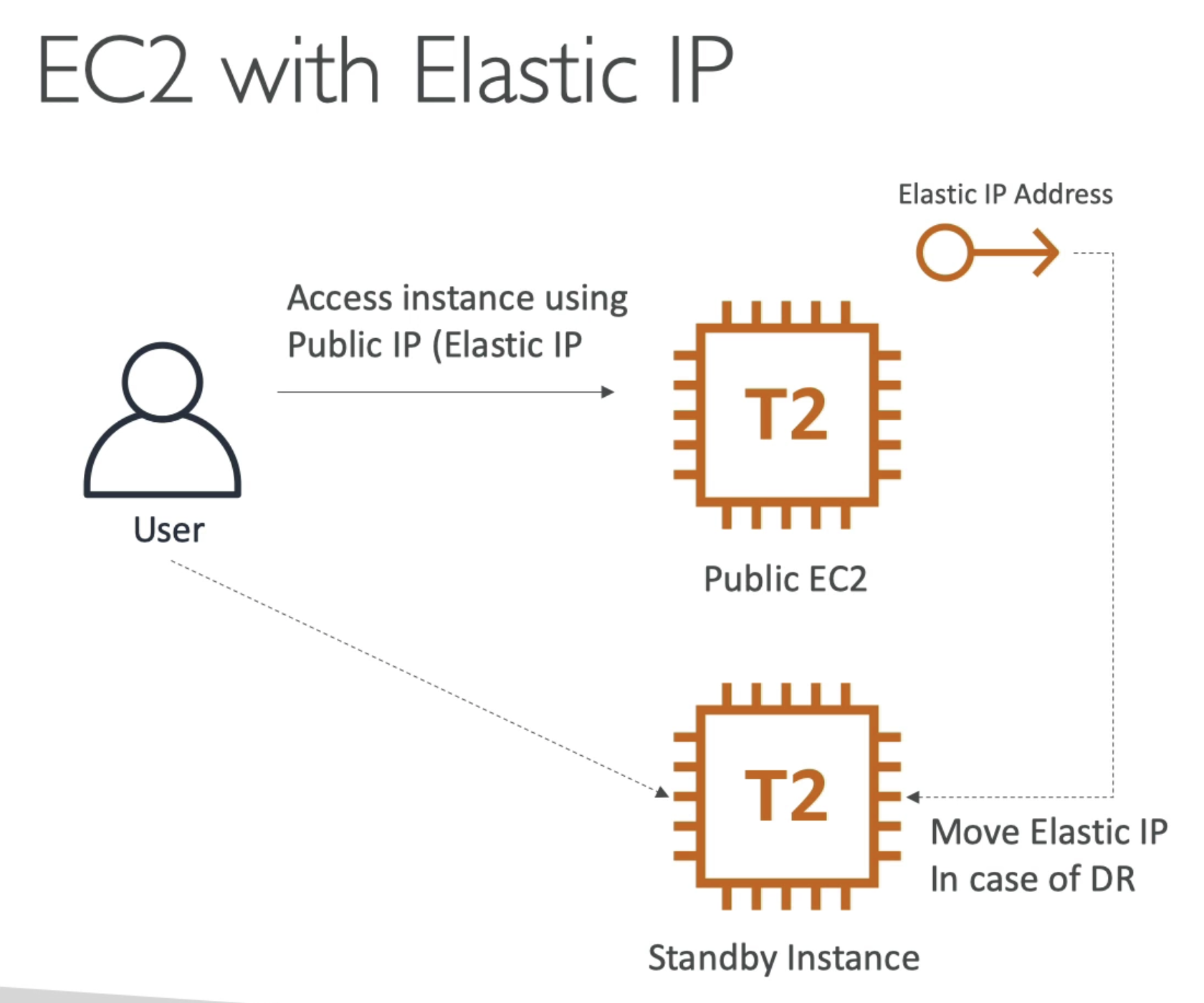
- User talks to a public EC2 instances access by EIP
- We want to have a failover instance
- ElP address points to failover instances
Summary
- Quick failover
- The client should NOT see the change happen
- Helpful if the client needs to resolve by static Public IP address
- Does not scale
- Cheap
Stateless web app - scaling horizontally
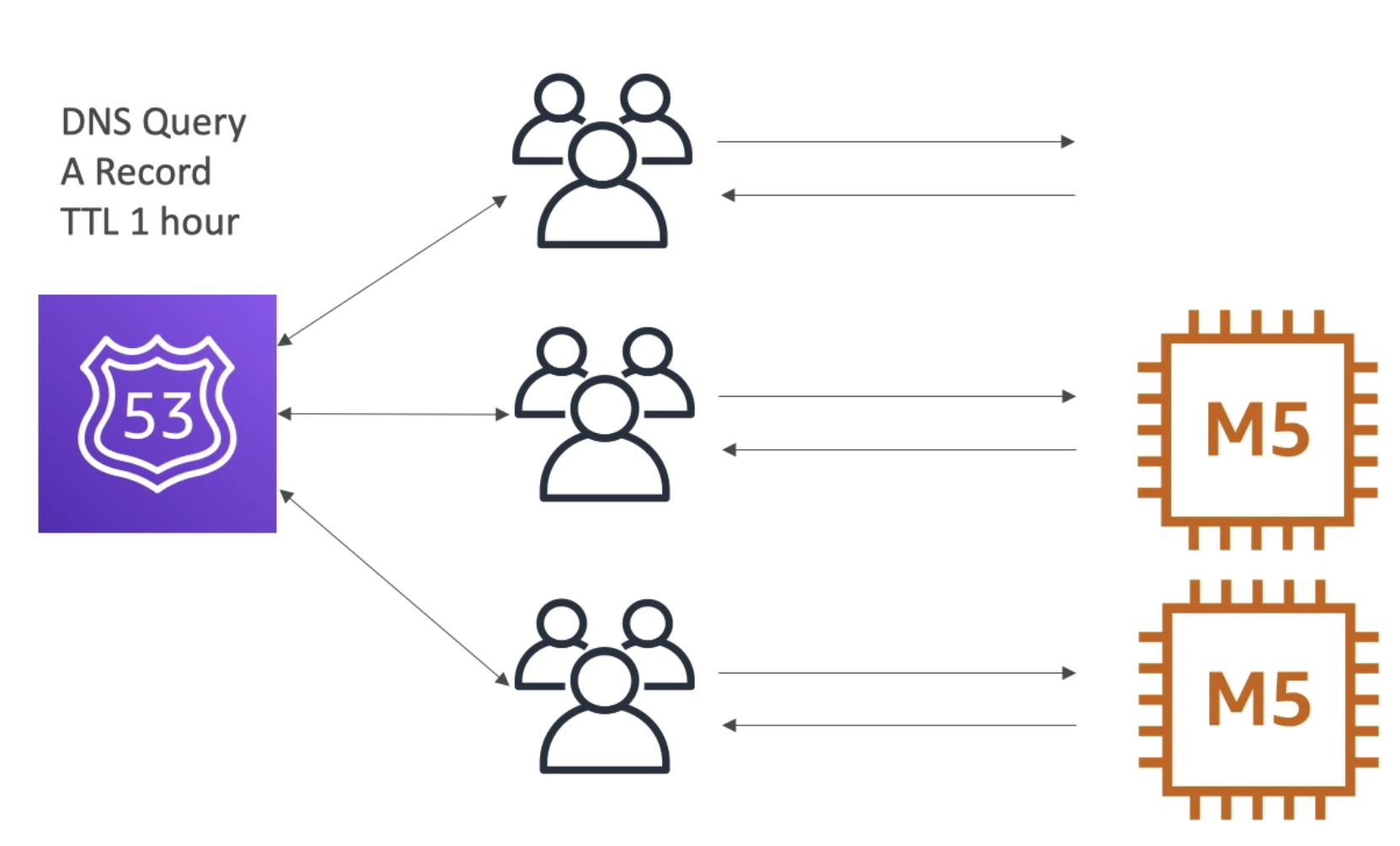
- There are three EC2 instances, no EIP
- We have Route 53 to create A record, users are routed to different EC2 instances
- There is TTL 1 hour for Route 53
- If one instance Fail, then users are routed to that instances cannot access web server anymore
Summary
- DNS-based load balancing
- Ability to use multiple instances
- Route53 TTL implies client may get outdated information
- Client must have logic to deal with hostname resolution failures
- Adding an instance may not receive full traffic right away due to DNS TTL
ALB + ASG

- Using Route53 Alias Record with TTL 1 hour
- ALB + Health checks + Multi AZs
- EC2 instances in ASG
Summary
- Scale well, classic architecture
- New instances are in service right away.
- Users are not sent to instances that are out-of-service
- Time to scale is slow (EC2 instance startup + bootstrap) - AMI can help
- ALB is elastic but cannot handle sudden, huge peak of demand (pre-warm)
- Could lost a few requests if instances are overloaded
- CloudWatch used for scaling
- Target utilization should be between 40% and 70%
- Cross-Zone balancing for even traffic distribution
ALB + ECS on EC2 (backed by ASG)

- Same properties as ALB + ASG
- Application is run on Docker
- ASG + ECS allows to have dynamic prot mappings
- Tough to orchestrate ECS service auto-scaling + ASG auto-scaling
ALB + ECS on Fargate
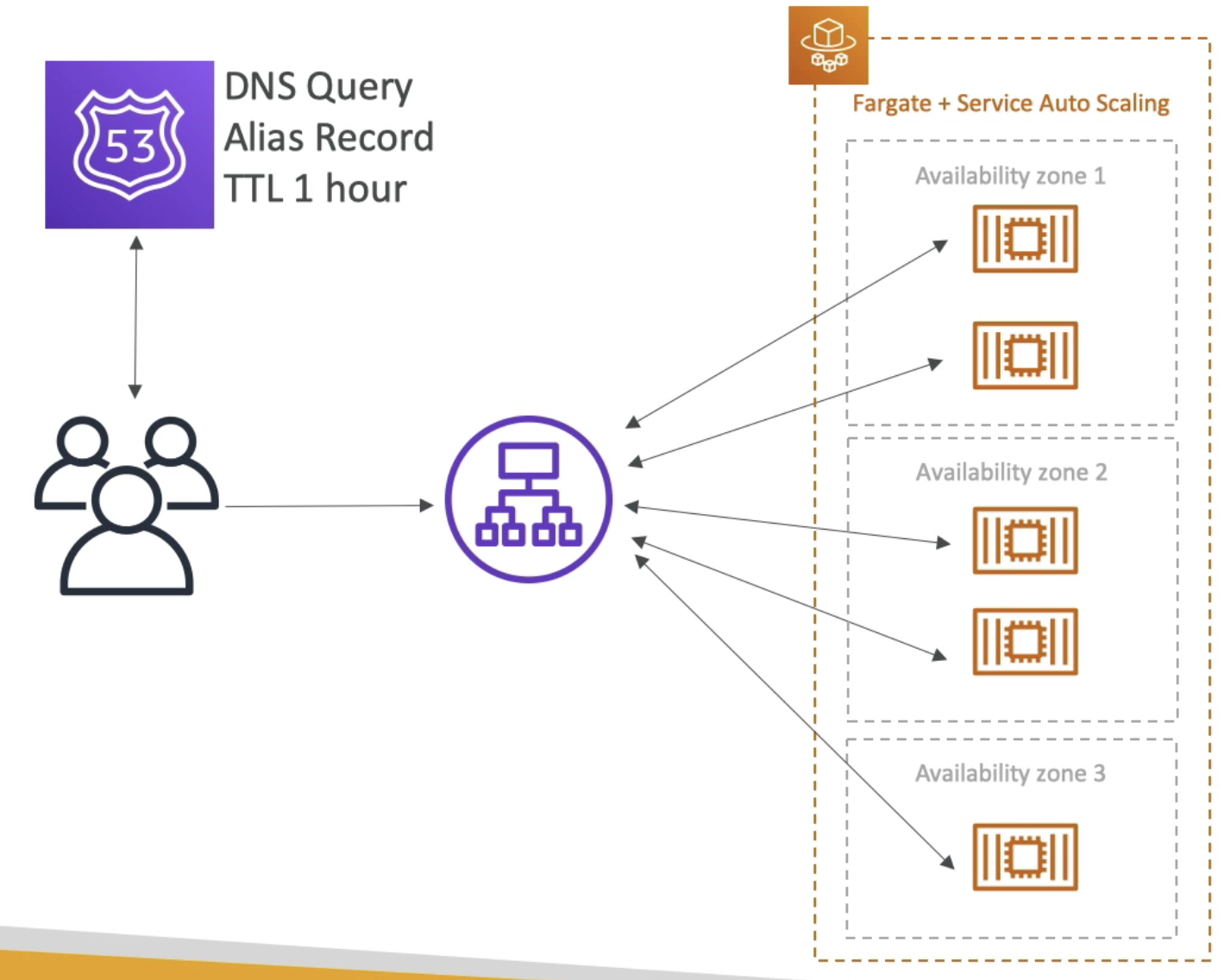
- Solution the scaling problem for ALB + ECS.
Summary
- Application is run on Docker
- Servcie Auto Scaling is easy
- Time to be in-service is quick (no need to launch an EC2 instances in advance)
- Still limited by the ALB in case of sudden peaks
- "serverless" application tier
- "managed" load balancer
ALB + Lambda
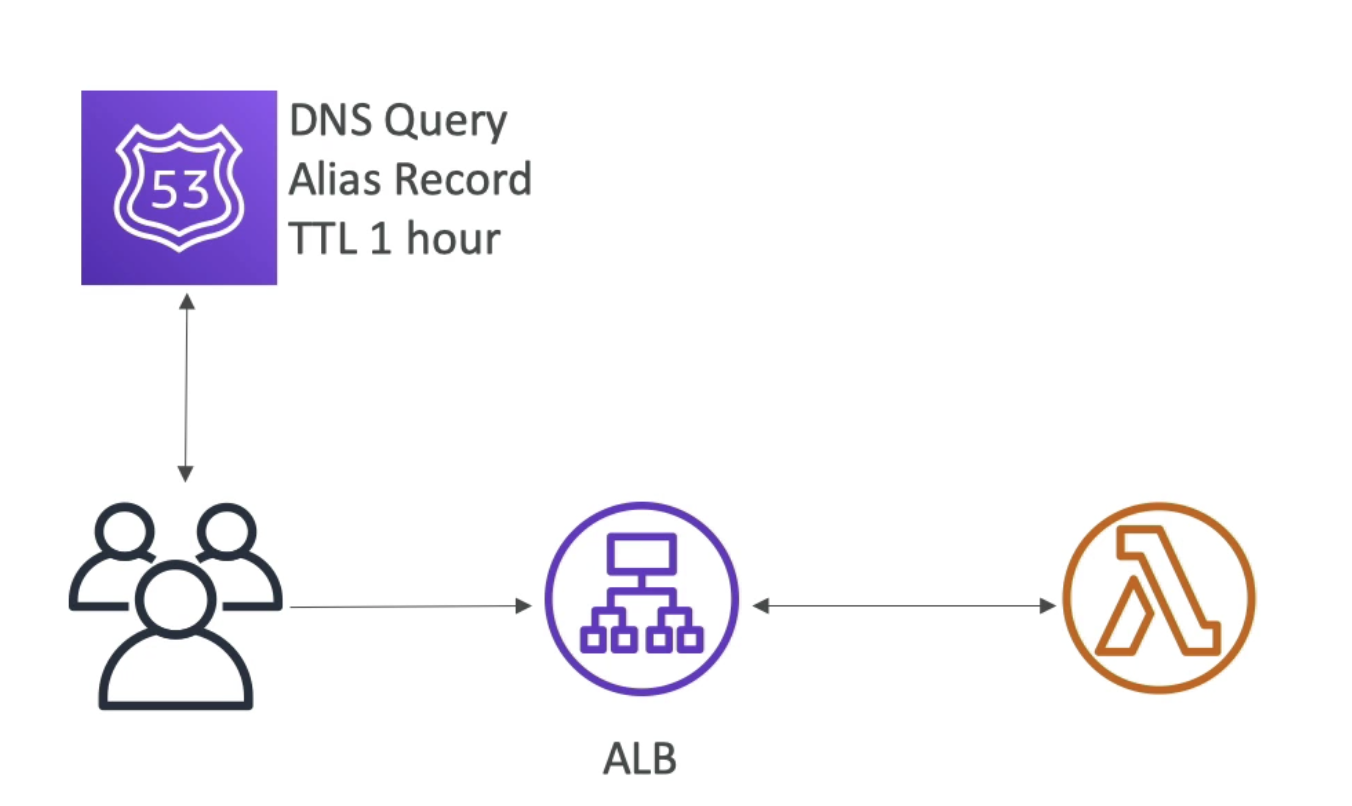
- Limited to Lambda's runtimes
- Seamless scaling thanks to the Lambda
- Simple way to expose Lambda functions as HTTP/S without all the features from API Gateway
- Can combine with WAF
- Good for hybrid microservices
- Example: use ECS for some requests, use Lambda for others
API Gateway + Lambda
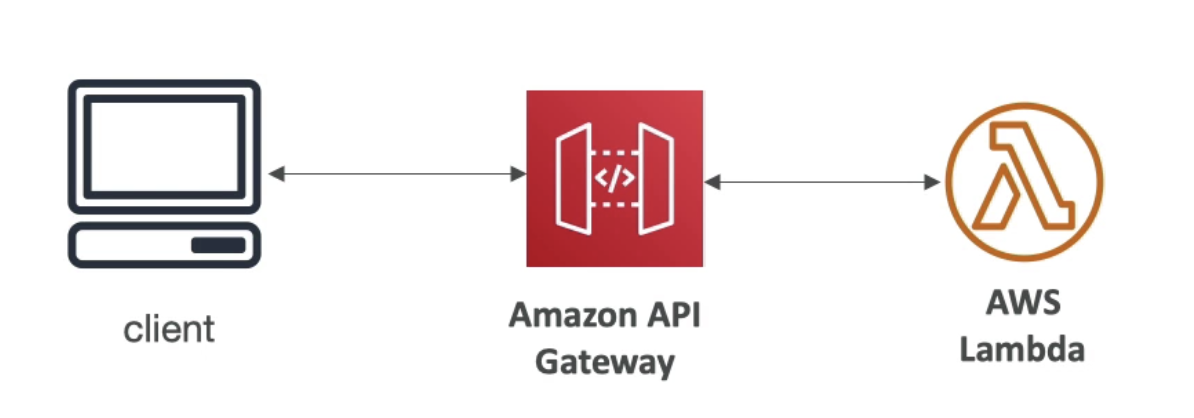
- Pay per request, seamless scaling, fully serverless
- Soft limits: 10000/s API Gateway, 1000 concurrent Lambda
- API Gateway features: authentication, rate limiting, caching, etc...
- Lambda Cold Start time may increase latency for some requests
- Fully integrated with X-Ray
API Gateway + AWS Service (as a proxy)
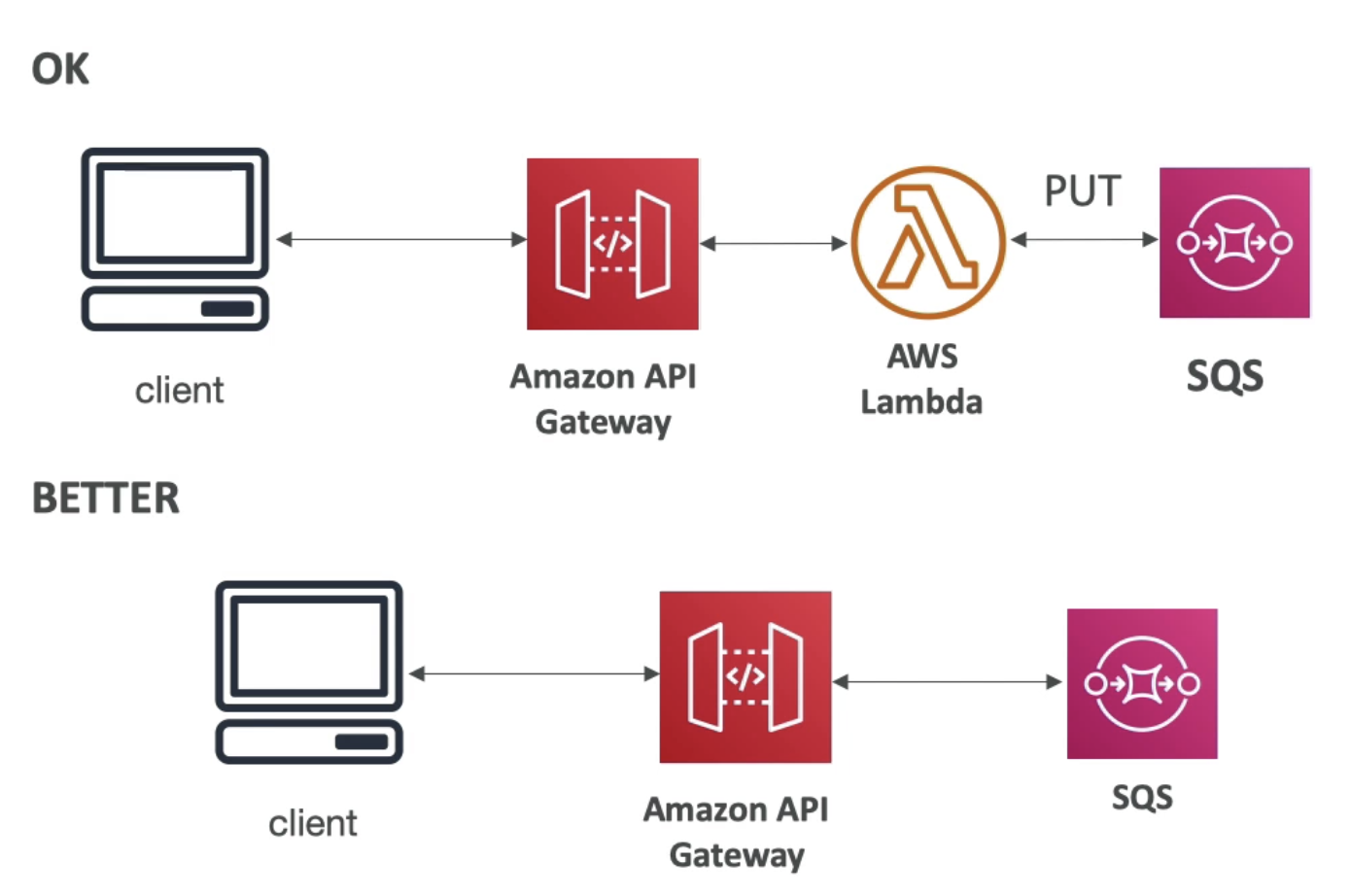
- Lower latency, cheaper
- Not using Lambda concurrent capacity, no custom code
- Expose AWS APIs securely through API Gateway
- SQS, SNS, Step Functions...
- Remember API Gateway has a payload limit of 10 MB (can be a problem for S3 proxy)
APi Gaeway + HTTP backend (ex: ALB)
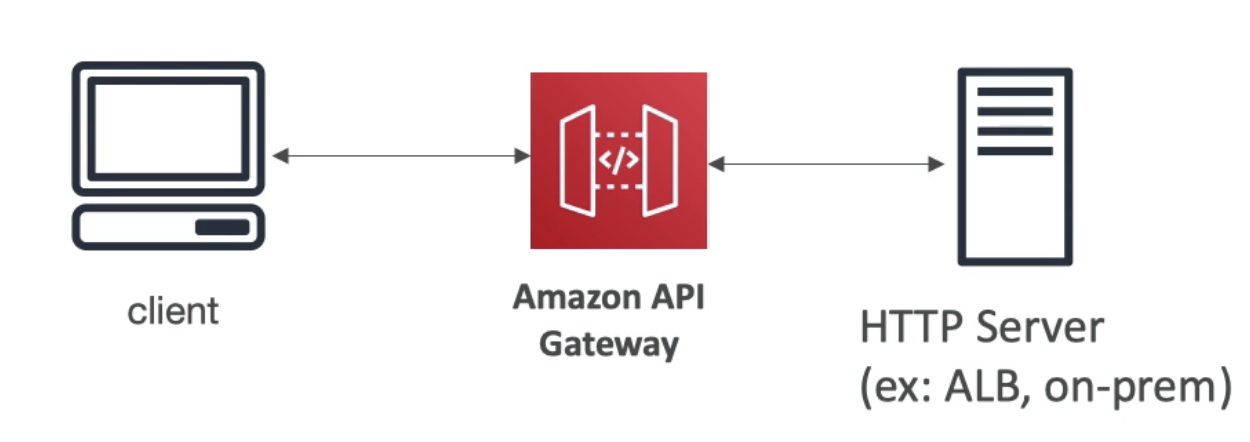
- Use API Gateway features on top of custom HTTP Backend (authentication, rate control, API keys, caching...)
- Can connect to
- On-premise service
- Application Load Balancer
- 3rd party HTTP service